Continuous beam bridge and method for determining inhaul cable sectional area and elastomer rigidity thereof
An elastic body, beam bridge technology, applied in bridges, bridge construction, bridge parts, etc., can solve the problems of easy damage, large bending moment at the bottom of fixed piers, damage to the whole bridge, etc., and achieve economical and low-cost solutions. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0058] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that those skilled in the art can understand the present invention. However, it should be clear that the embodiments described below are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention defined and determined by the appended claims, all other embodiments obtained by those skilled in the art without any creative effort shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
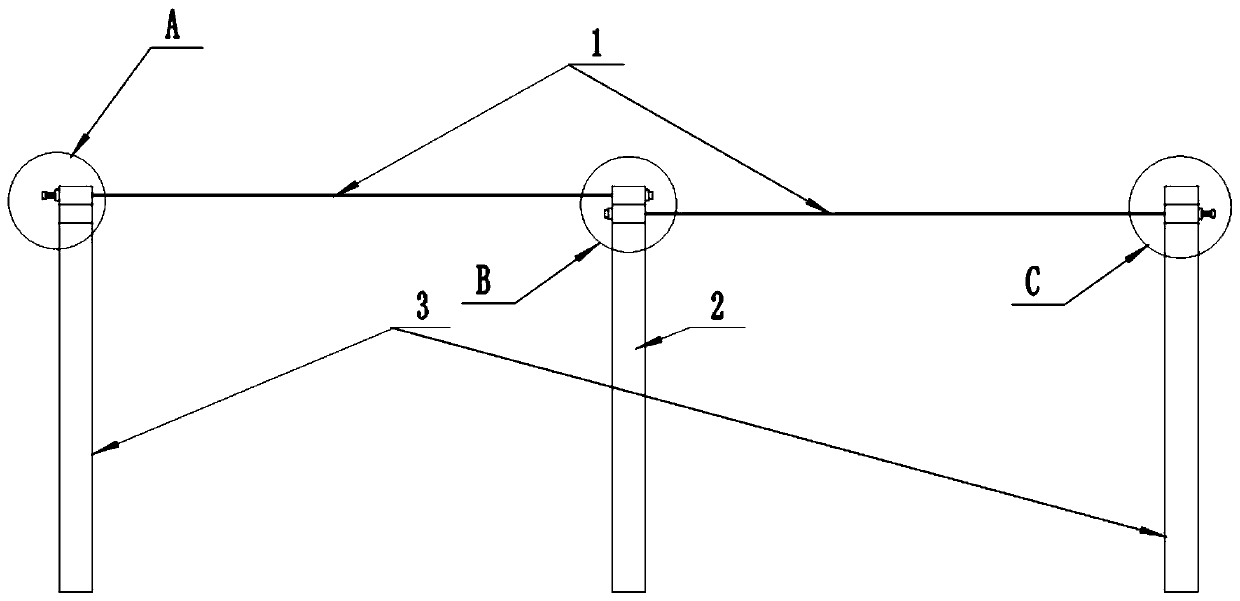
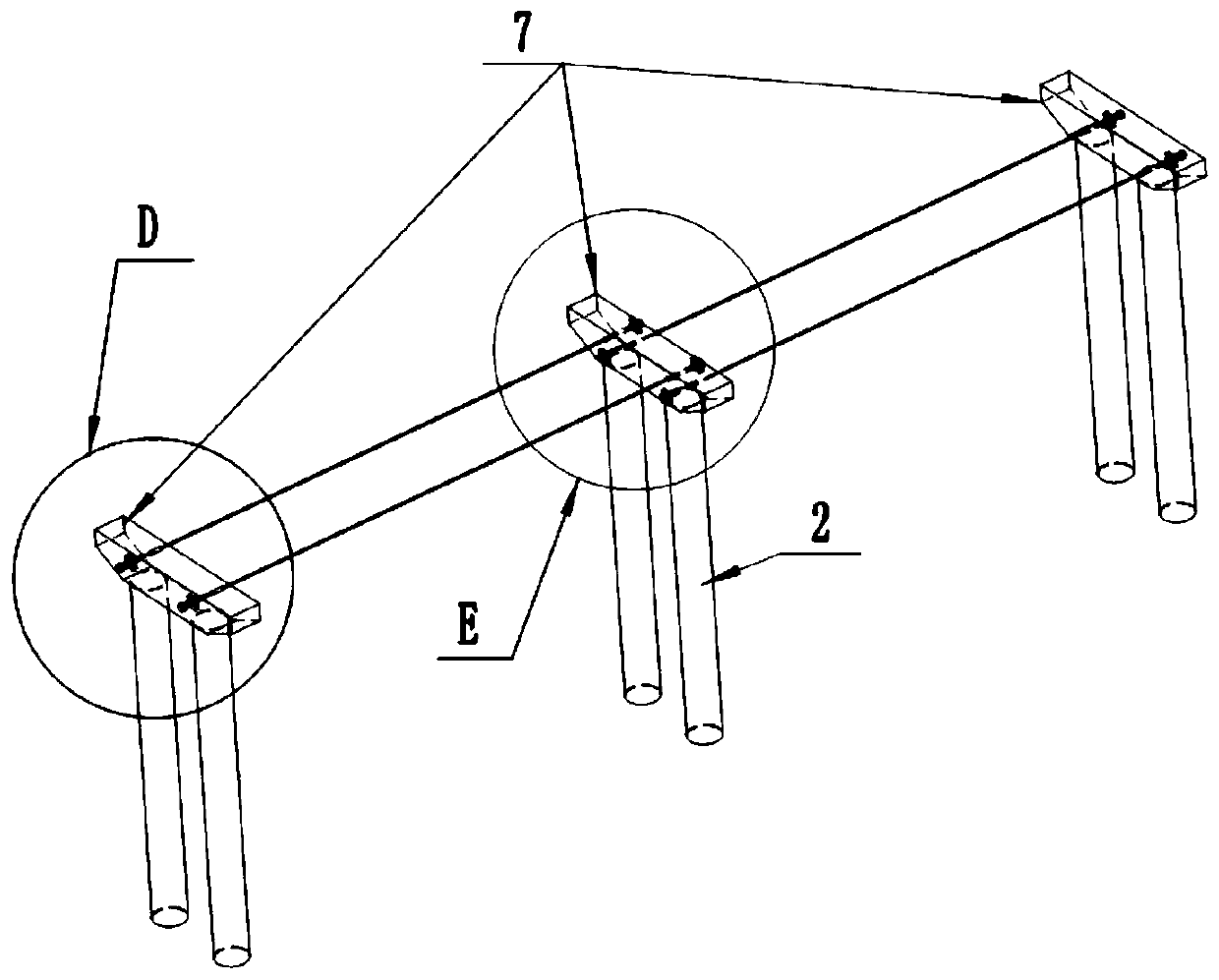
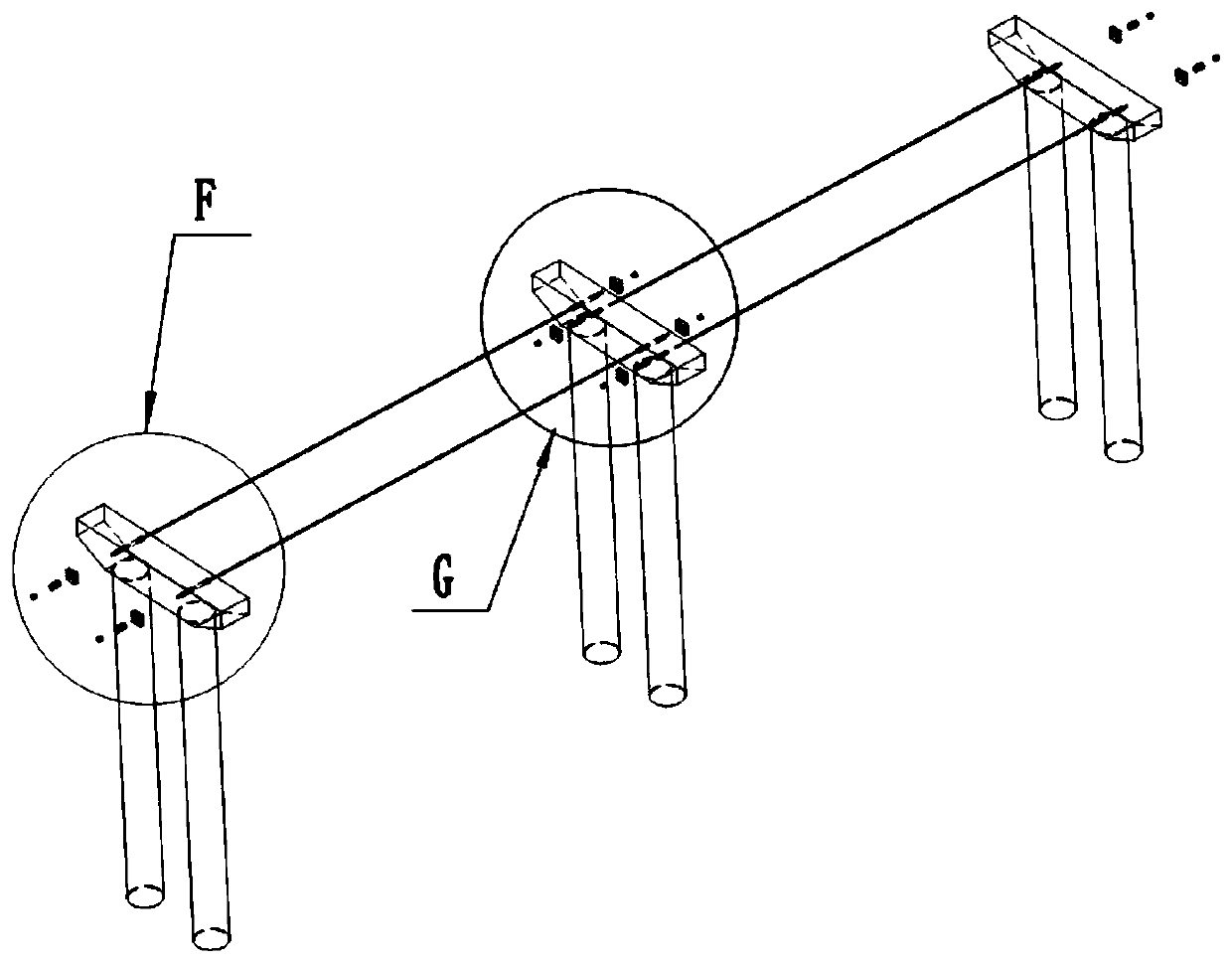
[0059] like Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, the continuous girder bridge includes a connecting cable device, a continuous main girder, piers and a plurality of pier cover girders 7 , and the piers include a fixed pier 2 in the middle and a plurality of non-fixed piers 3 on both sides of the fixed pier 2 . like Figure 4 and Figure 5 As shown, the pier cover beam 7 is provided wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com