Gene engineering adenovirus and it application
A technology for recombinant adenoviruses and viruses, which is applied in the directions of viruses/phages, medical preparations containing active ingredients, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve problems such as high target specificity of defective adenoviruses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1 Construction of Plasmids
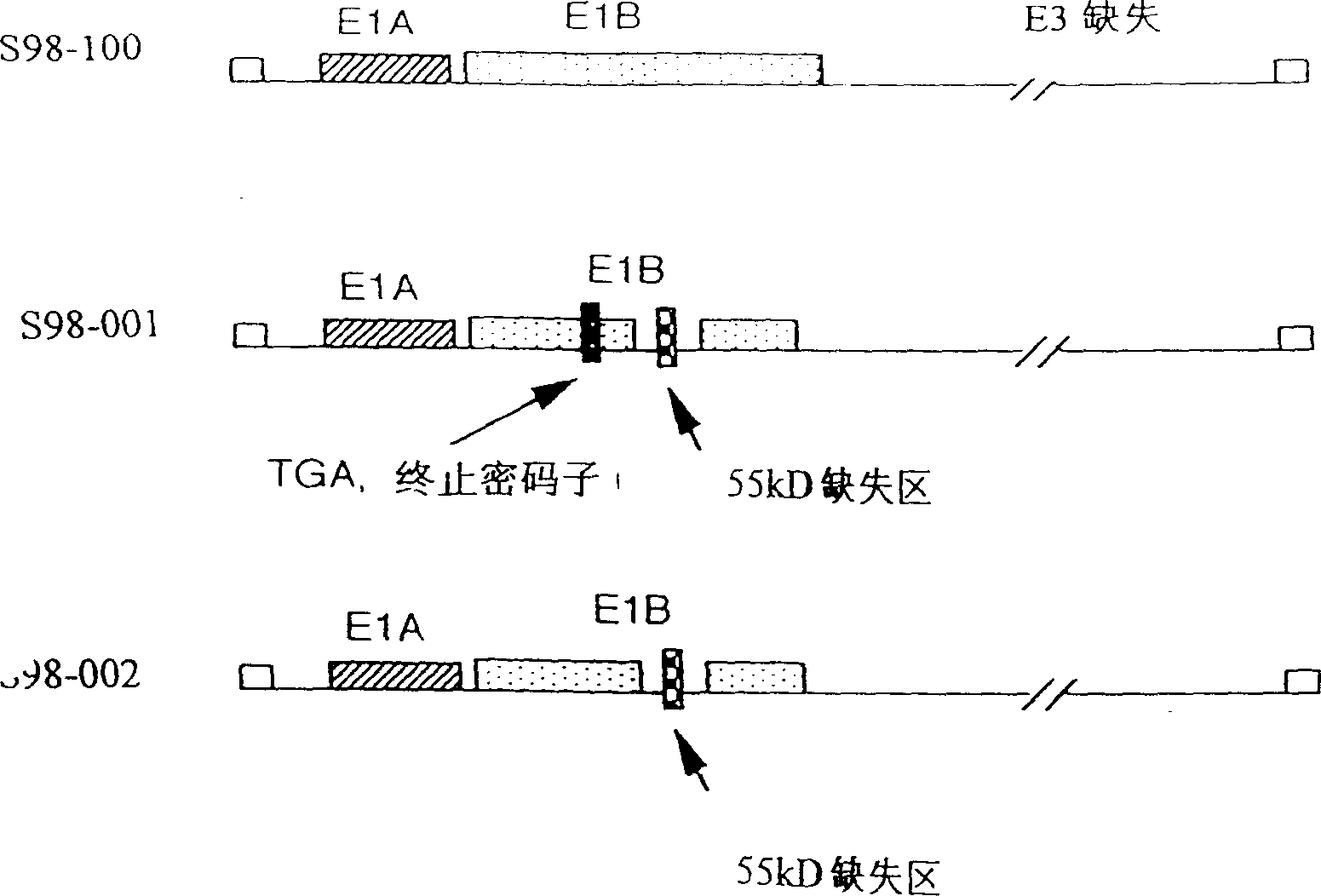
[0025] pXC-1 and pBHG11 were purchased from Microbix Biosystems. PXC-1 contains human adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) gene sequence from bp22 to 5790. pBHG11 contains the Ad5 gene sequence with two deletions: the deletion of the E1 region, from bp188 to 1339, the packaging signal used to form the viral DNA capsid protein, and the deletion of the E3 region, from bp27865 to 30995. The DNA of pBHG11 is not infectious, but co-transfection of pXC-1 and pBHG11 can generate infectious virus through homologous recombination.
