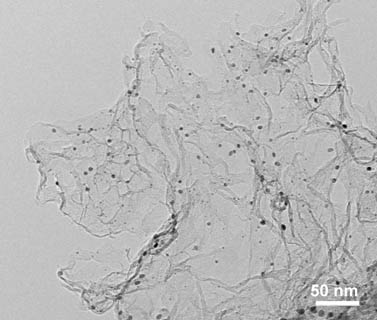
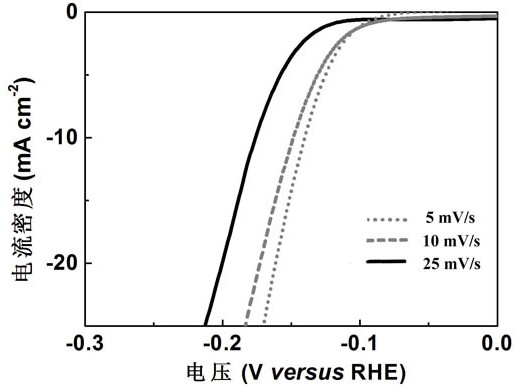
Preparation method, product and application of nitrogen-doped axial carbon fiber/graphene loaded cobalt nano electrocatalyst
A nitrogen-doped graphene, electrocatalyst technology, applied in physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, electrodes, etc., can solve the problem of burying active sites inside the graphene sheet, affecting the electron transport performance of metalloid characteristics, Catalytic active sites are doubled and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving catalytic activity, low price and easy control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] A nitrogen-doped axial carbon fiber / graphene-supported cobalt nano-electrocatalyst, using cellulose and nitrogen sources as raw materials, high-temperature in-situ carbonization to form a graphene fiber axial composite nitrogen-doped graphene sheet structure, while loading Co Nanoparticles obtain Mott-Schottky type heterojunctions, which are prepared as follows:
[0033] The first step, the preparation of carbon fiber and nitrogen-doped graphene axial composite nanomaterials: using coconut bacterial cellulose, urea, and melamine as raw materials, coconut bacterial cellulose, urea, and melamine were mixed in a mass ratio of 1:20:20 Mix evenly, then place it under the protection of nitrogen for calcination, control the calcination temperature to 1000 ℃, bacterial cellulose and urea are carbonized in situ to form graphite carbon fiber axial composite nitrogen-doped graphene sheet structure, and finally cool naturally to obtain carbon fiber and nitrogen-doped Miscellaneous ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A kind of nano electrocatalyst of nitrogen-doped axial carbon fiber / graphene supported cobalt, prepared according to the following steps:
[0039] The first step, the preparation of carbon fiber and nitrogen-doped graphene axial composite nanomaterials: using coconut bacterial cellulose, urea, and melamine as raw materials, coconut bacterial cellulose, urea, and melamine were mixed in a mass ratio of 1:20:20 Mix evenly, then place it under the protection of nitrogen for calcination, control the calcination temperature to 1200 ℃, bacterial cellulose and urea are carbonized in situ to form graphite carbon fiber axial composite nitrogen-doped graphene sheet structure, and finally cool naturally to obtain carbon fiber and nitrogen-doped Heterographene Axial Composite Nanomaterials.
[0040] The second step, the preparation of carbon fiber / nitrogen-doped graphene axial composite material supported cobalt electrocatalyst: add 2.0 g of carbon fiber and nitrogen-doped graphene ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A kind of nano electrocatalyst of nitrogen-doped axial carbon fiber / graphene supported cobalt, prepared according to the following steps:
[0043] The first step, the preparation of carbon fiber and nitrogen-doped graphene axial composite nanomaterials: using coconut bacterial cellulose, urea, and melamine as raw materials, coconut bacterial cellulose, urea, and melamine were mixed in a mass ratio of 1:20:20 Mix evenly, then place it under the protection of nitrogen for calcination, control the calcination temperature to 900 ℃, bacterial cellulose and urea are carbonized in situ to form graphite carbon fiber axial composite nitrogen-doped graphene sheet structure, and finally cool naturally to obtain carbon fiber and nitrogen-doped Heterographene Axial Composite Nanomaterials.
[0044] The second step, the preparation of carbon fiber / nitrogen-doped graphene axial composite material supported cobalt electrocatalyst: add 1.5 g of carbon fiber and nitrogen-doped graphene a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com