Parallel drug-target correlation prediction method based on sorting learning
A sorting learning and prediction method technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve the problems of further exploration of the degree of drug-protein correlation, not convincing, etc., to achieve the benefits of redirection, performance improvement, and redundancy removal Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
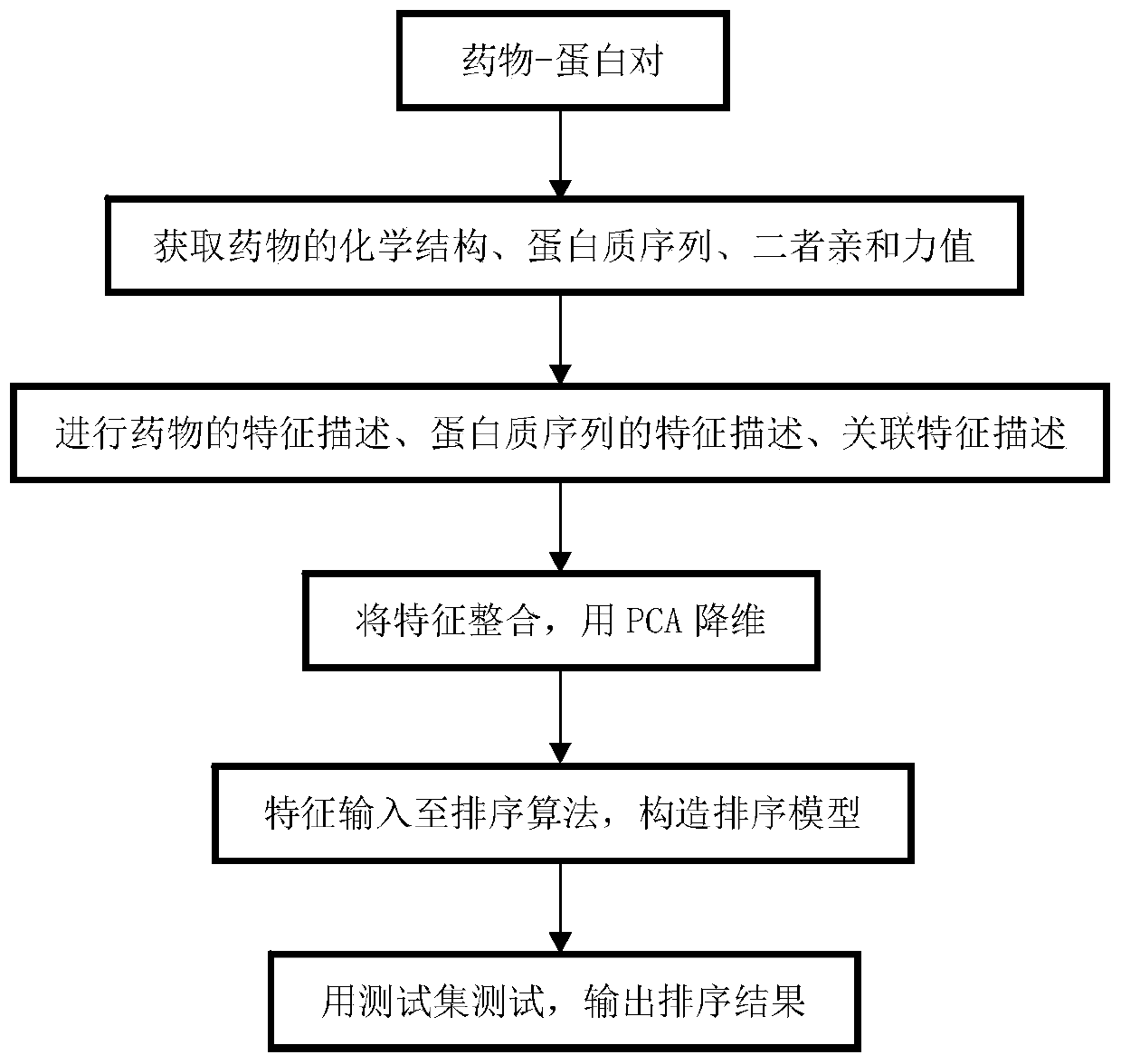
[0048] refer to figure 1 , a preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a parallel drug-target correlation prediction based on a ranking learning algorithm, including:
[0049] S1. Obtain the chemical structure sample set of the drug and the sequence sample set of the target;