[0026]In order to construct the subcloning of the Ad5 DNA fragment from bp1338 to bp2501 on pXC-1, the following two synthetic oligonucleotide fragments were used to amplify the PCR product from pXC-1, and the primers were as follows: HZ1 (5'-CTATCCTGAGACGCCCGAC- 3')HZ2(5'-GATCGGATCC AGGTCT CCAGTAAGTGGTAGCTGC-3') (the BgII site is underlined) and cloned into the pGEM-T vector (Promega), resulting in HZ102. To...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 In Vitro Detection Using Plaque Method
[0035] Firstly, the plaque method was used to detect the growth ability of such viruses in p53-deficient cells, that is, to quantitatively detect the ability of a specific virus to infect a certain cell line. Plaque method is applied to the following cell lines: ovarian cancer cell line (OVCAR-3, p53 mutant strain), liver cancer cell line (Hep3B, p53 mutant strain), glioma cell line (U373, p53 mutant strain), colon cancer cell line Strains (SW620, p53 mutant strain and RKO, p53 normal strain), breast normal cells (HBL-100, p53 normal strain). Because HYH cells express E1A and E1B proteins, S98 virus can efficiently form plaques against these cell lines.
[0036] Table 1 shows the average percentage of replicated samples of the tested viruses. For all cell lines, the titer of a particular virus was normalized to its titer in HYH cells so that the virus was comparable to the corresponding cell line. When the ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 in vitro cell test
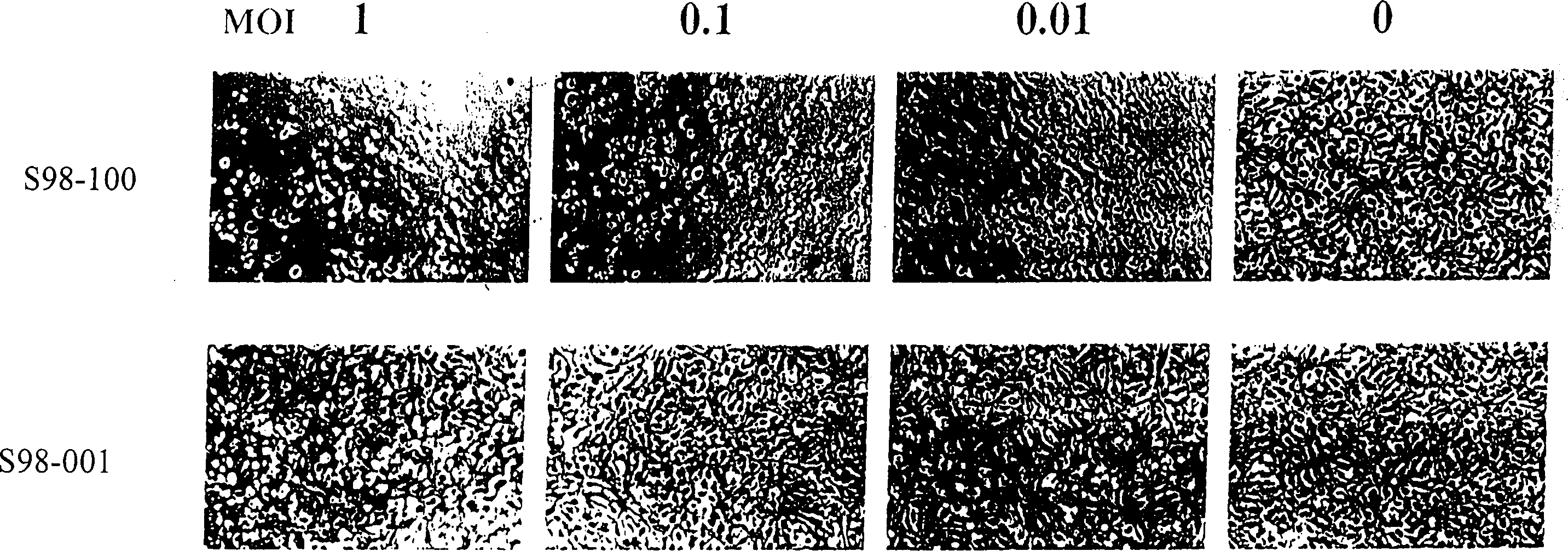
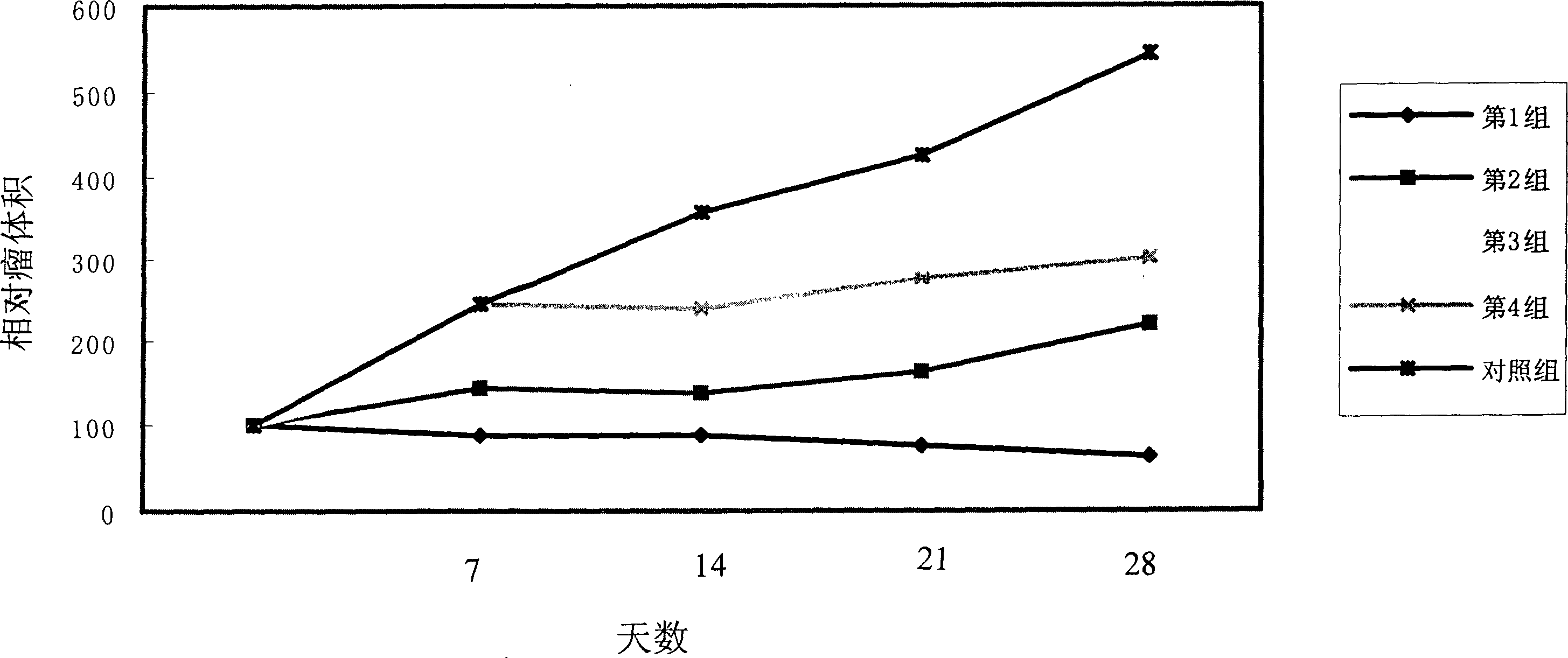
[0046] The second experiment is to observe the characteristics of different virus replication and the lesions produced by cells. The experimental process is as follows. Infect cells with increasing amounts of viral infection and monitor cell lesions. When it was observed that the MOI was 0.01, the wild-type adenovirus could completely lyse the cultured monolayer cells, which was the end point of the experiment. Human microtubule endothelial cells (hMVEC, derived from human lung), a primary non-renewable cell, were selected to detect its sensitivity to S98 genetically engineered virus and wild-type adenovirus in vitro.
[0047] The results showed that when the MOI of S98-100 was 0.01, the cultured monolayer cells could be completely lysed within 10 days. In contrast, normal monolayer cells infected with S98-002 showed no obvious cytopathic changes at the same time points at MOIs of 10, 1.0, 0.1, and 0.01, respectively. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com