Heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative effect mutant and application thereof
A transcription factor and negative effect technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., to achieve the effects of avoiding environmental pollution, growing environmentally friendly, and growing more
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1, construction of dn-Hsf1 expression vector
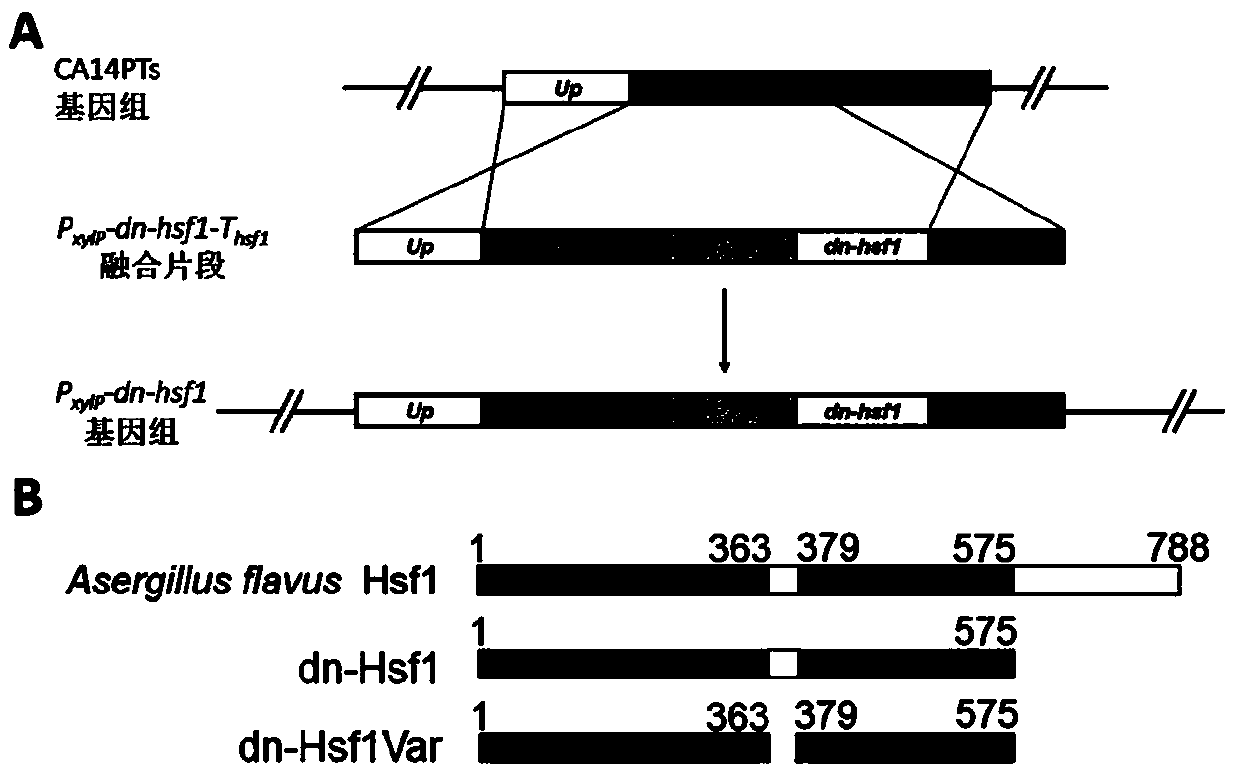
[0062] Studies in mammals have shown that deletion of the catalytic domain of about 150 amino acid residues at the C-terminus of the heat shock transcription factor 1 HSF1 protein can generate a mutant dn-cHSF1 with a dominant negative effect, which can inhibit the normal HSF1 functions in animals (DOI: 10.1021 / acschembio.5b00740). Therefore, the present inventors constructed a fungal-derived Hsf1 dominant-negative mutant dn-Hsf1 to inhibit the function of normal Hsf1 in fungi, thereby inhibiting the growth of fungi and achieving the purpose of preventing and controlling fungal contamination.
[0063] The present invention uses the amino acid sequence of the human heat shock transcription factor 1 HSF1 protein to find the predicted homologous protein Hsf1 (No. XP_002374014) and its coding gene (No. AFLA_025030) in Aspergillus flavus through the NCBI BLASTP homologous alignment method. The amino acid sequence sim...
