Enzymatic Low Field NMR Immunosensor for Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria
A low-field nuclear magnetic resonance, food-borne pathogenic bacteria technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry and food safety, can solve the problems of incompetent sensitivity and accuracy, low sensitivity, complex food samples, etc., to achieve the limit of broadening the detection range, Simplify the magnetic signal analysis process, the effect of simple suspension stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
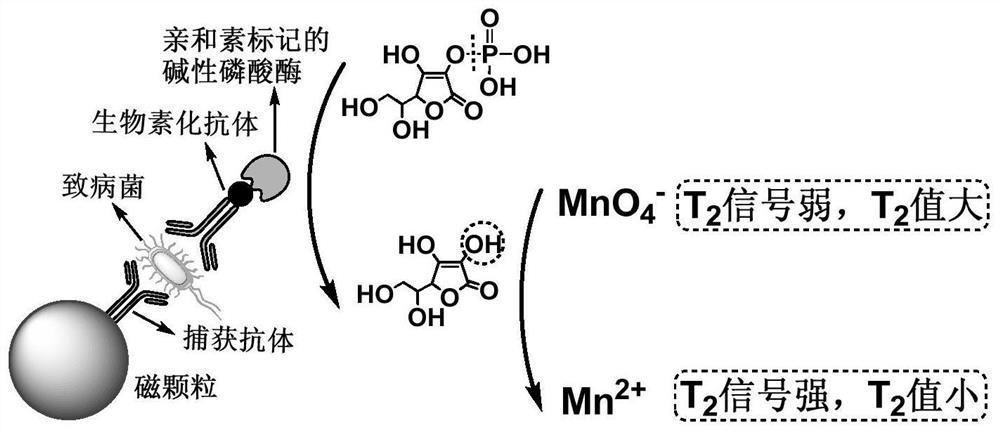
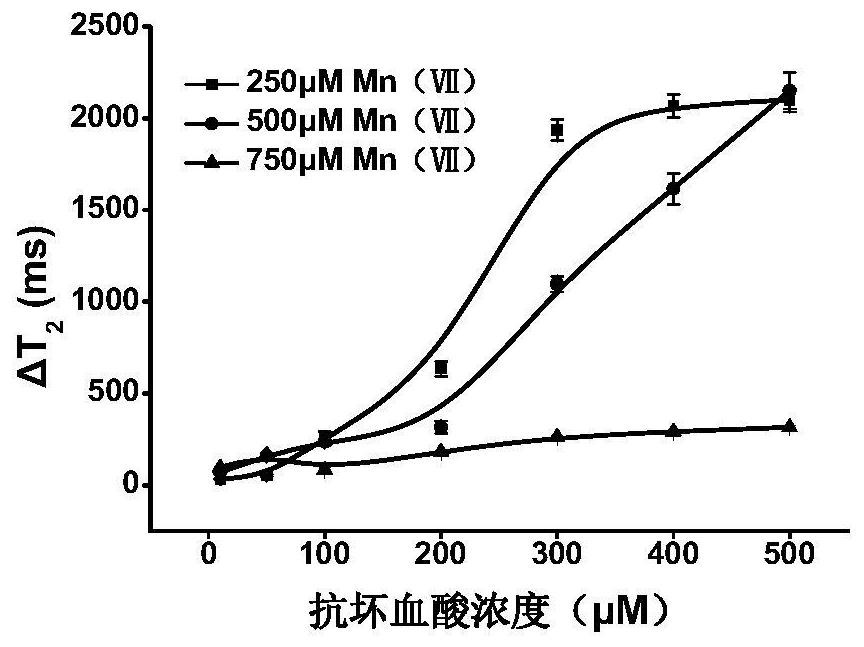
[0051] Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a labeling enzyme widely used in immunoassays. At the same time, ALP can catalyze its substrate (ascorbyl phosphate) to produce reducing ascorbic acid (AA). The redox reaction mediated by AA Can achieve MnO 4 - to Mn 2+ transformation, resulting in T 2 signal change. Given MnO 4 - The strong oxidation of AA and the strong reduction of AA, the redox reaction catalyzed by ALP can realize the ultrasensitive response to AA. Based on this principle, a magnetic immunosensor can be constructed to detect different targets.
