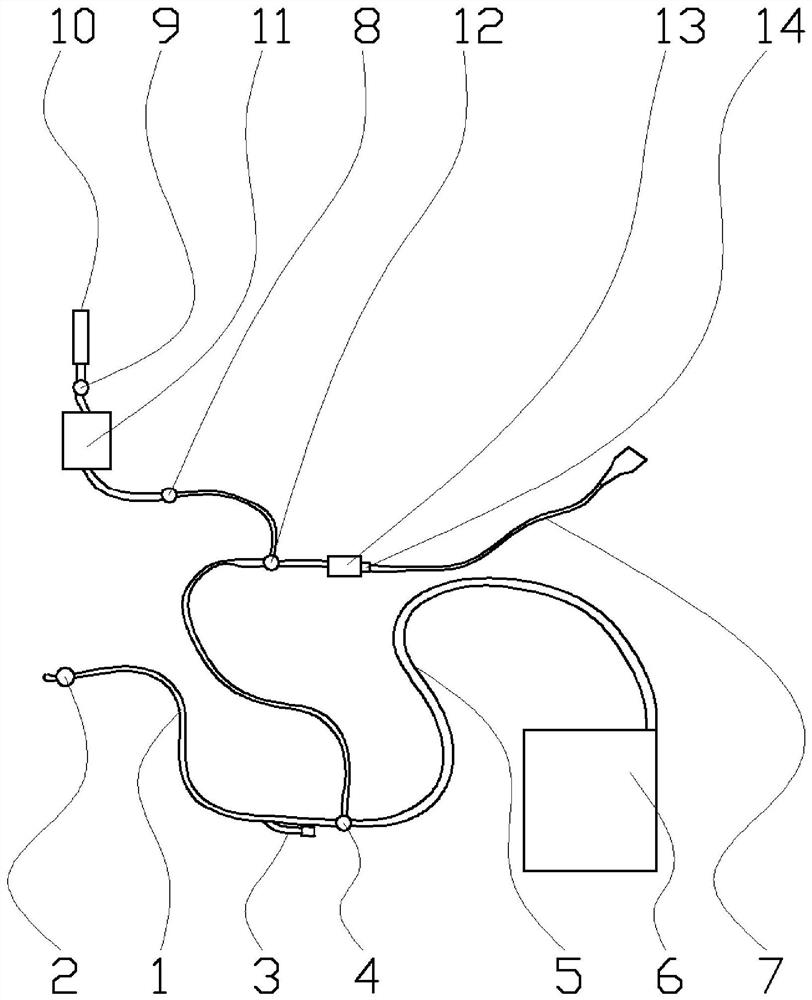
Method applied to intra-abdominal pressure monitoring of critical patient
A technology for patients and severe patients, applied in the field of physiological parameter monitoring, can solve the problems of insensitivity to fluctuations in bladder pressure, inaccurate monitoring data, and inapplicability to severe patients, etc., achieving good application prospects, accurate monitoring results, and high repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
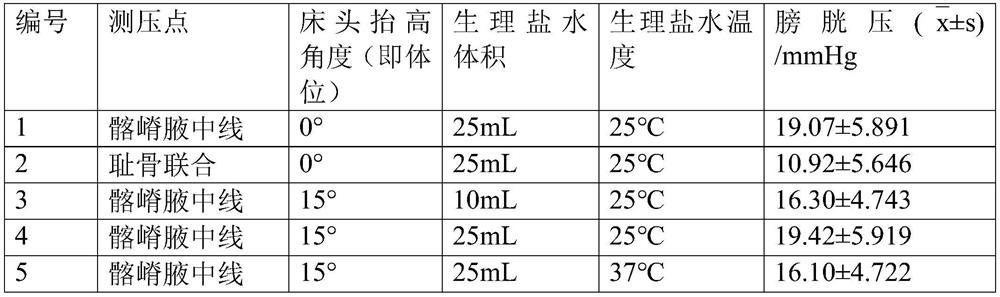
[0050] Example 1: Method for monitoring bladder pressure in critically ill patients using a bladder pressure monitoring instrument
[0051] The monitoring method is as follows:
[0052] (1) Insert the urinary catheter of the bladder pressure monitoring instrument into the urethra of critically ill patients under sterile conditions;
[0053] (2) Raise the head of the bed of critically ill patients by 15°;
[0054] (3) Empty the bladder, take the midaxillary line of the iliac crest as the pressure measurement point in critically ill patients, and adjust to zero;
[0055] (4) Slowly inject 25 mL of normal saline at 25°C into the bladder, and measure bladder pressure; monitor Q6h (that is, measure once every 6 hours), and monitor continuously for 72 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2: The method for monitoring the bladder pressure of critically ill patients with a bladder pressure monitoring instrument
[0057] The monitoring method is as follows:
[0058] (1) Insert the urinary catheter of the bladder pressure monitoring instrument into the urethra of critically ill patients under sterile conditions;
[0059] (2) Raise the head of the bed of critically ill patients by 15°;
[0060] (3) Empty the bladder, take the midaxillary line of the iliac crest as the pressure measurement point in critically ill patients, and adjust to zero;
[0061] (4) Slowly inject 10 mL of normal saline at 25°C into the bladder, and measure bladder pressure; monitor Q6h (that is, measure once every 6 hours), and monitor continuously for 72 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3: Utilize the method for monitoring bladder pressure of critically ill patient by bladder pressure monitoring instrument
[0063] The monitoring method is as follows:
[0064] (1) Insert the urinary catheter of the bladder pressure monitoring instrument into the urethra of critically ill patients under sterile conditions;
[0065] (2) Adjust the head of the bed of critically ill patients to raise by 15°;
[0066] (3) Empty the bladder, take the midaxillary line of the iliac crest as the pressure measurement point in critically ill patients, and adjust to zero;
[0067] (4) Slowly inject 25 mL of normal saline at 37°C into the bladder, and measure bladder pressure; monitor Q6h (that is, measure once every 6 hours), and monitor continuously for 72 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com