Inorganic phase-change constant-temperature material and preparation method thereof
An inorganic phase change, constant temperature technology, applied in heat exchange materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as degradation of thermophysical properties, and achieve the effects of good plasticity, stable performance, and easy large-scale production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
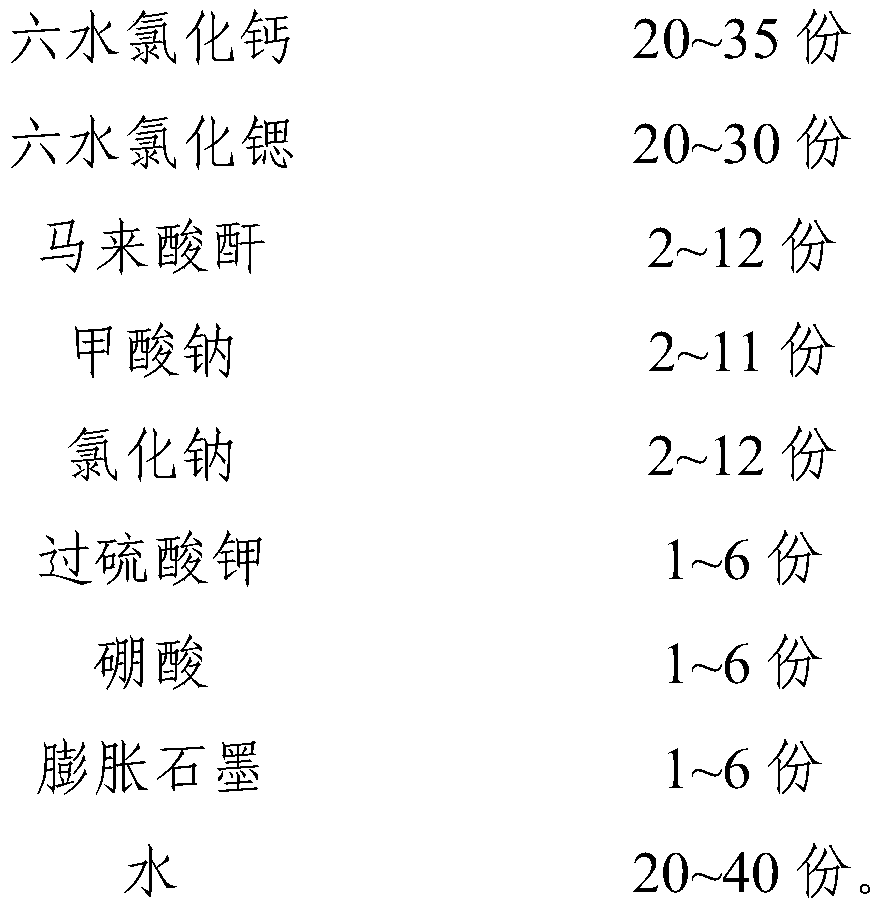
[0035] This embodiment provides an inorganic phase change constant temperature material, including the following components by weight:
[0036]
[0037]
[0038] The preparation method of the inorganic phase change constant temperature material is as follows:
[0039] (1) After mixing sodium formate and 15% water at 45-80°C, add strontium chloride hexahydrate to obtain mixed solution I;
[0040] (2) Add maleic anhydride to the mixed solution I, then add 6% water, and react at 60° C. for 1 hour to obtain the mixed solution II;
[0041] (3) After sodium chloride is mixed with 5% water, potassium persulfate is added to obtain mixed solution III;
[0042] (4) Add calcium chloride hexahydrate after mixing boric acid, expanded graphite, the mixed solution II and the mixed solution III, and react at 65° C. for 1 hour to obtain a polymer material;
[0043] (5) Mix the polymer material with the rest of the water, stir evenly, and leave it for 10-15 minutes.
[0044] The phase ...
