Method for preparing quartz glass millimeter-scale deep micropores by utilizing femtosecond laser filament effect
A technology of quartz glass and femtosecond laser, which is applied in laser welding equipment, welding equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of lower product performance, failure to achieve function and precision, and difficulties in high-precision micro-holes, and achieve large-scale processing. , high processing efficiency and high energy utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1, a kind of method that utilizes femtosecond laser filament effect to prepare the quartz glass millimeter level deep microhole, comprises the following steps:
[0024] 1) Select an area of 5×20mm 2 , a quartz glass sample with a thickness of 5 mm, its surface is ultrasonically cleaned with acetone, absolute ethanol and deionized water, and then dried with dry air to obtain a clean quartz glass sample;
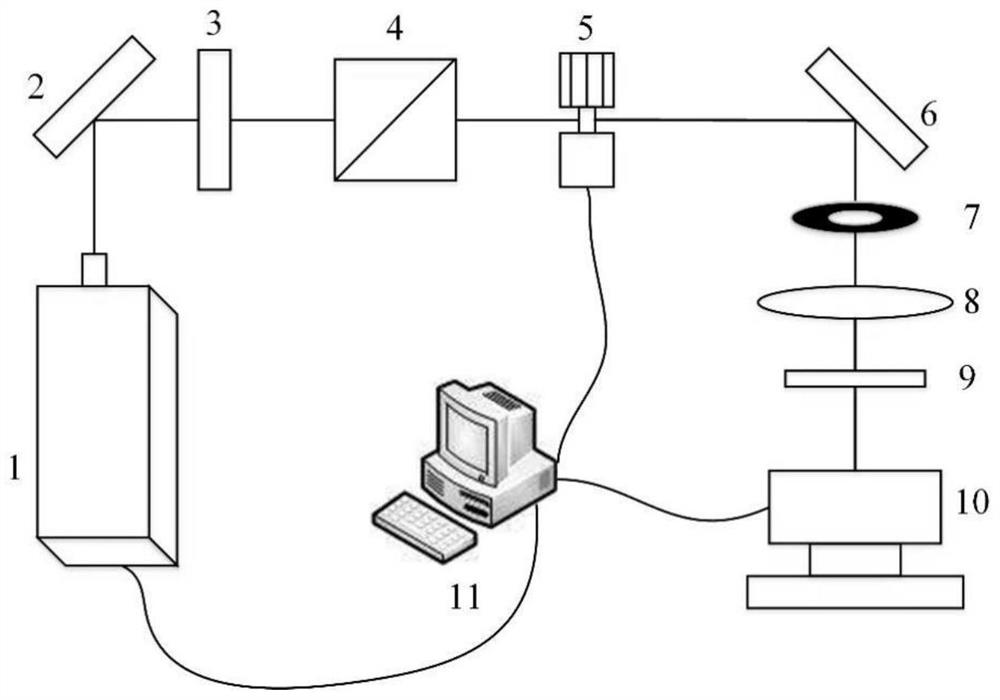
[0025] 2) Build an optical path, such as figure 2 As shown, the optical path includes a femtosecond laser 1, the output light of the femtosecond laser 1 passes through the reflector 2 to turn the optical path by 90°, and the reflected light passes through the half-wave plate 3, the beam splitting prism 4, the shutter 5, the reflector 6, and the aperture diaphragm in sequence 7. The plano-convex lens 8 and the λ / 4 wave plate 9 are vertically irradiated on the processing station of the mobile stage 10. The femtosecond laser 1, the shutter 5, and the mobile ...
