Method for producing L-lactic acid by continuous fermentation of lignocellulose
A technology of lignocellulose and cellulase, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problem that the efficiency of fermentation and the utilization rate of bacteria cannot meet the needs of industrial production, and the utilization rate of medium is still to be determined. Improvement, high equipment precision requirements, etc., to achieve the effect of promoting lactic acid production, improving the utilization rate of bacteria, and simplifying the production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 The amount of cellulase solution required for biomass materials
[0042] After pretreatment, the main components of biomass materials are cellulose and lignin, and cellulase can be used to enzymatically decompose cellulose into monosaccharides and disaccharides. The cellulase liquid is the fermentation supernatant produced by the fermentation of Trichoderma reesei. Adding a suitable cellulase liquid can save the cost of enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass materials. Add the cellulase liquid according to the quality of the pretreated biomass material. 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 FPU / g respectively, the pretreated biomass material accounted for 15% of the total enzymatic hydrolysis system mass ratio, and the rest was water. The enzymolysis temperature is 50° C., the enzymolysis time is 24 hours, and the stirring speed is 120-150 rpm. The contents of cellobiose, xylose and glucose in the supernatant after enzymolysis were measured, and the results are shown in Table...
Embodiment 2
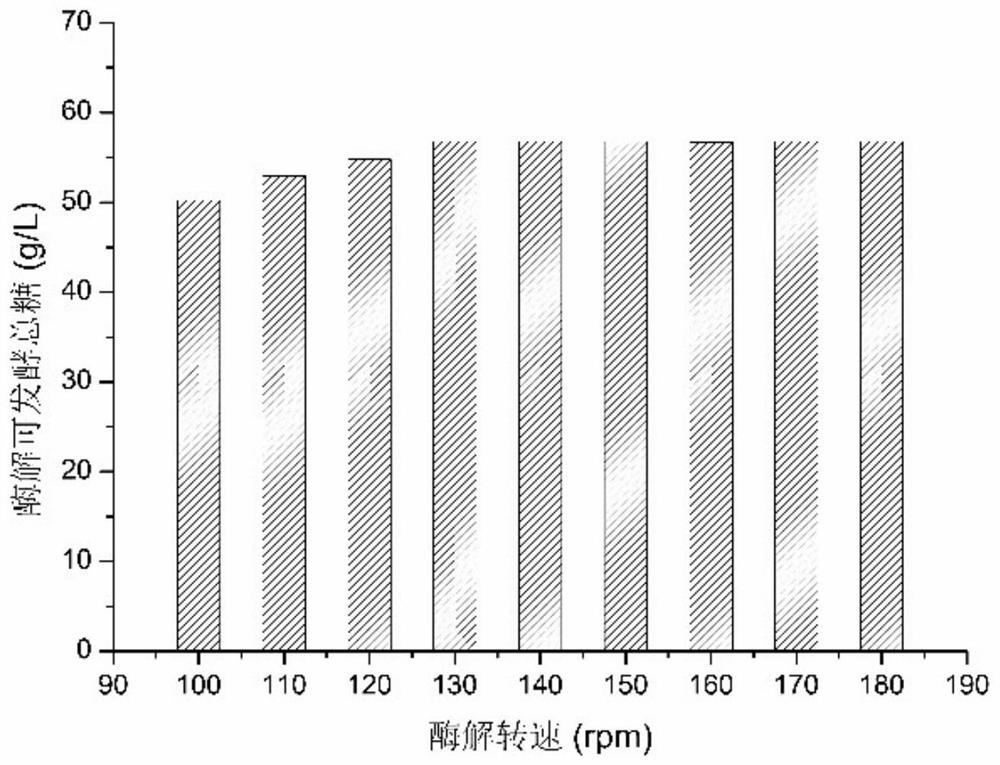
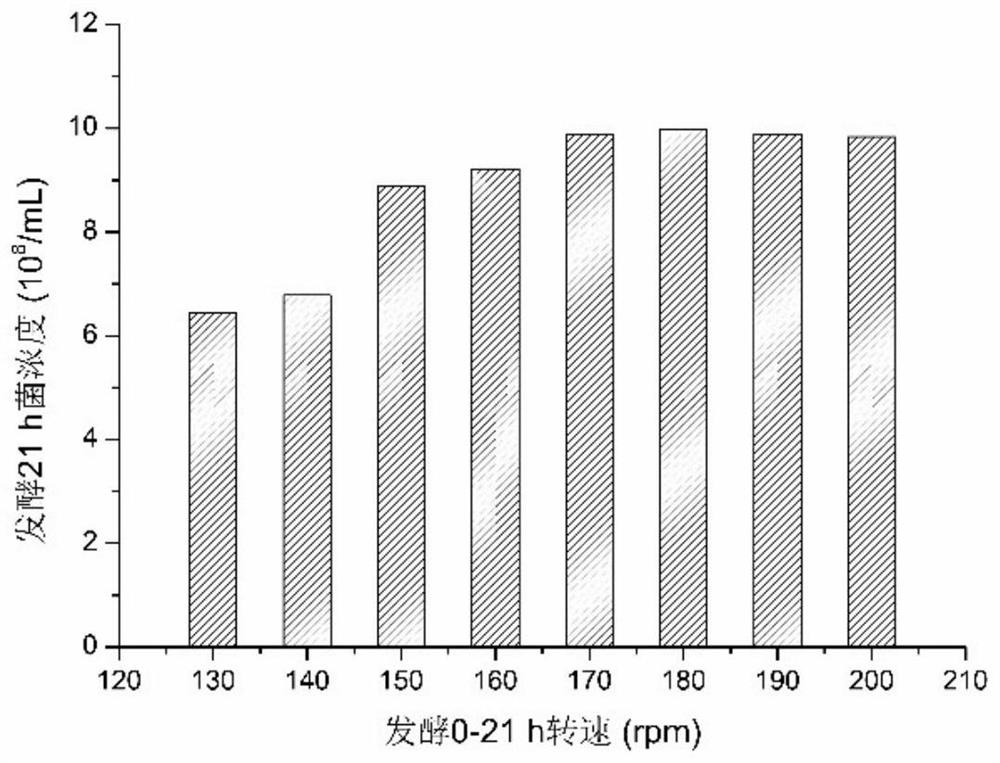
[0046] Example 2 Effect of speed
[0047] The continuous fermentation of the present invention can be divided into three stages, which are the enzymolysis stage at the initial stage of production, which lasts from the beginning to 12-15 hours; the middle stage of production is the stable growth stage of bacteria, which starts after the enzymolysis stage ends and lasts for 20-30 hours; Finally comes the later stage of production, the continuous fermentation stage. The present invention adopts different stepped rotating speeds at different stages, which can maximize production efficiency and increase production capacity.