[0050] S2. Based on the above sample set, multiple feature extraction algorithms are used to extract the drug, target, and drug-target in parallel to extract its chemical space features, gene space features, similarity and correlation features;
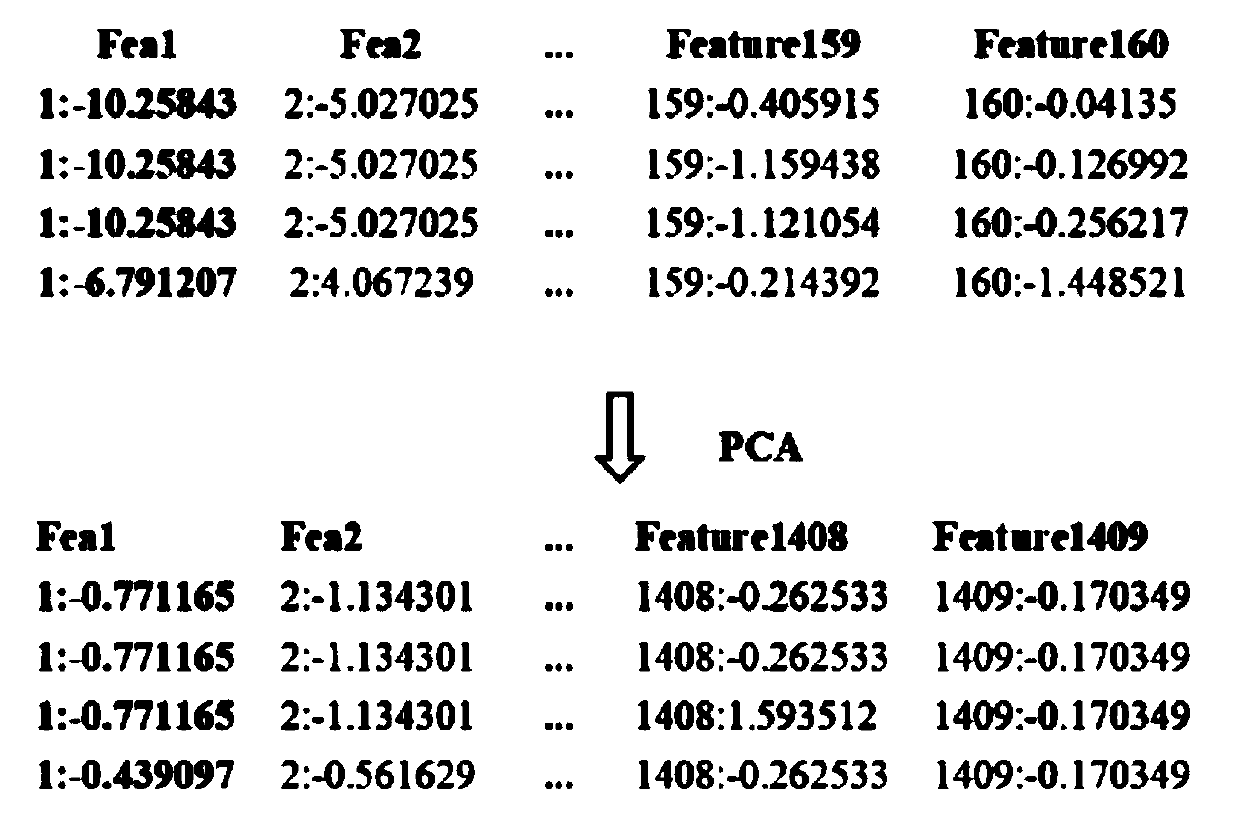
[0051] S3. Combine all the data features, and use principal component analysis (PCA) to perform dimensionality reduction processing on the feature set;
[0052] S4. Taking the feature set obtained by dimensionality reduction as input, using various sorting learning methods to sort the proteins or ligands that are relatively related to each query (drug or target), and calculate the correlation between each protein or ligand involved and the query S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com