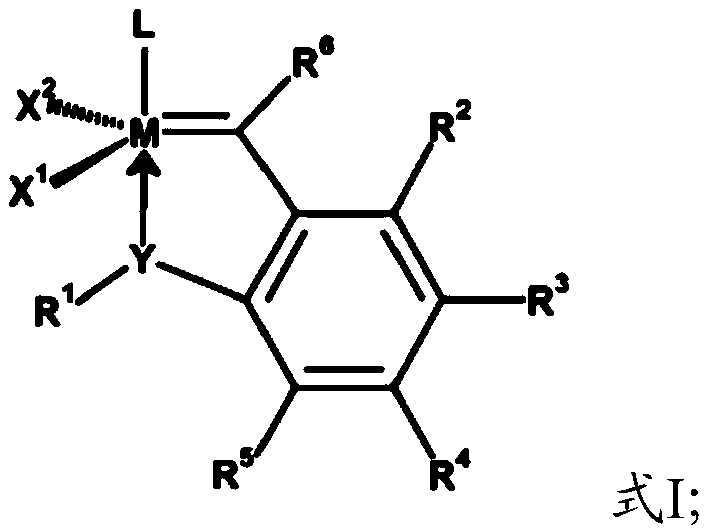
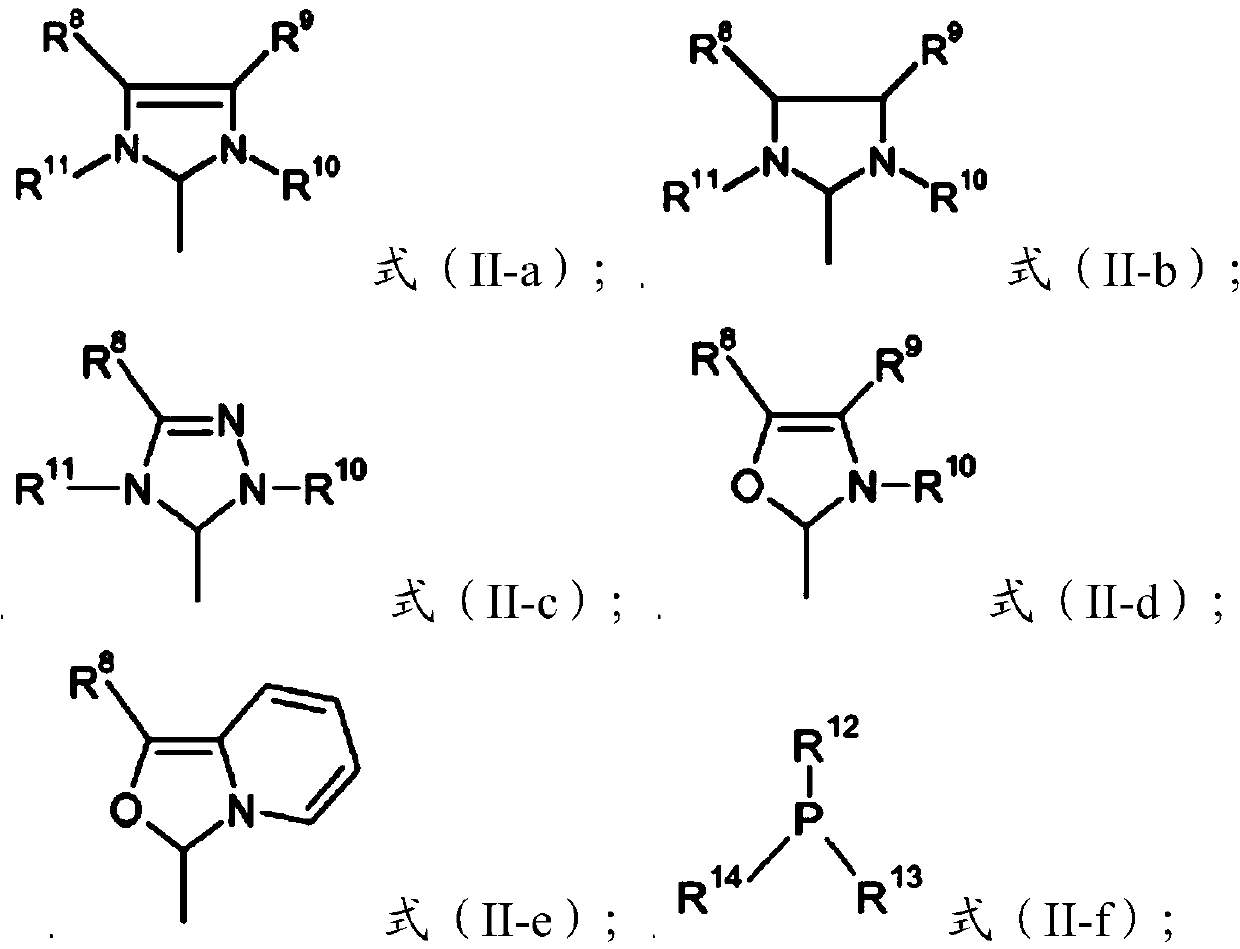
Catalyst composition and application thereof on selective hydrogenation of conjugated diene latexes
A conjugated diene and catalyst technology, applied in the field of catalyst composition and conjugated diene latex selective hydrogenation, can solve the problems of low conversion rate, slow hydrogenation reaction rate, inconvenience and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
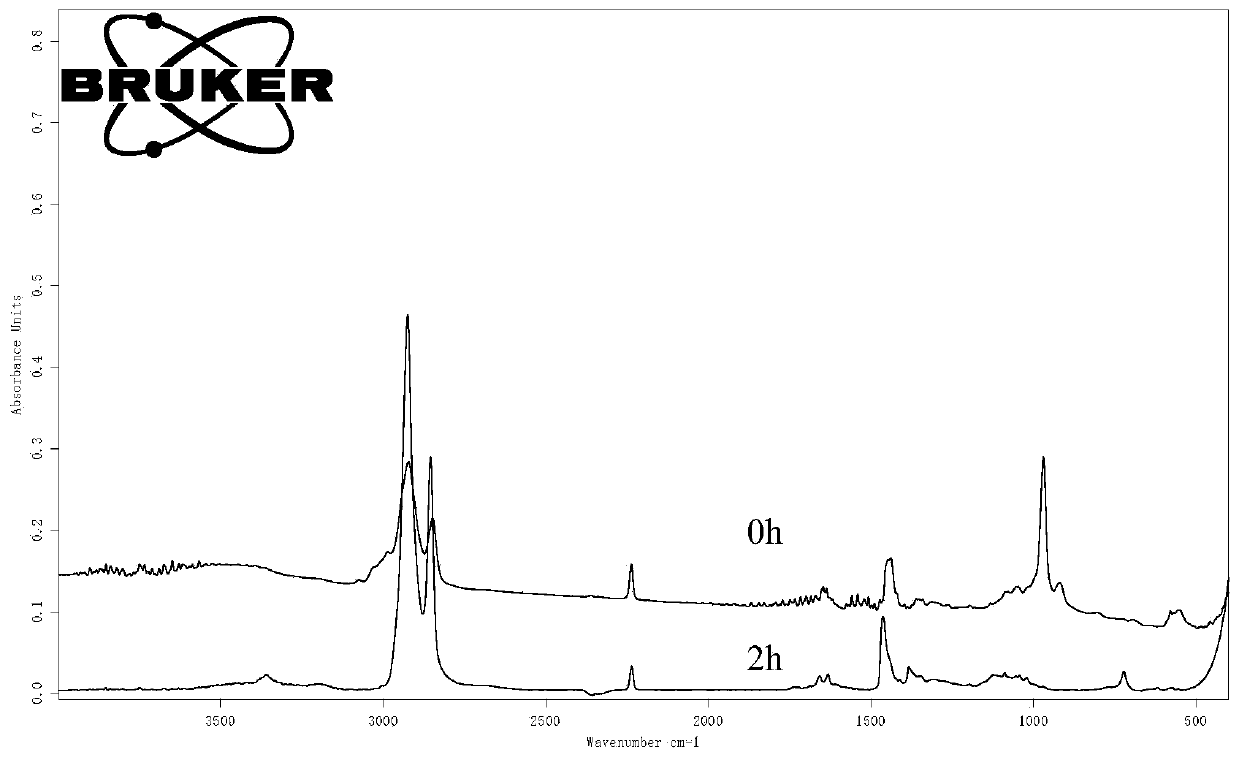
[0131] A 300 mL polytetrafluoroethylene high pressure reactor (Parr Instruments) with temperature control, stirrer and hydrogen addition point was used. A Nandi butadiene-acrylonitrile polymer latex having an acrylonitrile content of about 30% by weight and a Mooney viscosity (ML1+4@100°C) of 50 was used. The solids content of the latex was 25.7% by weight. The reactor was charged with 50 mL of latex, 0.00231 g of Heveda-Grubbs II, then 50 mL of latex, and then 2 g of sodium lauryl sulfate. Then use hydrogen to degas the latex. The degassing temperature is 25°C, the degassing pressure is 2Mpa, the degassing time is 60min, and the stirring speed is 200rpm during