Embodiment 2
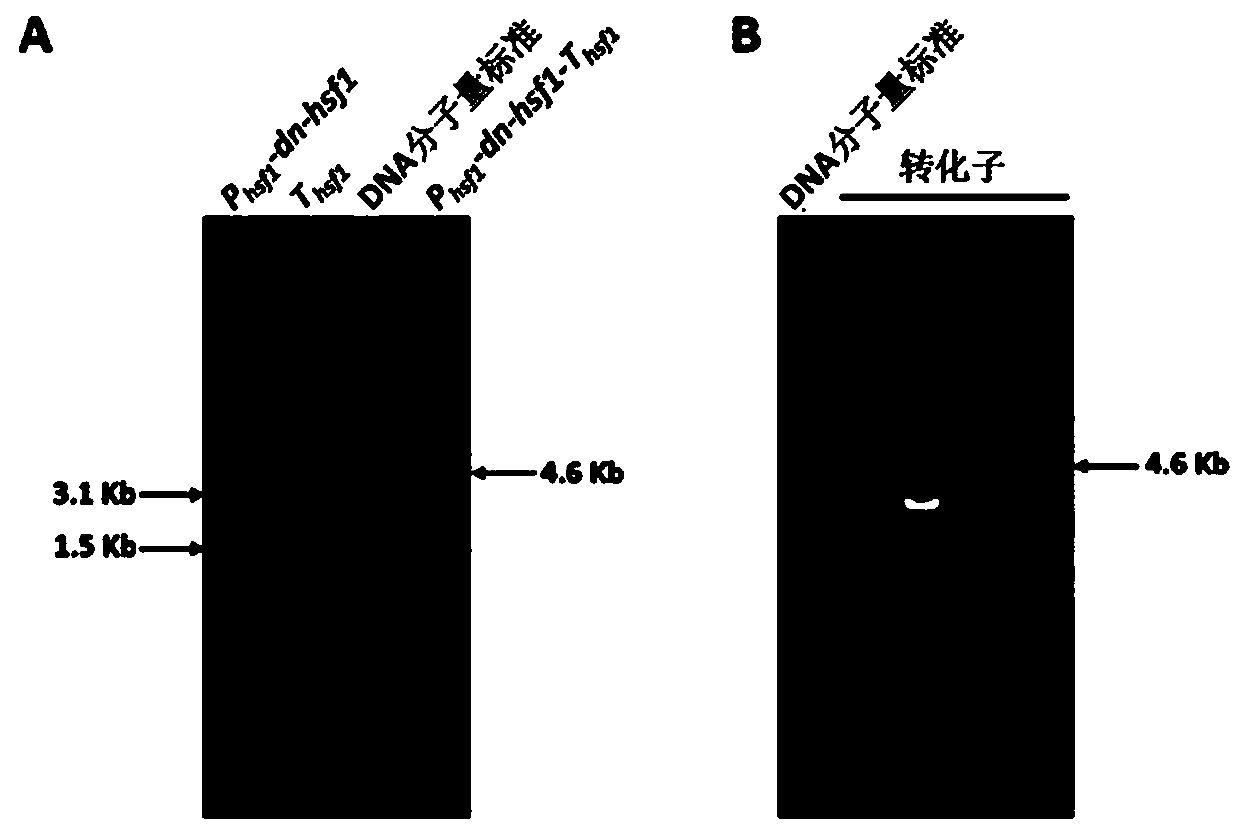
[0069] Embodiment 2, expression vector pPTR I -dn-hsf1 Aspergillus flavus
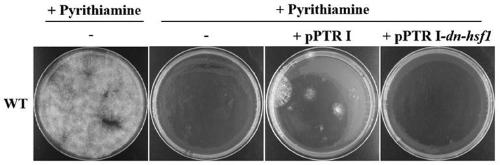
[0070] The expression vector plasmid pPTR I -dn-hsf1 The protoplasts of Aspergillus flavus WT strain were introduced, and the transformants of Aspergillus flavus were screened on the recovery medium containing pyrithiamine. After the transformation plate was cultured at 37°C for 5 days, the results were as follows: figure 2 As shown: the first and second culture plates are protoplasts without transformed nucleic acid. Since the first culture plate does not contain pyrithiamine screening pressure, many colonies grow on the culture plate to form a lawn, indicating that it is used for transformation The amount of protoplasts was sufficient, but the second culture plate was added with pyridinethiamine, and no clones were grown, indicating that the screening pressure of pyrithione was effective. The third culture plate was the protoplast transformed with pPTR I empty vector, and 10 clones grew out und...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3, Xylose promoter induced expression dn-Hsf1 inhibits the growth of Aspergillus flavus
[0072] In order to confirm the inhibitory effect of dn-Hsf1 on the growth of Aspergillus flavus, the present invention further expresses dn-Hsf1 protein from Aspergillus flavus hsf1 gene promoter P hsf1 Control changed to use a xylose-inducible promoter P xy1P to control (build strategies such as image 3 Shown in A), constructed by fusion PCR method containing upstream homologous sequences up , derived from Aspergillus fumigatus pyrG Nutritional screening marker gene, derived from Penicillium chrysogenum P xylP Xylose-inducible expression promoter, coding nucleotide and terminator of dn-Hsf1 T hsf1 The fusion fragment of P xylP -dn-hsf1-T hsf1 Fragment, transformed and integrated into the Aspergillus flavus genome, to obtain the inducible P xylP -dn-hsf1 strain. Observe the effects of dn-Hsf1 non-expression and induced expression on the growth of Aspe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com