Method for strengthening reduction of sulfonamide antibiotics in soil by earthworm intestinal contents
A content and sulfonamide technology, applied in the field of bioremediation of antibiotic-contaminated soil, can solve problems such as high-cost process materials and complex process processes, and achieve the effects of promoting degradation, avoiding process processes, and maintaining diversity and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
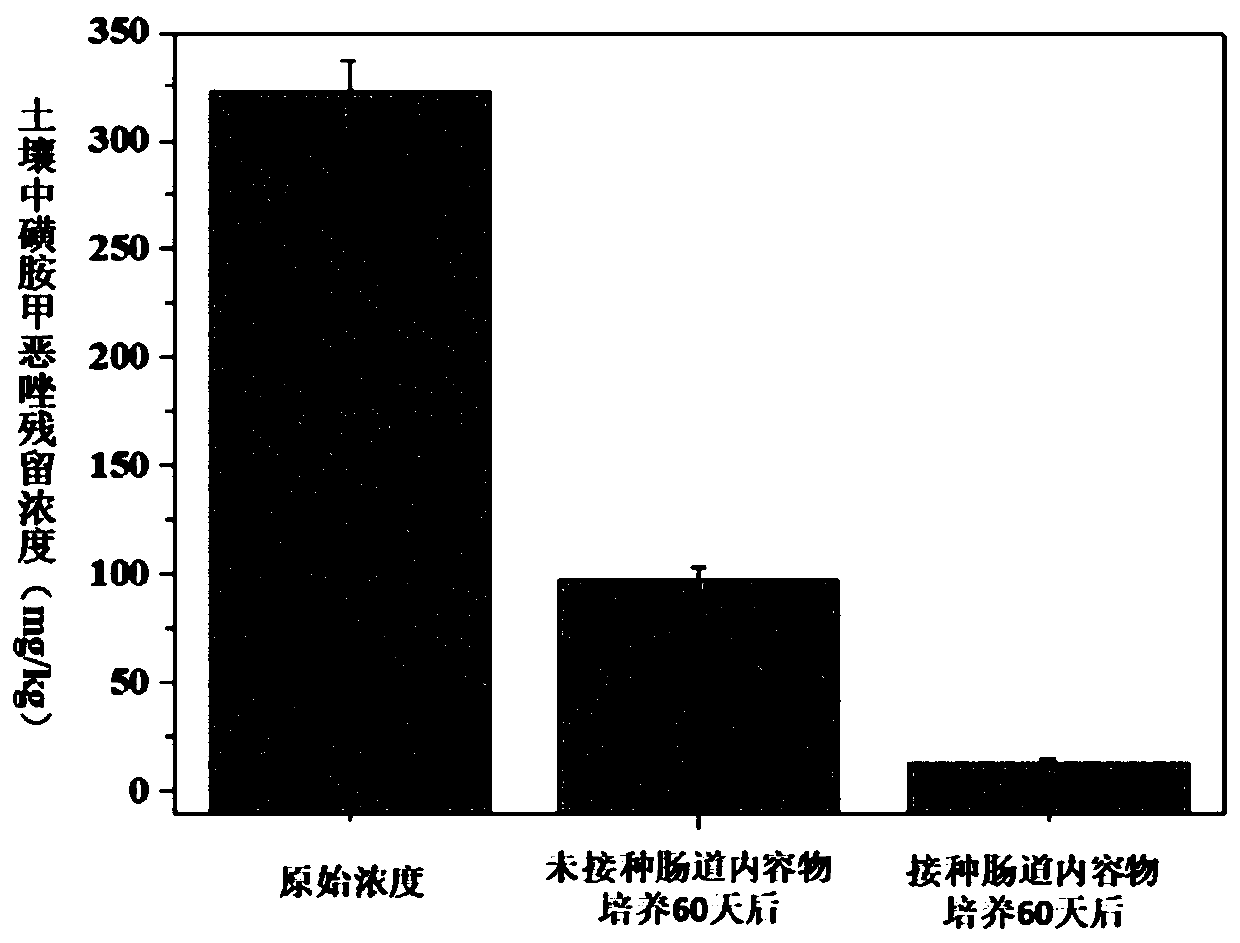
[0025] Example 1 The method of strengthening the elimination of sulfadiazine in soil by intestinal content of C. william coelophorum
[0026] Select fresh C. williams coelomum earthworms with obvious rings and strong vitality, each weighing between 4 ± 1 g, wash the body surface, and set aside. Weigh the corresponding weight of sulfadiazine analytically pure standard, dissolve it in pure water, add it to the corresponding clean soil, mix the sulfadiazine solution and soil particles evenly, and prepare sulfadiazine-contaminated soil with a concentration of 100 mg / kg. Add 100 of the above-mentioned cleaned worms to 100 mg / kg sulfadiazine-contaminated soil, keep them away from light and cultivate them at room temperature 25±2°C for 14 days, take out the earthworms, and use 0.9% physiological Wash the body surface of earthworms with salt water 2-3 times, put them in a sterile petri dish for 6 hours to make the earthworms clean their intestines completely; insert them into an ice b...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 The method of strengthening the reduction of sulfamethoxazole in soil by intestinal content of C. william coelophorum
[0029] Select fresh C. williams coelomum earthworms with obvious rings and strong vitality, each weighing between 4 ± 1 g, wash the body surface, and set aside. Weigh the corresponding weight of sulfamethoxazole analytically pure standard, dissolve it in pure water, add it to the corresponding clean soil, mix the sulfamethoxazole solution and soil particles evenly, and prepare a concentration of 100 mg / kg sulfamethoxazole azoles pollute the soil. Add 100 of the above-mentioned cleaned worms to 100 kg of 100 mg / kg sulfamethoxazole-contaminated soil, keep away from light and cultivate at room temperature 25±2°C for 14 days, take out the earthworms, and use 0.9% Wash the body surface of earthworms with normal saline for 2-3 times, put them in a sterile petri dish for 6 hours to make the earthworms clean their intestines completely; insert them ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3 The method of synchronous reduction and removal of sulfamethoxine, sulfadiazine, and sulfamethoxazole in the soil of the intestinal contents of C.
[0032] Select fresh C. williams coelomum earthworms with obvious rings and strong vitality, each weighing between 4 ± 1 g, wash the body surface, and set aside. Weigh the corresponding weight of sulfamethoxine, sulfadiazine, and sulfamethoxazole analytically pure mixed standard, dissolve it in pure water, add it to the corresponding clean soil, and mix the above three types of standard solutions with soil particles evenly to prepare The compound antibiotics with a concentration of 10 mg / kg sulfamethoxine + 10 mg / kg sulfadiazine + 10 mg / kg sulfamethoxazole polluted the soil. Add 100 of the above-mentioned cleaned worms to 100 kg of the above-mentioned sulfonamide compound-contaminated soil, keep them away from light and cultivate them at room temperature for 14 days, take out the earthworms, and wash the surface of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com