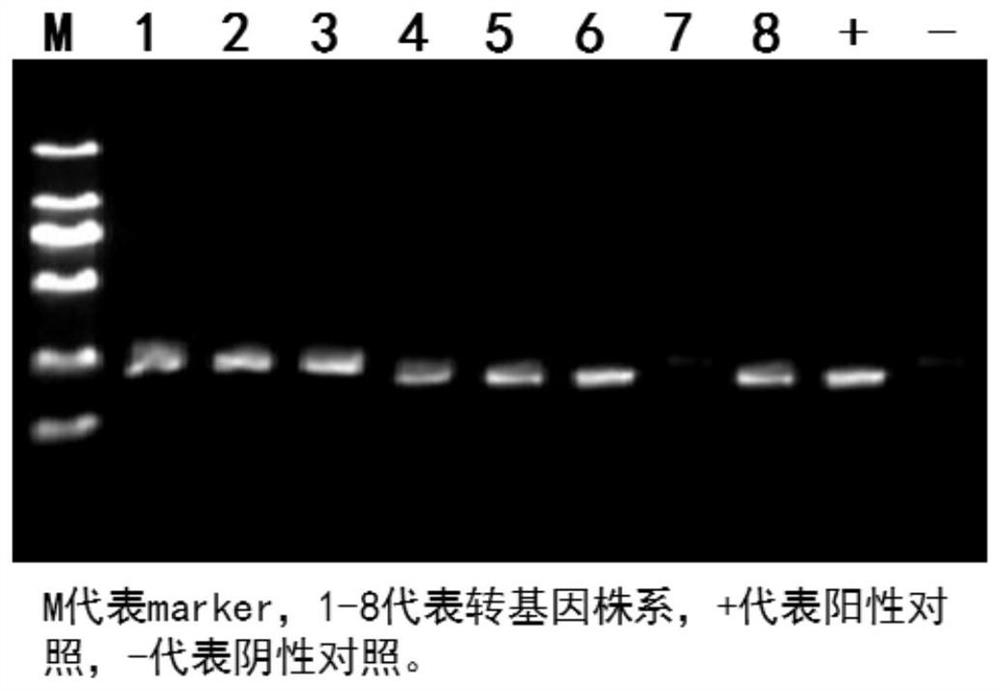
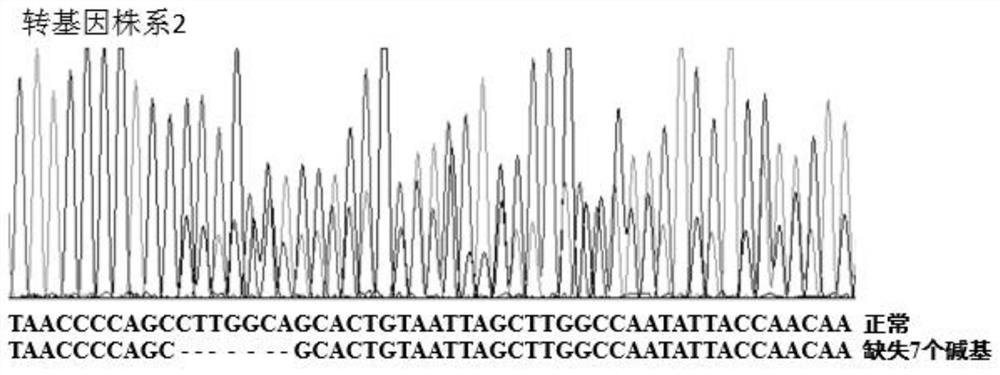
Two oligo DNA groups of sgRNA for fixedpoint knockout of rice OsPLS4 gene
A site-specific knockout, DNA sequence technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of weakened accumulation, weakened drought resistance and water retention capacity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1, design and synthesis of rice OsPLS4 gene sgRNA sequence
[0027] The coding region sequence of the rice OsPLS4 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.9.
[0028] In this embodiment, the CRISPR / Cas9 editing target sequence is 19bp in length, located in the 672-690 and 766-784 nucleic acid sequences of the eighth and ninth exons of the conservative sequence of the OsPLS4 gene coding region, and the edited target sequence is (SEQ ID NO .1): TTACAGTGCTGCCAAGGCT, (SEQ ID NO.2): TGTCAGATGCAATGAAACC, this sequence is specific on the rice genome, and the off-target probability is extremely low.
[0029] Synthesize four oligo DNAs according to the target sequence:
[0030] (SEQ ID NO. 3)PLS4(1)F: GGCATTACAGTGCTGCCAAGGCT
[0031] (SEQ ID NO. 4)PLS4(1)R: AAACAGCCTTGGCAGCACTGTAA
[0032] (SEQ ID NO. 5)PLS4(2)F: GGCATGTCAGATGCAATGAAACC
[0033] (SEQ ID NO. 6)PLS4(2)R: AAACGGTTTCATTGCATCTGACA
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2, OsPLS4 editing vector pYL-Hs-PLS4-cas9 construction
[0035] Add ddH to two oligo DNA groups PLS4(1)F and PLS4(1)R, PLS4(2)F and PLS4(2)R respectively 2 Dissolve O to 10 μM, mix according to the reaction system, heat at 95°C for 3 minutes, cool and anneal naturally to form a dimer structure between PLS4(1)F / R and PLS4(2)F / R, and form a dimer structure through annealing reaction , and then respectively connected with the vector pYL-Hs that fused the rice U3 promoter and gRNA backbone sequence. The ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli by the heat shock method, and a single colony was picked and cultured in LB liquid medium (+kan) for 12 hours, and then sequenced. Select the bacteria with correct sequencing to extract the plasmid DNA, and obtain the editing vector pYL-Hs-PLS4-cas9 containing the target sequence of the rice OsPLS4 gene. For the vector map, see figure 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3, pYL-Hs-PLS4-cas9 carrier Agrobacterium transformation
[0037] Transform pYL-Hs-PLS4-cas9 plasmid into Agrobacterium by freeze-thaw method, add 10 μL of plasmid DNA to 200 μL of Agrobacterium EHA105 competent, ice bath for 30 minutes, freeze in liquid nitrogen for 3 minutes, 37 ° C water bath for 5 minutes, add 1 mL of YEB medium , shake culture at 28°C for 3-4h. Centrifuge at 6000 rpm for 1 min at room temperature, discard the supernatant, add 200 μL of YEB medium to resuspend the bacteria, spread on YEB solid medium (+rifampicin), and incubate at 28°C for 3 days. Single-pick colony identification.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com