[0048] In the same fermenter, first carry out enzymatic hydrolysis of waste straw for 12-15 hours, then inoculate the seed culture solution of Bacillus coagulans (B. coagulans) and cultivate for 21 hours, and start to continuously feed and separate the fermentation solution. In this process, the early stage of production is the enzymatic hydrolysis stage, a...
Embodiment 3
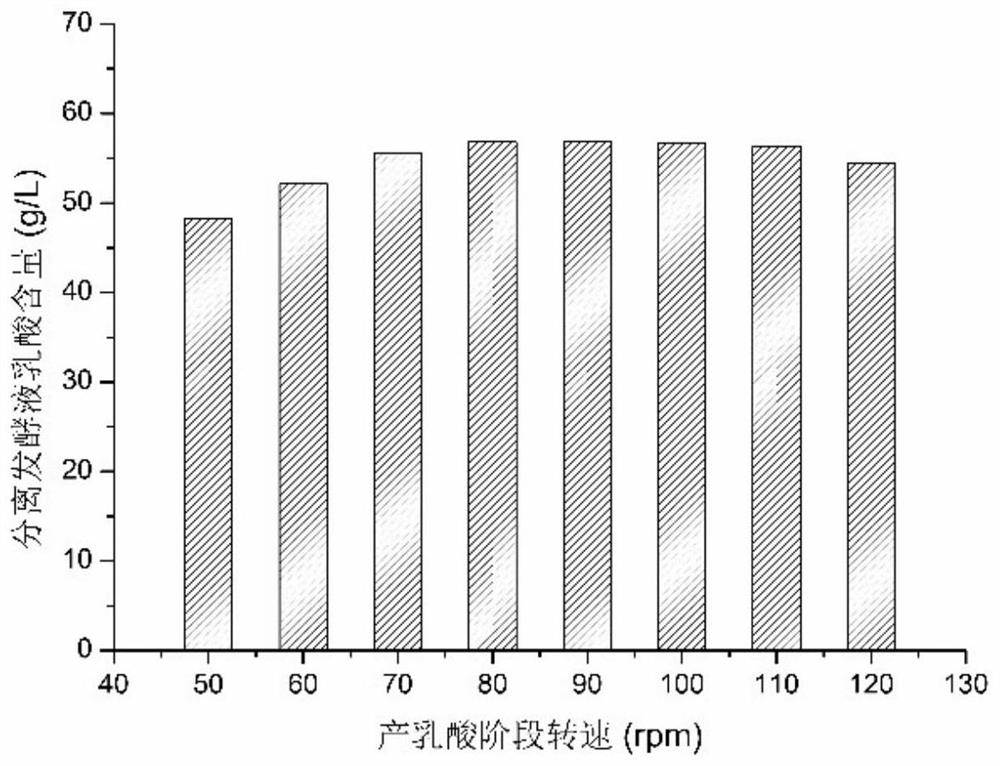
[0051] Example 3 The rate of feeding liquid and separating fermentation liquid in lactic acid continuous fermentation
[0052] After the first 21 hours of continuous lactic acid fermentation, feed feeding and separation of fermentation broth are started. Different separation rates determine the quality of the separated products. Choosing the most suitable separation rate can make the biomass materials fully utilized. The thermophilic Bacillus coagulans grows and reproduces in the fermenter while using the fermentable sugar in the enzymolysis liquid to produce lactic acid. The fermentation feed liquid is added from the top of the fermenter, and the fermented liquid is separated from the bottom. The fermentation system maintains a dynamic balance. Feeding and separating too fast will lead to insufficient utilization of the biomass material in the feeding liquid, insufficient concentration of lactic acid produced, and cellulose mixed in the solid product; too slow separation wil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com