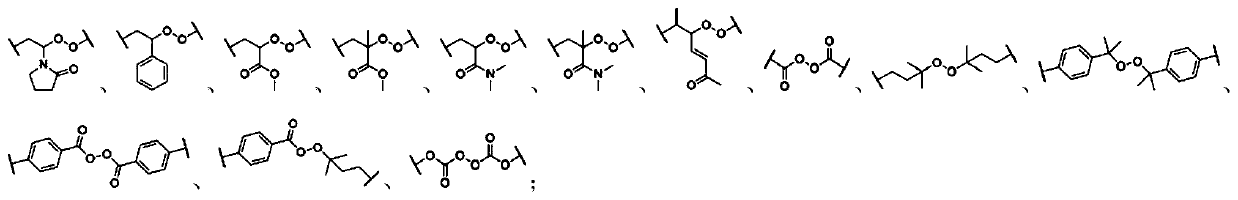
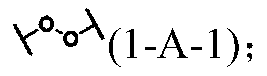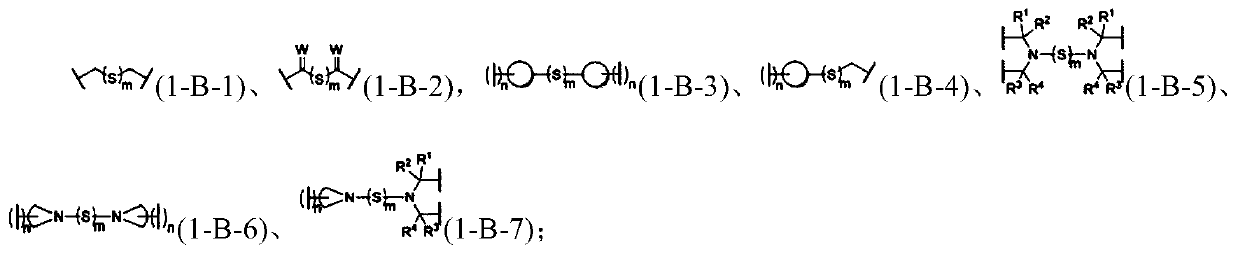Force-induced responsive supramolecular polymer
A supramolecular polymer and supramolecular technology, applied in the field of force-responsive supramolecular polymers, can solve the problems of single properties and performance, difficulty in meeting the needs of multifunctional and intelligent materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[1741] In the preparation process of the mechanoresponsive supramolecular polymer composition, there is no special limitation on the amount of each component raw material of the mechanoresponsive supramolecular polymer. performance adjustments.
[1742]In an embodiment of the present invention, the form of the mechanoresponsive supramolecular polymer can be solution, paste, glue, common solid, elastomer, gel (including hydrogel, organogel, oligomer swelling gels, plasticizer-swelled gels, ionic liquid-swelled gels), foams, etc. Among them, the content of soluble small molecular weight components contained in ordinary solids and foam materials is generally not higher than 10wt%, while the content of small molecular weight components contained in gels is generally not lower than 50wt%. Ordinary solids have relatively fixed shape and volume, better mechanical strength, and are not bound by organic swelling agents or water. Elastomers have the general properties of ordinary soli...
Embodiment 1
[1757] Using the triol compound a containing the lysensitizing group as the initiator, the ring-opening polymer reaction of 15 molar equivalents of ε-caprolactone was initiated under the catalysis of stannous octoate to obtain the three-armed polyester c whose terminal group is hydroxyl. React 1 molar equivalent of the obtained polymer c with 3 molar equivalents of pyridine-4-acyl chloride under the catalysis of triethylamine to convert terminal hydroxyl groups into pyridyl groups to obtain a three-armed polyester d whose terminal groups are pyridyl groups. Compound e containing a ligand group is reacted with excess trimellitic acid chloride under the catalysis of triethylamine to obtain compound f. 10 molar equivalents of ε-caprolactone were initiated by 1 molar equivalent of 4-hydroxymethylpyridine to carry out ring-opening reaction to obtain polyester g with a hydroxyl group at one end. Polyester h is obtained by reacting 1 molar equivalent of compound f with 2 molar equiva...
Embodiment 2
[1761] Refluxing 1,4,5,8-naphthalene tetracarboxylic anhydride and excess glycine tert-butyl ester in 1,4-dioxane to obtain compound a. Compound a is hydrolyzed under the catalysis of trifluoroacetic acid to convert tert-butyl ester group into carboxyl group to obtain compound b. Compound b is amidated with excess 1,8-naphthyridine-2,7-diamine to obtain compound c. The obtained compound c is reacted with excess adipoyl chloride under the catalysis of triethylamine to obtain compound d. 1 molar equivalent of compound d and 2 molar equivalents of ureidopyrimidinone e with a hydroxyl group at one end are reacted under the catalysis of triethylamine to obtain small molecular supramolecular monomer f.
[1762] Sonogashira coupling reaction was performed on p-bromophenol and excess molar equivalent of 4,7-diynylbenzothiadiazole to obtain compound g. 1 molar equivalent of 5-bromoresorcinol and 2 molar equivalents of compound h were reacted under the catalyst of triethylamine to obt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com