Real-time monitoring method for enteroscope withdrawal time based on random forest algorithm
A random forest algorithm and real-time monitoring technology, applied in the field of medical assistance, can solve problems such as long learning process, many setting parameters, over-fitting, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the quality of colonoscopy examination and ensuring objectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
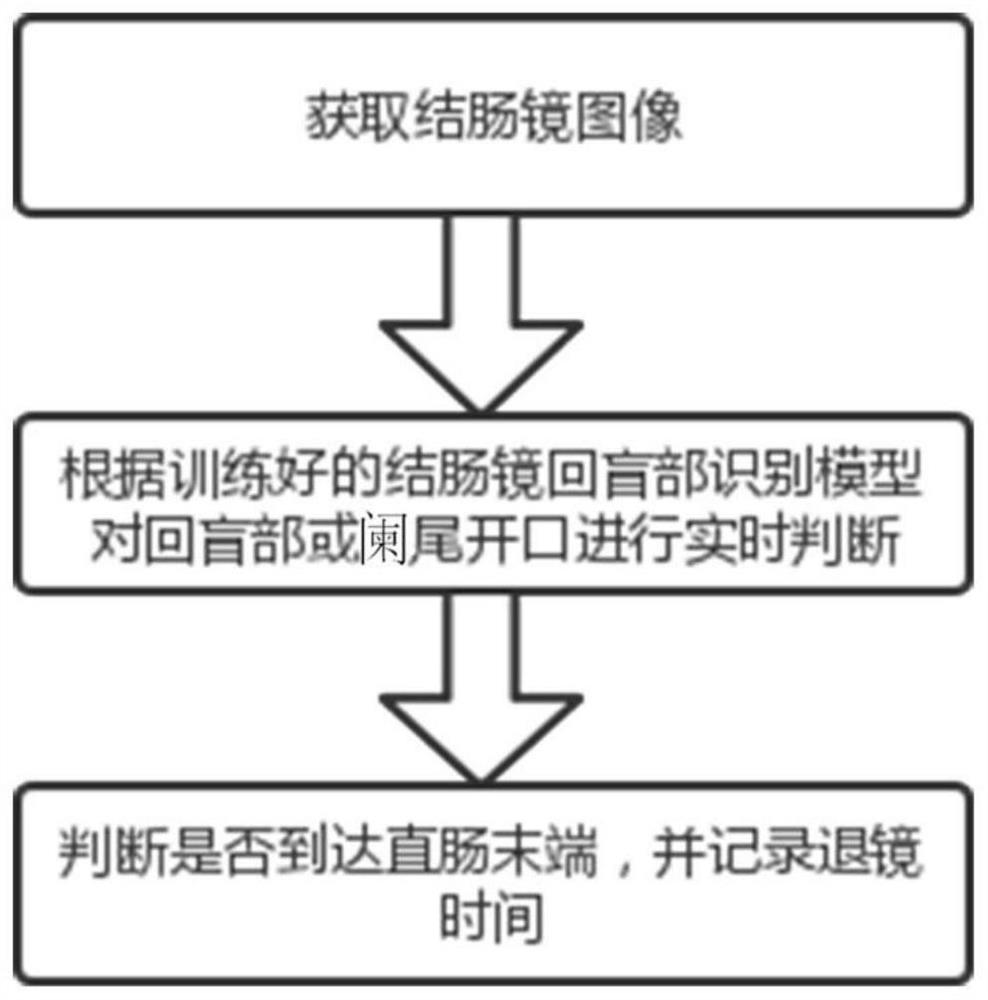
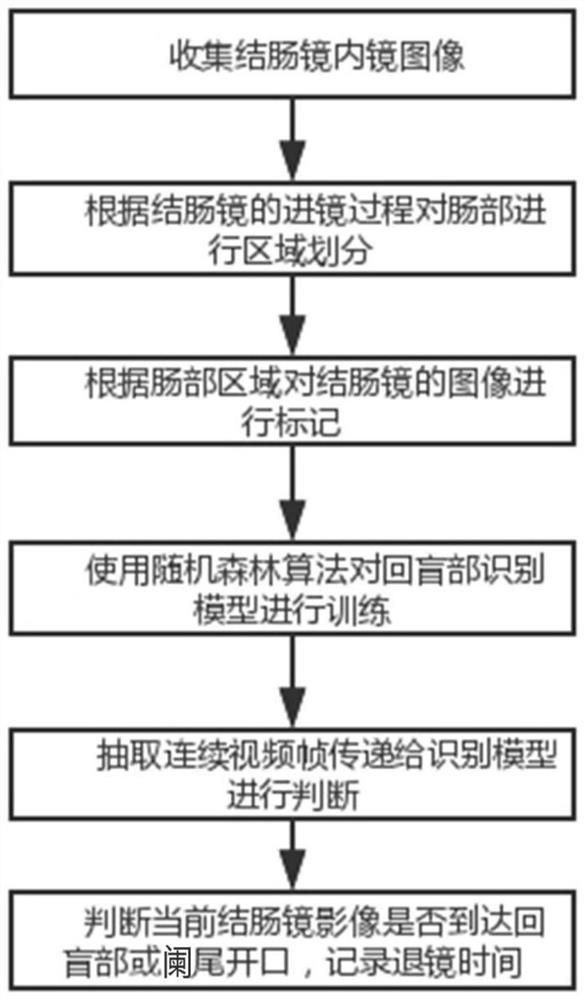
[0030] S1. Collect endoscopic image data of non-cecum, ileocecum and appendix opening in the intestine;
[0031] S2. Divide and mark the image data of the non-cecum, ileocecum, and appendix opening according to the sequence of colonoscopy examination to obtain a colonoscopy data set;
[0032] S3. Based on the random forest algorithm, construct and train the identification model of the ileocecal part of the colonoscope;
[0033] The S3.1 colonoscopy image data set enhances the image features in the training set through image enhancement technology based on color and texture features;
[0034] Specific enhancements include:
[0035] 1. Color enhancement: use image brightness, saturation, and contrast changes to increase the amount of data;
[0036] 2. Principal component analysis: Calculate the mean and standard deviation according to the three RGB color channels, then calculate the covariance matrix on the entire training set, perform eigendecomposition, and obtain the eigenv...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The difference technology with embodiment one is:
[0045] S4.1 Since the number of colonoscopy video image frames is too high, it is necessary to obtain colonoscopy pictures by drawing frames at equal time intervals, arrange the acquired pictures in chronological order, and input them into the colonoscopy ileocecal recognition model for judgment;
[0046] S4.2 Each decision tree is trained according to its extracted sample set, by generating a series of rules, and then classifying pictures based on these rules;
[0047] S4.3 Synthesize the classification results of each decision tree, vote for each record, and finally judge the location.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The difference technology with embodiment two is:
[0050]In step S4, the final judgment result of whether the ileocecal part or the opening of the appendix is reached is based on the multiple consecutive sub-results returned by the ileocecal part recognition model, and is given after 9 out of 5 analysis, so that the results are fast and accurate It can judge the type of digestive endoscopy in real time, without waiting for the end of the examination to give the result.
[0051] The final judgment result is based on the multiple consecutive sub-judgment results returned by the ileocecal recognition model of the colonoscope, and is given after the analysis of 9 out of 5 (9 out of 5 or 7 out of 4 can be adjusted as needed). The probability of identifying errors, while ensuring that the method can realize the real-time judgment of the ileocecal portion or appendix opening of the colonoscope, without waiting for the end of the inspection to give a judgment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com