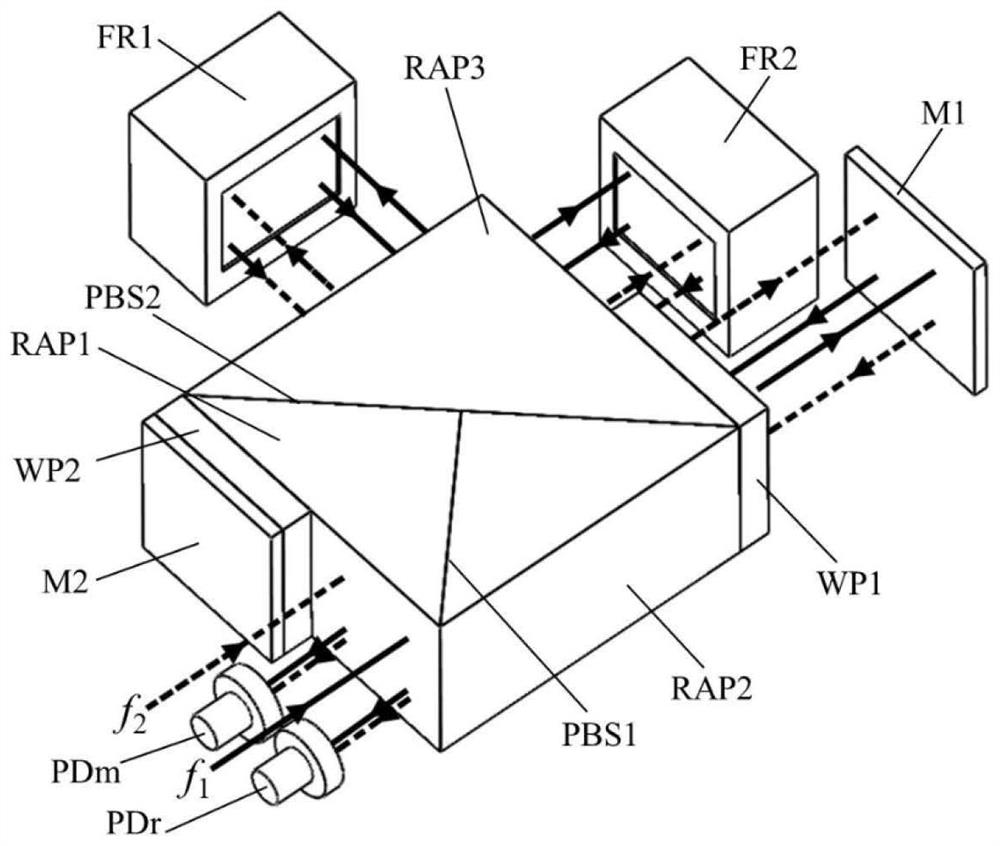
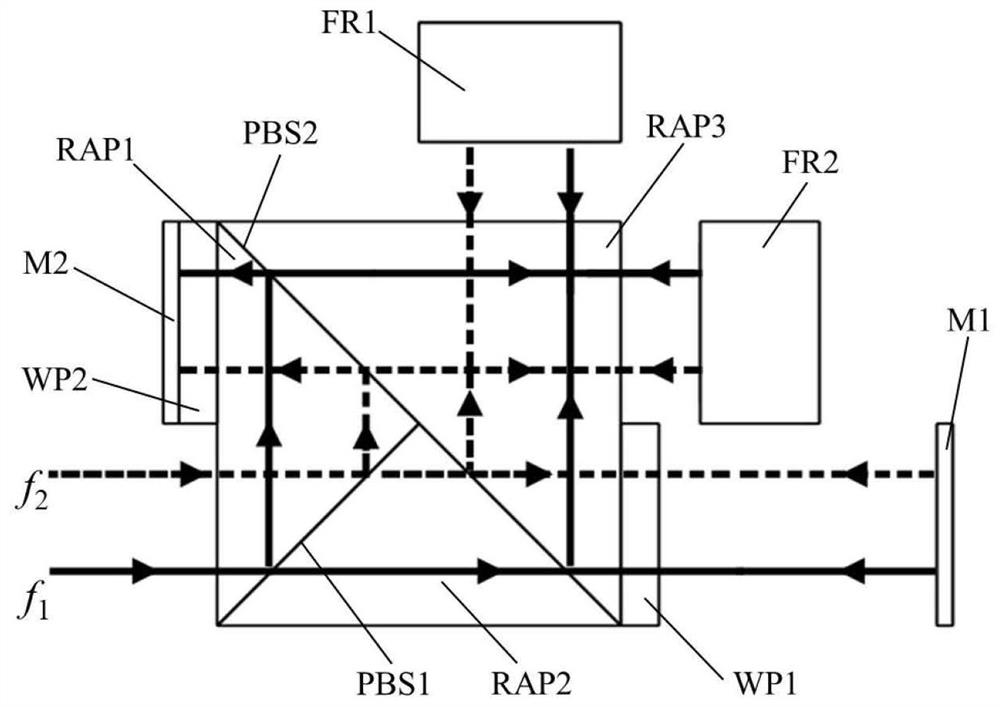
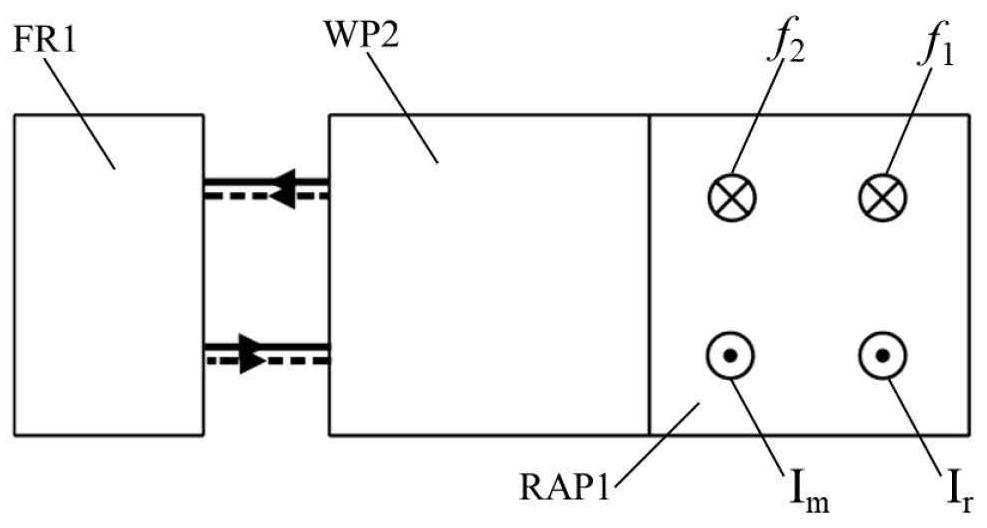
[0003] In heterodyne laser
interferometry, nanoscale periodic nonlinear errors severely limit the further improvement of measurement accuracy and resolution
Researches at home and abroad have shown that periodic nonlinear errors originate from optical
aliasing in the interference
optical path, and traditional heterodyne laser interferometers cannot avoid optical
aliasing. Therefore, scholars from various countries have changed their research ideas and proposed a heterodyne laser
interferometry based on spatially separated optical paths. Technology, which reduces or eliminates optical
aliasing by spatially separated
beam delivery to reduce or even eliminate periodic nonlinear errors
[0004] Based on the design concept of spatially separated optical paths, domestic and foreign scholars have successively developed different types of heterodyne laser interferometers, whose periodic nonlinear errors are significantly reduced, but there are certain limitations.
[0005] The heterodyne laser interferometer (Michelson
Interferometry with 10pm Accuracy. Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2000, 71(7): 2669-2676) developed by foreign scholars such as John Lawall is complex and complicated in composition, and the measuring beam is only reflected by the target plane Reflecting the mirror once will make the interference
signal contrast easily affected by the angular swing of the target
plane mirror, that is, the tolerance angle is small, and the
optical path imbalance between the measuring beam and the
reference beam causes the
thermal stability of the heterodyne laser interferometer to be relatively poor. Poor and therefore not widely available
[0006] The heterodyne laser interferometer (
Heterodyne Interferometer with Subatomic Periodic Nonlinearity.Appl.Opt., 1999,38(19):4089-4094) designed by Wu Chien-ming, a scholar in Taiwan, China, is extremely complex in composition, difficult to integrate and assemble, and the measurement beam It is only reflected once by the target
plane mirror so that the contrast of the interference
signal is easily affected by the angular swing of the target
plane mirror, that is, the tolerance angle is small, and there is also the problem of poor
thermal stability caused by the unbalanced
optical path[0007] Although the heterodyne laser interferometer (A
