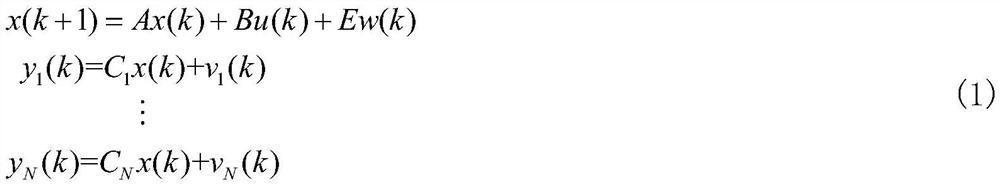Distributed fault diagnosis method based on centrosymmetric polyhedron
A centrosymmetric, fault diagnosis technology, applied in instruments, adaptive control, control/regulation systems, etc., to solve problems such as thresholds that cannot be generated online
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
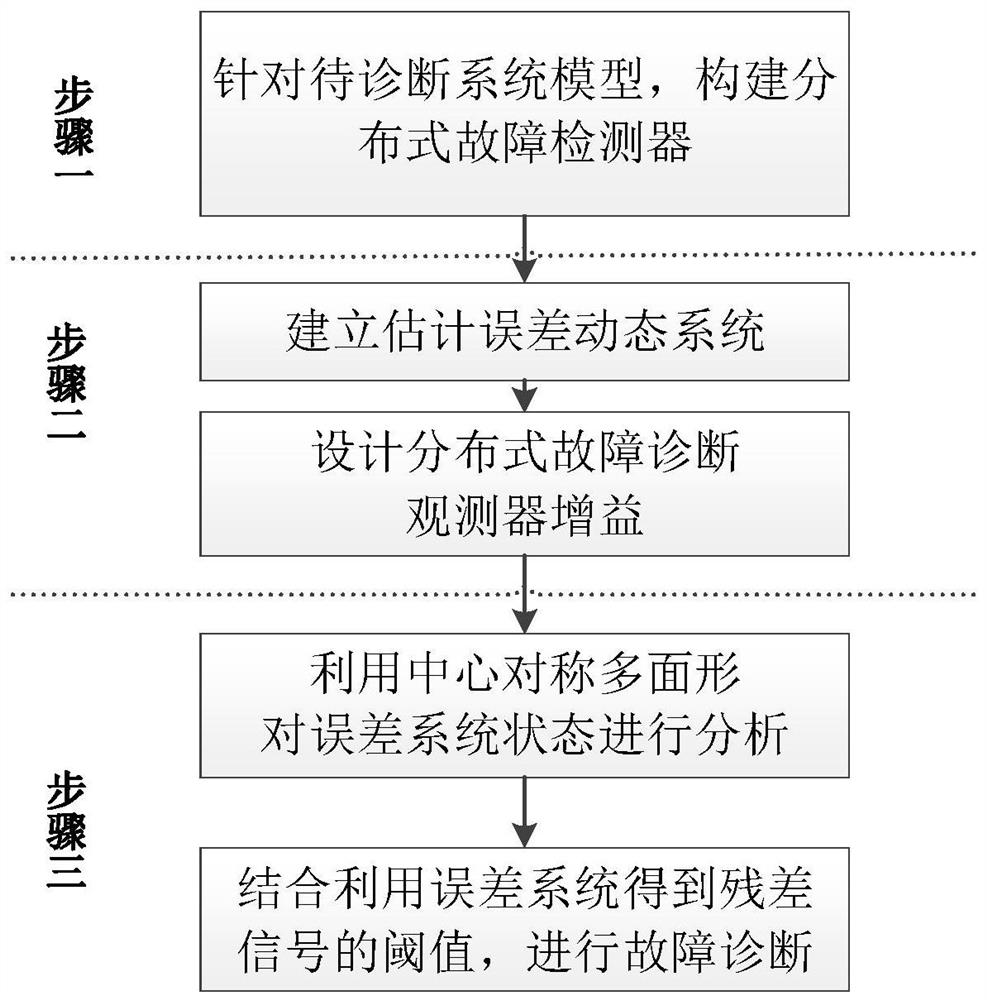
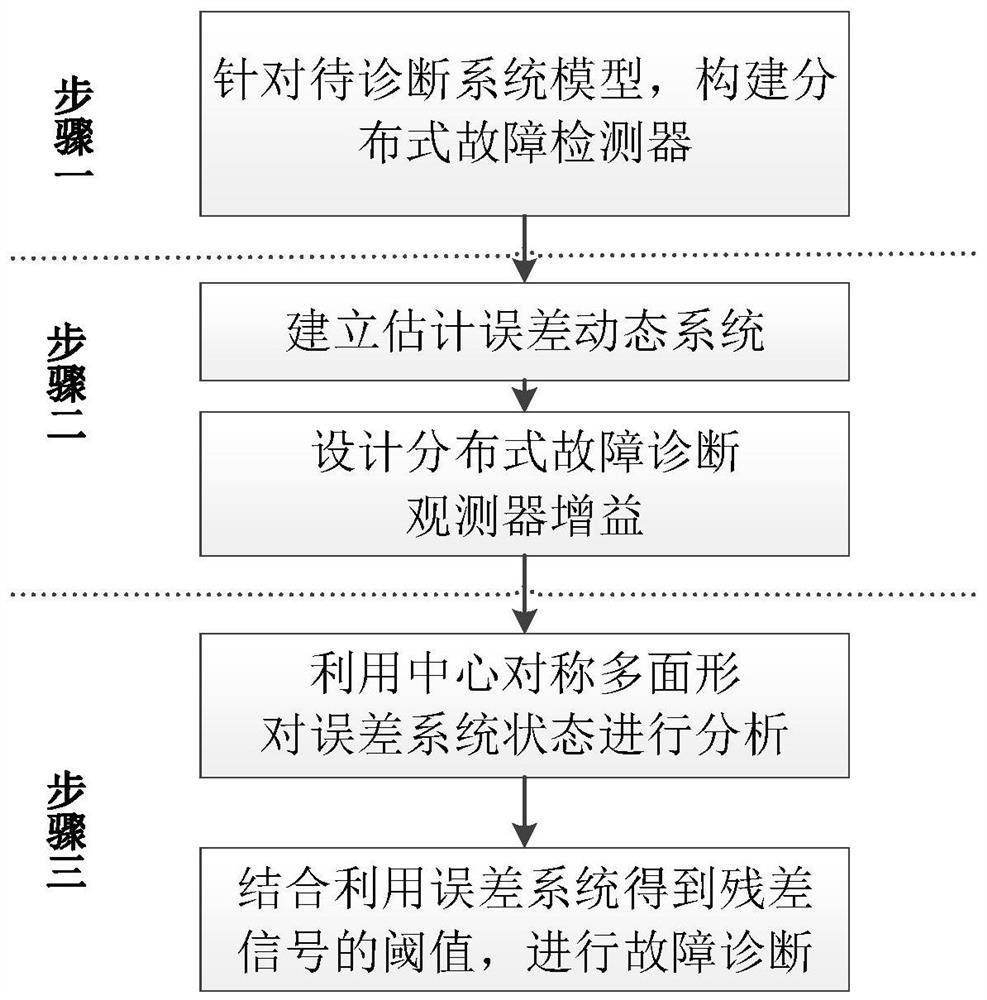
[0131] Step 1: Construct a distributed fault diagnosis observer based on the system model to be estimated;
[0132] Based on the system model to be estimated, it is established as a discrete linear system
[0133]
[0134] Where the system state is the voltage, ω=100πrad / s represents the fundamental angular frequency, T=0.0025s represents the sampling time, Δu=10 -3 u 0 sin(ωkT) represents the voltage difference in the sampling interval, and the measurement error is v i (k)=0.002(1+0.1i)U 0 sin(ωkT). The matrix parameters in formula (6) are C 1 =[1.1 0],C 2 = [1.2 0], C 3 = [1.3 0].
[0135] The range of system disturbance and measurement noise is described by the centrosymmetric polyhedron as:
[0136] w(k)∈W=w ,H w >, v i (k)∈V=i v ,H v >
[0137] For the convenience of subsequent calculations, here we set p w =p w = 0,
[0138] In this implementation example, distributed fault diagnosis is performed on the voltage according to the local measurement...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com