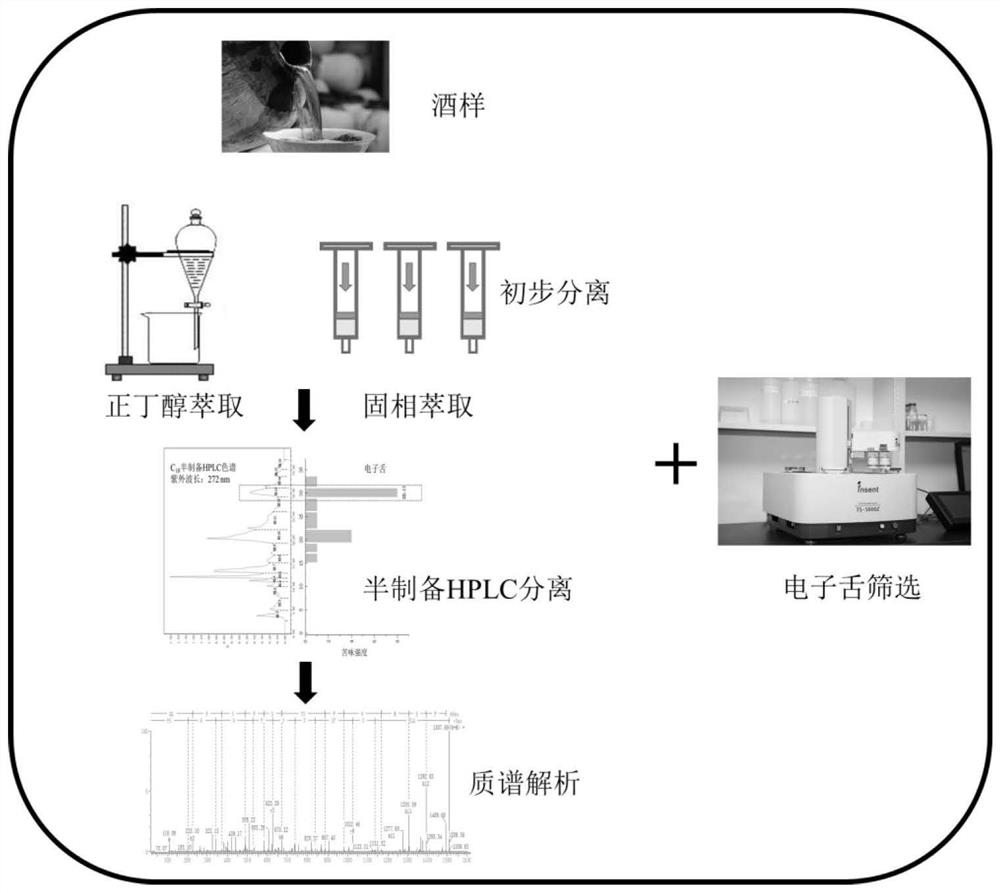
Method for separating and identifying bitter polypeptides in yellow rice wine
A technology for bitterness and rice wine, applied in material separation, analysis materials, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of result interference, high material components, complexity, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the possibility of false positives
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Electronic Tongue Evaluation of Bitterness Intensity
[0040] The freeze-dried components were dissolved in 100 mL of deionized water, centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 10 min, and 80 mL of the supernatant was taken for electronic tongue detection. First, wash in the cleaning solution for 90s, then wash with the reference solution for 120s, then wash with another reference solution for 120s, the sensor returns to zero at the equilibrium position for 30s, after reaching equilibrium, soak in the separated component for 30s for measurement. Do 4 cycles for each sample, remove the first cycle, and take the average value of the last 3 cycles. And complete data processing in TS-5000Z in the database of its instrument terminal system server to obtain relative bitterness intensity.
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Preliminary Separation of Yellow Rice Wine Samples
[0042] (1) Separation of rice wine samples by distillation under reduced pressure
[0043] Take 300mL of rice wine and carry out vacuum distillation (conditions of vacuum distillation: -0.1MPa, 45°C, 90rpm), when the volume of rice wine is less than 30mL, stop the rotary evaporation, and freeze-dry the remaining low-volatile components to obtain difficult Volatile component F was stored at -20°C for later use, and its bitterness intensity was evaluated by electronic tongue.
[0044] (2) ethanol alcohol precipitation to separate difficult volatile components F
[0045] Take the less volatile component F, dissolve it with 20mL of water, slowly add ethanol so that the final concentration of ethanol is 80%, and keep shaking and mixing, and let it stand at 4°C for 12h to obtain the ethanol phase, alcohol precipitation phase, and ethanol phase Distilled under reduced pressure (-0.1Mpa, 45°C, 90rpm), freeze-drie...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3: Separation of F-1-1-Ⅲ by semi-preparative HPLC
[0055] F-1-1-III (200 mg) was dissolved in 20 mL of water, filtered through a membrane (0.45 μm), and separated by semi-preparative HPLC.
[0056] Column: Xbridge Prep C 18 (5μm, 10mm×250mm); mobile phase: A ultrapure water, B methanol; elution conditions: 0min A / B (80:20), 5min A / B (70:30), 15min A / B (70: 30), 16min A / B(50:50), 25min A / B(50:50), 26min, A / B(30:70), 31min A / B(30:70), 32min A / B(0 :100), 40min, A / B(0:100), 41min A / B(80:20), 45min A / B(80:20); flow rate: 4mL / min; detection wavelength: 272nm; injection volume: 600 μL. According to the chromatographic peaks, fractions F-1-1-Ⅲ were divided into 16 fractions, respectively denoted as III-1~Ⅲ-16, and the same fractions were combined, lyophilized after rotary evaporation, and stored at -20°C for later use .
[0057] Chromatographic results such as figure 2 As shown, by semi-preparing C 18 The chromatographic column divides F-1-1-III into 16 compone...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com