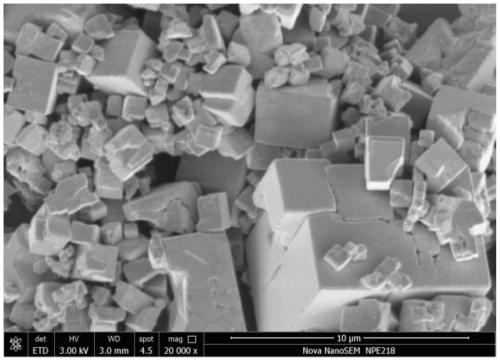
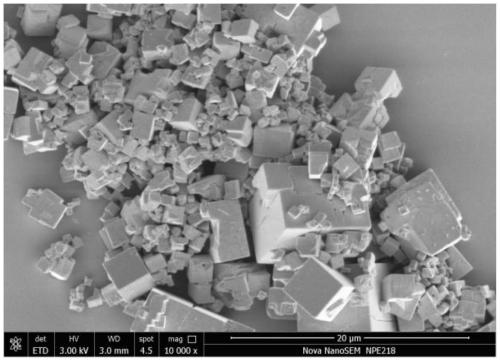
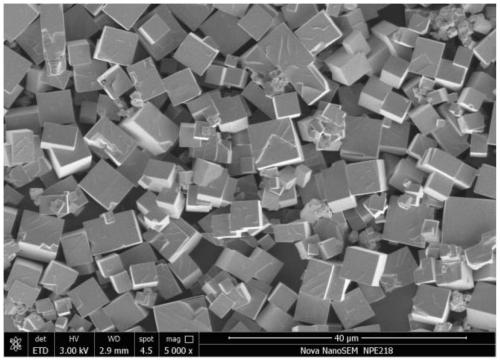
Sodium-ion battery positive electrode material, preparation method thereof and sodium-ion battery
A technology of sodium ion battery and positive electrode material, applied in battery electrodes, electrolyte battery manufacturing, secondary battery and other directions, can solve the problem of FeHCF crystal defects and other problems, and achieve the effect of excellent electrochemical performance, low cost and good cycle performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Preparation of FeHCF
[0062] The present embodiment relates to a kind of Prussian blue material, the preparation method of FeHCF, comprises the following steps:
[0063] (1) Dissolve 0.2g of sodium ferrocyanide, 1g of citric acid and 1g of sodium citrate in a mixed solution of 40ml of water and 10ml of ethanol, stir evenly, then transfer to a 100ml polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and seal the reactor Put it in a metal shell, and then place it in a blast drying oven at 120 degrees to react for 12 hours.
[0064] (2) The reactor is cooled down, the product is centrifuged, and vacuum-dried at 120 degrees for 12 hours to obtain the Prussian blue-type sodium-ion battery cathode material FeHCF (Na 1.95 Fe[Fe(CN) 6 ] 0.995 ·□ 0.005 ), D50 is 6.98 microns.
Embodiment 2
[0066] Preparation of FeHCF
[0067] The present embodiment relates to a kind of Prussian blue material, the preparation method of FeHCF, comprises the following steps:
[0068] (1) 1g of sodium ferrocyanide, 10g of citric acid and 10g of sodium citrate are dissolved in a mixed solution of 40ml of water and 10ml of ethanol, stirred evenly, then transferred to a 100ml polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and the reactor is sealed in Put it in a metal shell, and then place it in a blast drying oven at 80 degrees to react for 16 hours.
[0069] (2) The reactor is cooled down, the product is centrifuged, and vacuum-dried at 120 degrees for 12 hours to obtain the Prussian blue-type sodium-ion battery cathode material FeHCF (Na 1.84 Fe[Fe(CN) 6 ] 0.981 ·□ 0.019 ), D50 is 7.86 microns.
Embodiment 3
[0071] Preparation of FeHCF
[0072] The present embodiment relates to a kind of Prussian blue material, the preparation method of FeHCF, comprises the following steps:
[0073] (1) Dissolve 2g of sodium ferrocyanide, 20g of citric acid and 20g of sodium citrate in a mixed solution of 40ml of water and 10ml of ethanol, stir evenly, then transfer to a 100ml polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and seal the reactor in In a metal shell, it was then placed in a blast drying oven at 160°C for 8 hours of reaction.
[0074] (2) The reactor is cooled down, the product is centrifuged, and vacuum-dried at 120 degrees for 12 hours to obtain the Prussian blue-type sodium-ion battery cathode material FeHCF (Na 1.86 Fe[Fe(CN) 6 ] 0.990 ·□ 0.010 ), D50 is 8.28 microns.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com