degassing. After the degassing is completed, continue to stir for 4h to facilitate the full dispersion of the catalyst. For activation, the temperature was raised to 90° C., the hydrogen pressure was raised to 800 psi (5.52 MPa), and the reaction was carried out for 4 hours. After the reaction, the hydrogenated NBR la...
Embodiment 2
[0134] A 300 mL polytetrafluoroethylene high pressure reactor (Parr Instruments) with temperature control, stirrer and hydrogen addition point was used. A Nandi butadiene-acrylonitrile polymer latex having an acrylonitrile content of about 30% by weight and a Mooney viscosity (ML1+4@100°C) of 50 was used. The solids content of the latex was 25.7% by weight. The reactor was charged with 50 mL of latex, 0.00231 g of Heveda-Grubbs II, then 50 mL of latex, and then 10 g of sodium lauryl sulfate. Then use hydrogen to degas the latex. The degassing temperature is 25°C, the degassing pressure is 2Mpa, the degassing time is 60min, and the stirring speed is 200rpm during degassing. After the degassing is completed, continue to stir for 4h to facilitate the full dispersion of the catalyst. For activation, raise the temperature to 90°C, raise the hydrogen pressure to 800psi (5.52MPa), and react for 2h. After the reaction, the hydrogenated NBR latex was coagulated with ethanol to obtain...
Embodiment 3
[0138]A 300 mL polytetrafluoroethylene high pressure reactor (Parr Instruments) with temperature control, stirrer and hydrogen addition point was used. A Nandi butadiene-acrylonitrile polymer latex having an acrylonitrile content of about 30% by weight and a Mooney viscosity (ML1+4@100°C) of 50 was used. The solids content of the latex was 25.7% by weight. The reactor was charged with 50 mL of latex, 0.000257 g of Heveda-Grubbs II, then 50 mL of latex, and then 2 g of sodium lauryl sulfate. Then use hydrogen to degas the latex. The degassing temperature is 25°C, the degassing pressure is 2Mpa, the degassing time is 60min, and the stirring speed during degassing is 200rpm. After the degassing is completed, continue to stir for 4h to facilitate the full dispersion of the catalyst. For activation, the temperature was raised to 90°C, the hydrogen pressure was raised to 800psi (5.52MPa), and the reaction was carried out for 6h. After the reaction, the hydrogenated NBR latex was c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com