Embodiment 2
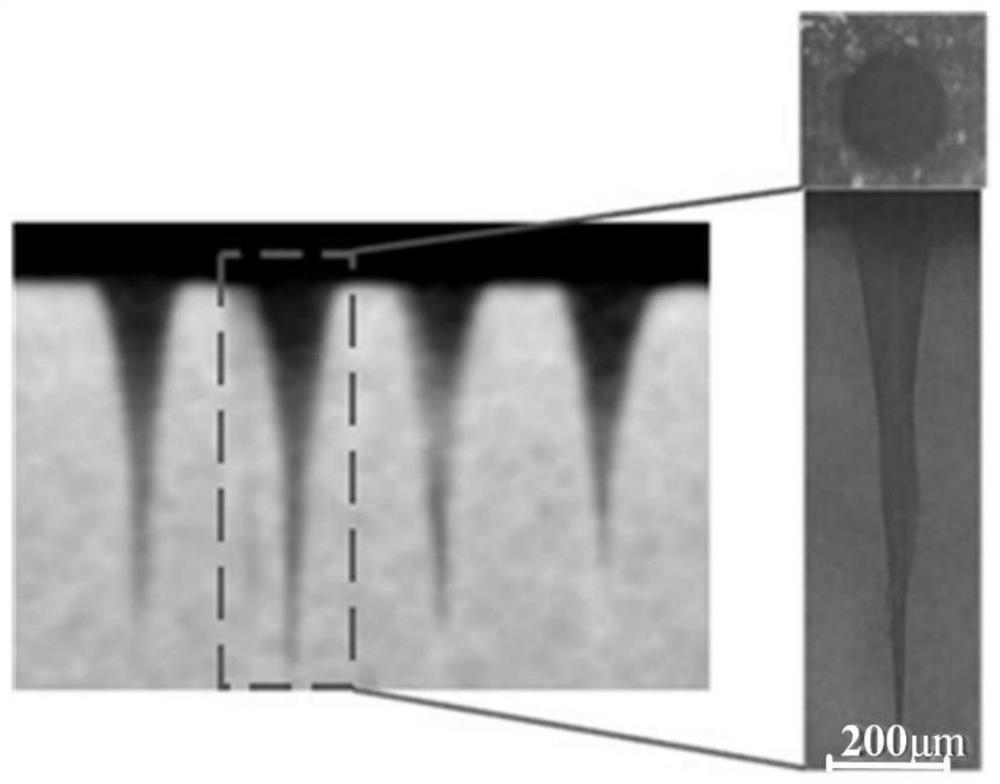
[0031] In Example 2, the combination of processing parameters in Step 5) of Example 1 was changed to: laser power of 2.4W, defocus of -2mm, processing time of 23s, diameter of aperture stop 7 of 12mm, and circularly polarized light processing. Its processing effect refers to Figure 4 As shown, millimeter-scale deep micropores with an entrance aperture of 221 μm, a pore depth of 1220 μm, a depth-to-diameter ratio of 5.5:1, a taper of 5.19°, and a roundness of 88.2% were obtained, and the surface of the micropore was basically free of damage.
[0032] The beneficial effects of this embodiment are: Figure 4 , the depth of the deep micropores of the quartz glass obtained in this embodiment is slightly increased compared with Example 1 but remains almost unchanged. The taper of the hole is slightly increased; this kind of deep microhole is suitable for the manufacture of deep microholes that require large opening diameters, such as quartz glass microchannel diversion holes that ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] In Example 3, the combination of processing parameters in Step 5) of Example 1 was changed to: laser power of 2W, defocus of 0 mm, processing time of 17 s, diameter of aperture stop 7 of 12 mm, and circularly polarized light processing. Its processing effect refers to Figure 5 As shown, millimeter-scale deep micropores with an entrance aperture of 195 μm, a pore depth of 1025 μm, a depth-to-diameter ratio of 5.3:1, a taper of 5.44°, and a roundness of 88.5% were obtained, and the surface of the micropore was basically free of damage.
[0034] The beneficial effects of this embodiment are: Figure 5 , the deep micropore depth of the quartz glass obtained in this embodiment is reduced compared with Example 1, but still can reach the millimeter level, and the reduction rate of the micropore depth is greater than the reduction rate of the micropore opening diameter, so the taper of the deep microhole increases. This structure It is the smallest experimental parameter to a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com