Heterodyne Interferometer with Periodic Nonlinearities Smaller than ± 10pm. Meas. Sci. Technol., 2012, 23 (9): 094005-094011) designed by German scholar Christoph Weichert has good thermal stability, but Its structure is complex, component customization and integrated assembly are difficult, and the measurement beam is only reflected once by the target plane mirror, which makes the interference signal contrast easily affected by the angular swing of the target plane mirror, that is, the tolerance angle is small, and it is not easy promotional use
[0008] Another foreign scholar, Steven R. Gillmer, developed a heterodyne laser interferometer (Development of a Novel
Fiber-Coupled Three Degree-of-Freedom Displacement Interferometer. University of Rochester Master Thesis, 2013), although the structure is simple and symmetrical and has good thermal stability. However, the measurement beam is only reflected once by the target plane mirror, which also makes the interference signal contrast easily affected by the angular swing of the target plane mirror, that is, the tolerance angle is small, so it is not easy to popularize and use
[0009] In addition, Korean scholar Ki-Nam Joo et al. developed a new space-separated heterodyne laser interferometer in the patent WO2010030179A1, but the heterodyne laser interferometer only has thermal The characteristics of good stability and large tolerance angle; Jonathan D.Ellis later changed the target corner cube
prism into a target plane reflector (
Fiber-coupled displacement
interferometry without periodic nonlinearity.
Optics Letters, 2011, 36(18): 3584-3586 .), but its complex structure and unbalanced optical paths of measuring light and reference light lead to poor thermal stability, and it is not easy to popularize and use
Hu Pengcheng of Harbin Institute of Technology and others proposed an improvement (Highly stable
heterodyne interferometer without periodic nonlinearity. Technisches Messen: Sensoren, Gerate, Systeme, 2014.) to balance the total optical path of the measurement light output and the
reference beam in multiple beam-splitting prisms. The thermal stability is improved, but the structure of the improved heterodyne laser interferometer is more complicated, the integration and assembly are more difficult, and it is not easy to promote
[0010] In summary, the existing space-separated heterodyne laser interferometers are difficult to meet the requirements of good thermal stability and large tolerance angle at the same time, which seriously limits the improvement of the measurement capability of heterodyne laser interferometers.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More