Embodiment 2
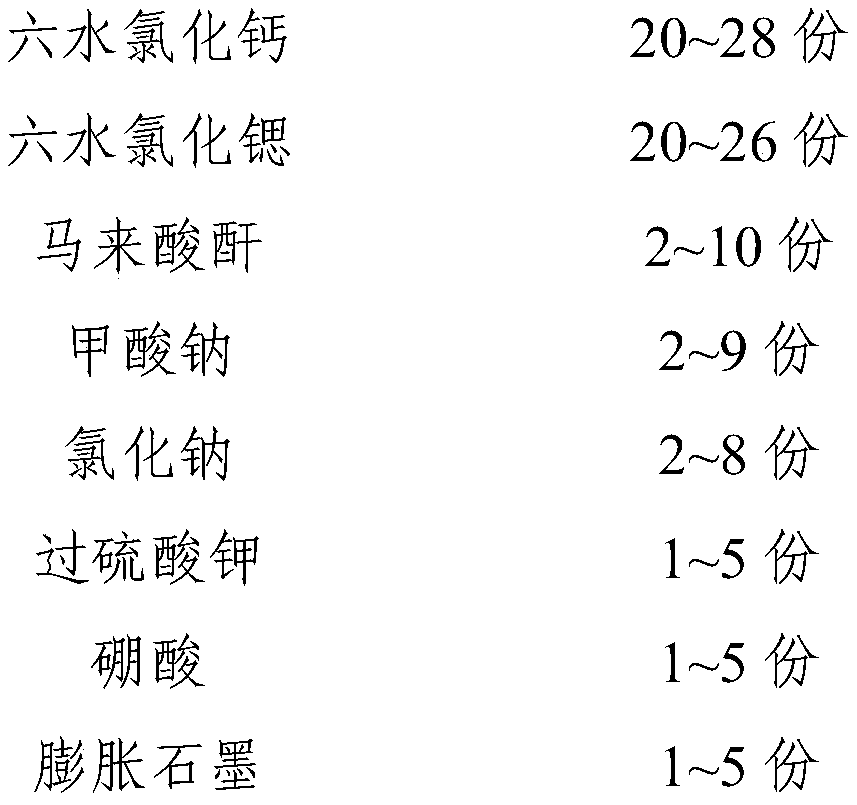
[0046] This embodiment provides an inorganic phase change constant temperature material, including the following components by weight:
[0047]
[0048]
[0049] The preparation method of the inorganic phase change constant temperature material is as follows:
[0050] (1) After mixing sodium formate and 10% water at 45-80°C, add strontium chloride hexahydrate to obtain mixed solution I;
[0051] (2) Add maleic anhydride to the mixed solution I, then add 4% water, and react at 60° C. for 1 hour to obtain the mixed solution II;
[0052] (3) After sodium chloride is mixed with 5% water, potassium persulfate is added to obtain mixed solution III;
[0053] (4) Add calcium chloride hexahydrate after mixing boric acid, expanded graphite, the mixed solution II and the mixed solution III, and react at 60° C. for 1 hour to obtain a polymer material;
[0054] (5) Mix the polymer material with the rest of the water, stir evenly, and leave it for 10-15 minutes.
[0055] The phase ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] This embodiment provides an inorganic phase change constant temperature material, including the following components by weight:
[0058]
[0059]
[0060] The preparation method of the inorganic phase change constant temperature material is as follows:
[0061] (1) After mixing sodium formate and 12% water at 45-80°C, add strontium chloride hexahydrate to obtain mixed solution I;
[0062] (2) Add maleic anhydride to the mixed solution I, then add 5% water, and react at 60° C. for 1 h to obtain the mixed solution II;
[0063] (3) After sodium chloride is mixed with 4% water, potassium persulfate is added to obtain mixed solution III;
[0064] (4) adding calcium chloride hexahydrate after mixing boric acid, expanded graphite, the mixed solution II and the mixed solution III, and reacting at 70° C. for 1 hour to obtain a polymer material;
[0065] (5) Mix the polymer material with the rest of the water, stir evenly, and leave it for 10-15 minutes.
[0066] The phase...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition enthalpy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition enthalpy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com