Compact and firm multi-degree-of-freedom bionic joint and manufacturing method thereof
A bionic joint and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as large joint volume, material fatigue, deformation, etc., and achieve the effects of simple joint structure, high impact resistance, and reduced manufacturing costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
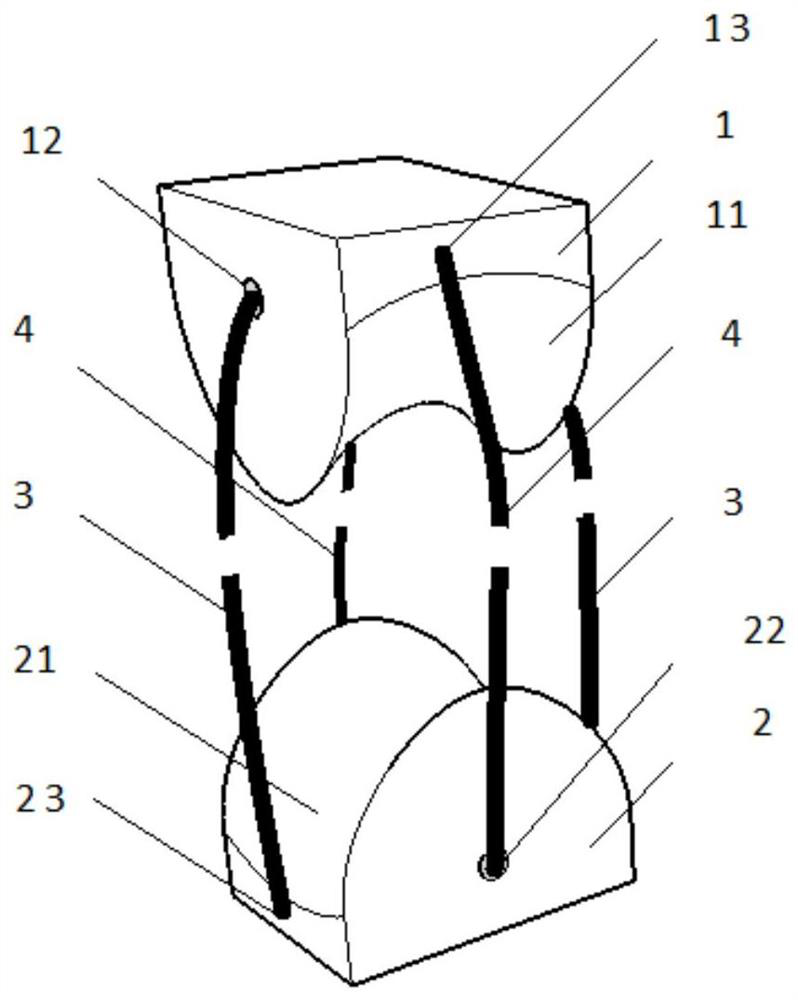
[0054] Reference attached figure 1 and attached figure 2 , showing a 2-DOF biomimetic joint. attached figure 1 is an exploded diagram, with figure 2 is a stereogram.
[0055] The first joint 1 includes a first curved surface 11, a first installation hole 12 in the X direction, and a first installation hole 13 in the Y direction. The first installation hole 12 in the X direction is located at the axis of the curved surface, and the first installation hole 13 in the Y direction is located at the outer edge of the curved surface. ;
[0056] The second joint member 2 includes a second curved surface 21, a second installation hole 23 in the X direction, and a second installation hole 22 in the Y direction. The second installation hole 22 in the X direction is located at the axis of the second curved surface 21, and the second installation hole 23 in the Y direction is located the outer edge of the second curved surface 22;
[0057] The X-direction connecting fiber 3 passes ...
Embodiment 2
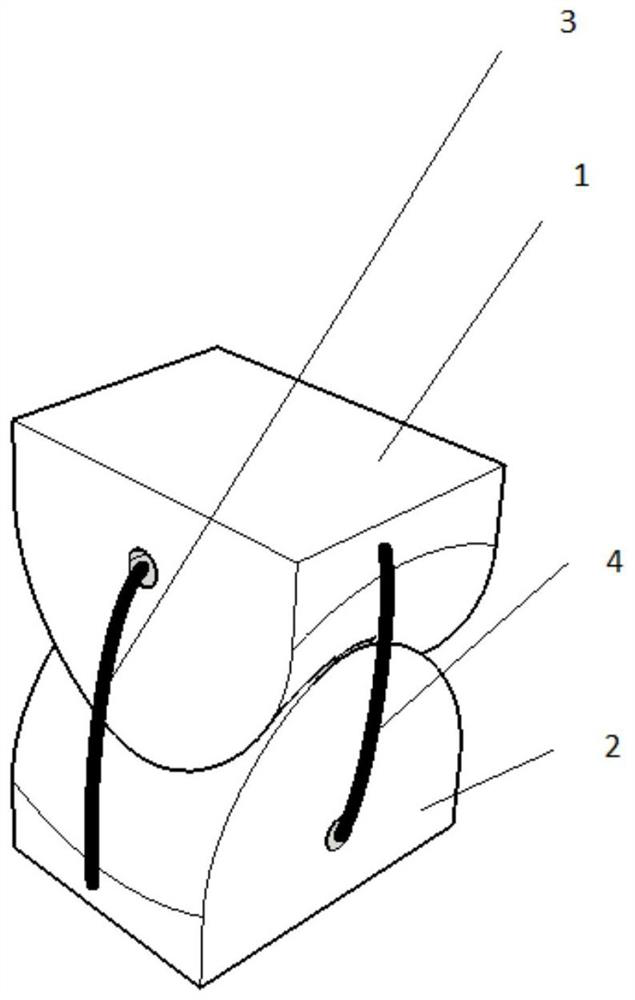
[0062] Reference attached image 3 , showing a 3-DOF bionic joint.
