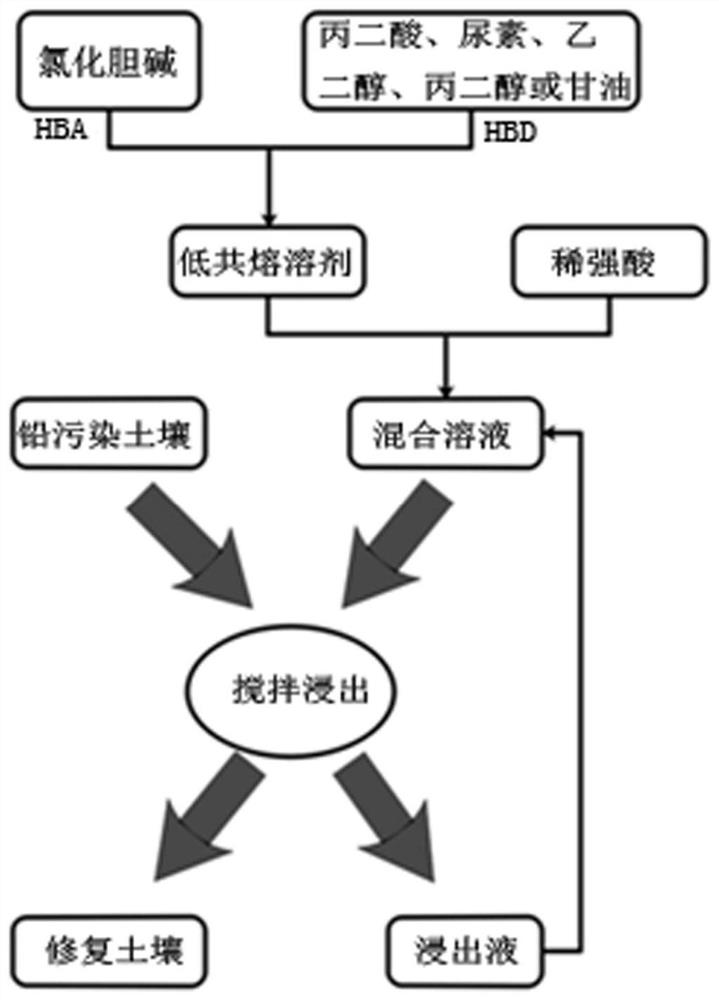
Heavy metal lead contaminated soil remediation method based on choline chloride eutectic solvents
A technology of lead-contaminated soil and low eutectic solvent is applied in the restoration of polluted soil and other directions to achieve the effects of cost reduction, efficient treatment and restoration, and no secondary pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Choline chloride and malonic acid were weighed at a molar ratio of 2:1, placed in a beaker, and heated in a water bath at 80°C for 7 hours to synthesize a colorless and transparent solution, namely DES. DES and 0.5wt% nitric acid solution were prepared into a mixed solution at a volume ratio of 3:2. Add 10 g of lead-contaminated soil (lead content about 15000 mg / kg), 50 ml of mixed solution and a stirring bar into a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask with a stopper. Set the stirring speed of the magnetic stirrer to 200 rpm and the temperature to 40 °C and continue stirring for 0.5-6 hours. After the reaction was completed, the Erlenmeyer flask was placed at room temperature and cooled for 20 min, and the leaching concentration of metallic lead in the supernatant was analyzed by ICP-OES.
[0021] After analysis, after continuous stirring for 0.5 h, the lead concentration in the original soil leachate was 12533.28 mg / L, which could remove 83.56% of the lead in the soil.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Choline chloride and malonic acid were weighed at a molar ratio of 2:1, placed in a beaker, and heated in a water bath at 80°C for 7 hours to synthesize a colorless and transparent solution, namely DES. DES and 0.5wt% nitric acid solution were prepared into a mixed solution at a volume ratio of 3:2. Add 10 g of lead-contaminated soil (lead content about 7000 mg / kg), 50 ml of mixed solution and a stirring bar into a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask with a stopper. Set the stirring speed of the magnetic stirrer to 200 rpm and the temperature to 40 °C and continue stirring for 0.5-6 hours. After the reaction was completed, the Erlenmeyer flask was placed at room temperature and cooled for 20 min, and the leaching concentration of metallic lead in the supernatant was analyzed by ICP-OES.
[0024] After analysis, after continuous stirring for 0.5 h, the lead concentration in the original soil leachate was 13,014.50 mg / L, which could remove 85.76% of the lead in the soil.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Choline chloride and malonic acid were weighed at a molar ratio of 2:1, placed in a beaker, and heated in a water bath at 80°C for 7 hours to synthesize a colorless and transparent solution, namely DES. DES and 0.5wt% nitric acid solution were prepared into a mixed solution at a volume ratio of 3:2. Add 10 g of lead-contaminated soil (lead content about 15000 mg / kg), 50 ml of mixed solution and a stirring bar into a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask with a stopper. Set the stirring speed of the magnetic stirrer to 200 rpm, and keep stirring for 0.5-6 hours at room temperature (25°C). After the reaction was completed, the Erlenmeyer flask was placed at room temperature and cooled for 20 min, and the leaching concentration of metallic lead in the supernatant was analyzed by ICP-OES.
[0027] After analysis, after continuous stirring for 0.5 h, the lead concentration in the original soil leachate was 10,428.47 mg / L, which could remove 69.52% of lead in the soil.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com