Method for recovering platinum from laboratory waste noble metal material through potassium borohydride-ammonium chloride reduction
A technology of potassium borohydride and ammonium chloride, which is applied in the field of precious metal recovery, can solve problems such as difficult operation, high risk, and difficult storage, and achieve the effects of avoiding waste and loss, simple operation, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
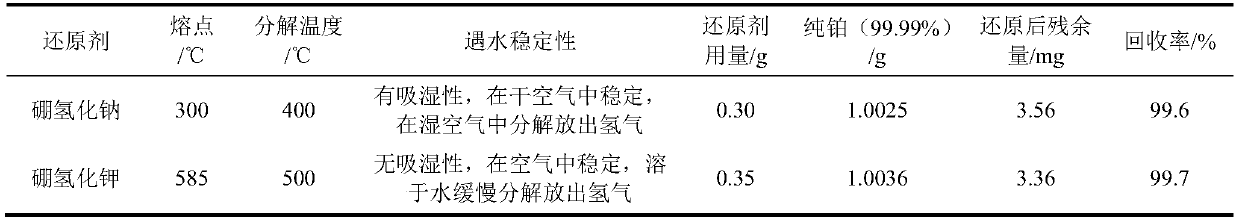
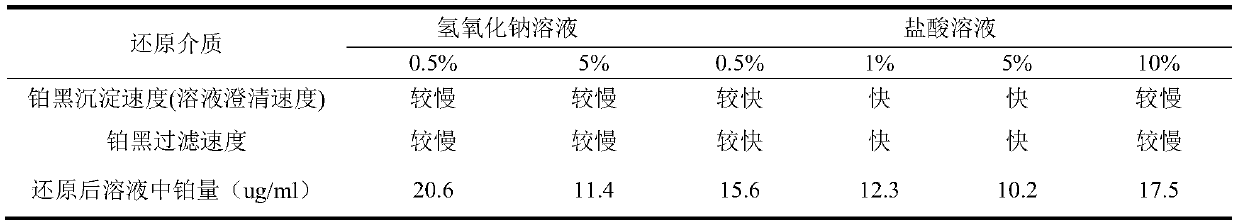
[0019] The method of potassium borohydride-ammonium chloride reduction and recovery of platinum in waste precious metal materials in the laboratory of this embodiment is as follows:
[0020] (1) Dissolution of platinum in the sample
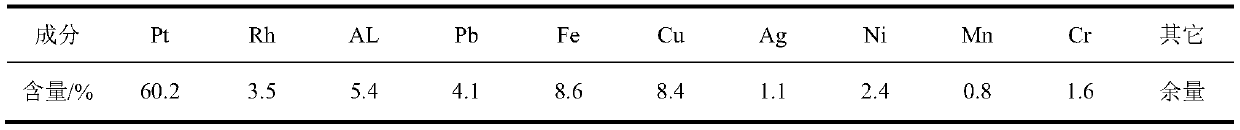
[0021] Weigh 20.0 g of experimental raw materials, put it into a 500 ml beaker, add 100 ml of distilled water, slowly add nitric acid with a volume ratio of 1:1, and keep stirring until there are no more bubbles in the solution, then continue to over-add about 50 ml, and The total volume is controlled to be about 200 milliliters. Heat to dissolve and remove metals such as copper, lead, and aluminum that are soluble in nitric acid from the raw materials. Take them off and cool them, place them for clarification, and discard the upper clear liquid. Add about 100 ml of aqua regia to the residue, place it on an electric heating plate at 120°C, and dissolve it in a slight boiling, and continue to add aqua regia until the platinum is fully dissolved. Conti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com