[0063] The first joint member 1 includes a first curved surface 11, and the first curved surface 11 is a convex spherical surface.
[0064] The second joint member 2 includes a second curved surface 21, and the second curved surface 21 is a concave spherical surface.
[0065] The X-direction connecting fibers 3 and Y-direction connecting fibers 4 connect the first joint part 1 and the second joint part 2 .
[0066] When the first joint part 1 rotates relative to the second joint part 2, the X-direction connecting fibers 3 and Y-direction connecting fibers 4 tighten the first curved surface 11 and the second curved surface 21 to ensure the accuracy of the motion trajectory, while defining The range of rotation of the joint.
[0067] The X-direction connecting fiber 3 and the Y-direction connecting fiber 4 are manufactured by mixing 70% Kevlar fiber and 30% elastic polyurethane fiber material, so that the co...
Embodiment 3
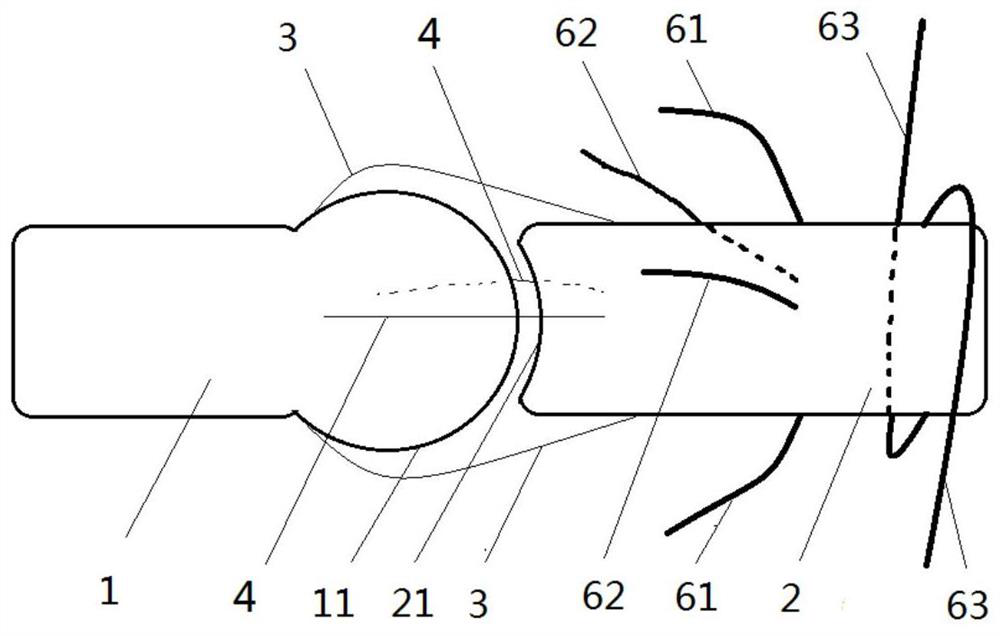
[0070] Reference attached Figure 4 , shows the schematic diagram of the motion of the bionic joint with variable degrees of freedom.
[0071] attached Figure 4 It is shown that the limiting fiber 7 is tightened as the second joint member 2 rotates. Adding a limit fiber 7 between the first joint part 1 and the second joint part 2 can further limit the degree of freedom of joint movement. The connection position between the limiting fiber 7 and the first curved surface 11 deviates from the axis of the first curved surface 11, and the connection position with the second joint part 2 is located near the edge of the second curved surface 21. When the second joint part 2 gradually rotates clockwise, The limiting fiber 7 is gradually tightened from the relaxed state, restricting the second joint member 2 from further clockwise rotation and lateral swinging, and at this time the degree of freedom of the joint is reduced.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com