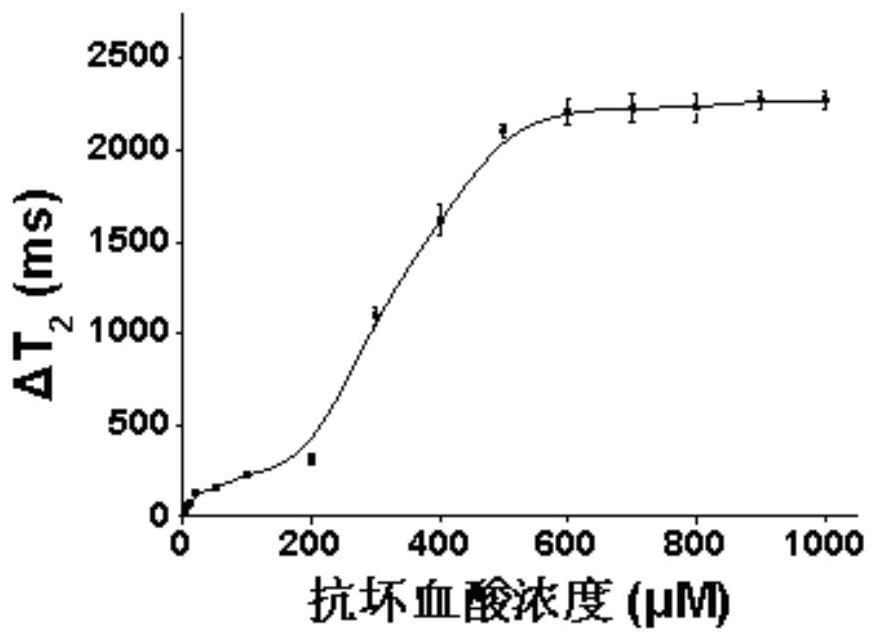
[0052] 1)T 2 Magnetic sensor response to ascorbic acid (AA)
[0053] Add 100 μL of ascorbic acid solutions with different concentrations (1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 and 1000 μM) to 100 μL of 0.5 mM KMnO 4 solution, reacted for 5 minutes, and measured the T 2 signal, the result of which is figure 2 Shown, T 2 The change in value becomes larger with the increase of ascorbic acid ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The detection of embodiment 2 Salmonella
[0065] (1) Preparation of MNPs-capture antibody conjugates: Take 500 μL 1000nm COOH-MNPs, wash twice with pure water, and resuspend with 2 mL pure water; add 100 μL EDC (10 mg / mL) and 50 μL NHS (10 mg / mL ) activation for 30 minutes; resuspend with 2mL PBS (pH=7.4) after magnetic separation; add 0.2mg Salmonella capture antibody (Ab 1 ), reacted with gentle shaking for 3 hours, added 500 μL of 3% BSA for 30 minutes to block unbound sites; washed 4 to 5 times with PBST, and finally resuspended with 2 mL of PBS and stored at 4°C for later use.
[0066] (2) Biotinylation of Salmonella detection antibody: first, EZ-Link TM Sulfo-NHS-LC-LC-Biotin was diluted to 1mg / mL with dimethylformamide, and the Salmonella detection antibody (Ab 2 ) was diluted to 1 mg / mL with PBS; then the two were mixed at a molar ratio of 30:1 (biotin / detection antibody), and the reaction was shaken at room temperature for 4 hours to realize the biotinylatio...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3 detects the specificity investigation of Salmonella
[0075] (1) Dilute the cultured Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria and Vibrio parahaemolyticus to 10% respectively with normal saline 5 CFU / mL, take 400 μL each to a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, then add 100 μL MNPs-Salmonella capture antibody solution, mix well and react gently at 37°C for 30 minutes.
[0076] (2) Magnetic separation, washing with PBST for 3 times, then adding biotinylated Salmonella detection antibody to each centrifuge tube, and reacting gently at 37°C for 30 minutes.
[0077] (3) The excess biotinylated antibody was removed by magnetic separation, and the resulting complex was washed 3 times with PBST.
[0078] (4) Add a certain amount of streptavidin-labeled alkaline phosphatase to the complex obtained in (3), react gently at 37°C for 30 minutes, magnetically separate, wash the complex 4 times with PBST, and finally use Resuspend the complex in 100 μL pure wat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com