Resonant cavity type two-dimensional material photothermal effect measuring device
A technology of two-dimensional materials and photothermal effects, which is applied in the directions of measuring devices, analyzing materials, and material analysis through optical means, etc., can solve the problems of complex devices for the photothermal effects of two-dimensional materials, and achieve simple optical paths, high detection sensitivity, and experimental Simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The present invention provides a resonant cavity-type two-dimensional material photothermal effect measurement device, including: a light source, a photodetector, a substrate, and a first rectangular noble metal part 1 placed on the substrate, a second rectangular noble metal part 2, a resonant cavity 3, Sensitive Materials Section 4. Two-dimensional materials. like figure 1 As shown, the first rectangular noble metal part 1 and the second rectangular noble metal part 2 are parallel and form a metal-dielectric-metal waveguide, and the metal-dielectric-metal waveguide includes a waveguide input end and a waveguide output end. The material of the first rectangular noble metal part 1 and the second rectangular noble metal part 2 is noble metal. Preferably, the material of the first rectangular noble metal part 1 and the second rectangular noble metal part 2 is gold. The width of the metal-dielectric-metal waveguide is less than 100 nanometers. A light source generates l...
Embodiment 2
[0025] On the basis of Example 1, such as figure 2 As shown, the sensitive material part 4 is circular, and the size of the sensitive material part 4 is the same as that of the resonant cavity 3 . That is to say, the sensitive material portion 4 fills the resonant cavity 3 . At this time, the two-dimensional material is circular, and the two-dimensional material is not in contact with the second rectangular noble metal part 2 . During preparation, the resonant cavity 3 can be filled with sensitive materials, and the preparation is simple.
Embodiment 3
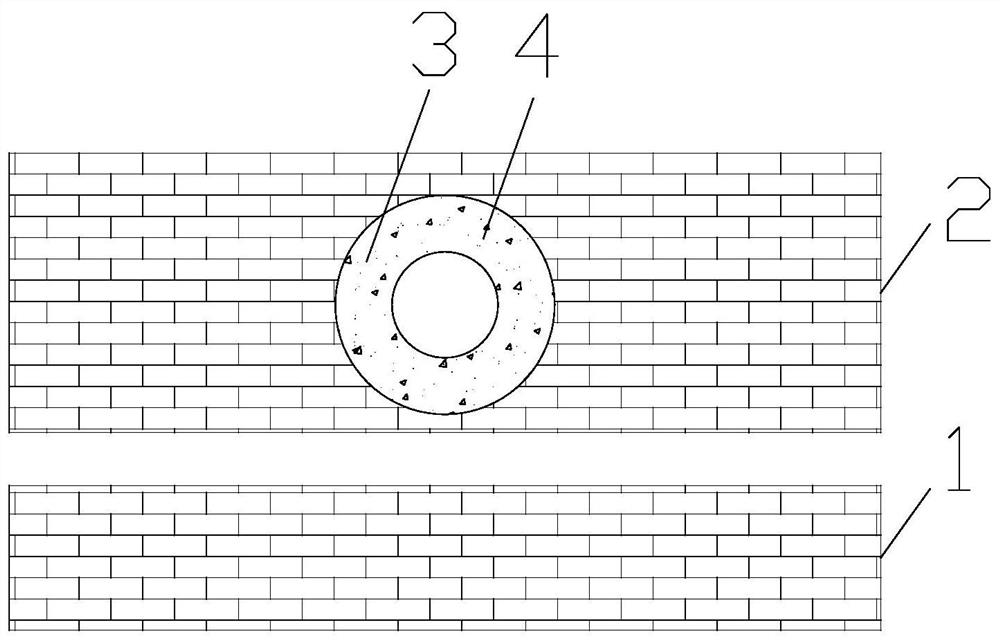
[0027] On the basis of Example 2, such as image 3 As shown, the sensitive material part 4 is circular, and the center of the sensitive material part 4 coincides with the center of the resonant cavity 3 . 2D materials are circular. The two-dimensional material is in contact with the ring-shaped sensitive material portion 4 . In this way, the amount of sensitive material in the sensitive material portion 4 is small. When the two-dimensional material generates heat, the temperature of the sensitive material part 4 is higher, the refractive index of the sensitive material part 4 is changed more, and the resonant wavelength of the resonant cavity 3 is changed more, thereby improving the sensitivity of the photothermal effect detection of the two-dimensional material.
[0028] Furthermore, the sensitive material portion 4 is in contact with the resonant cavity 3 . In the resonant cavity 3, the electric field is mainly distributed inside the resonant cavity 3, that is, the place ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com