A Road Network Trajectory Clustering Analysis Method Based on Improved DPC Algorithm
A road network and trajectory clustering technology, which is applied in the field of cluster analysis, can solve the problems that the classic trajectory cannot represent the whole situation, and there are too many parameter settings, so as to reduce the influence of custom parameters, improve adaptability, and get rid of human interference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
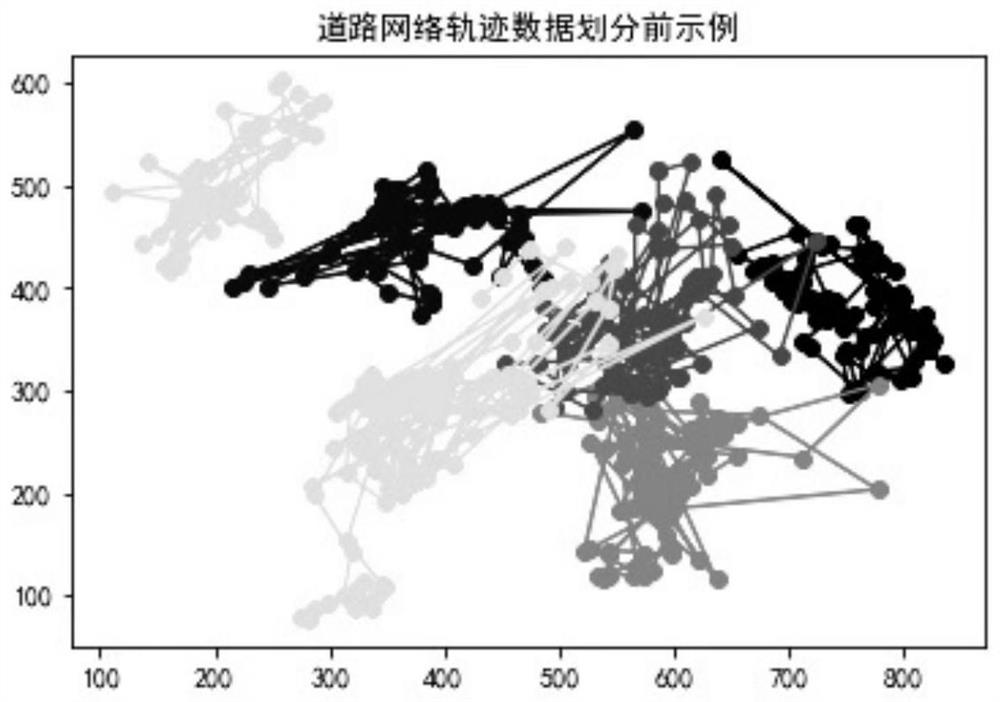
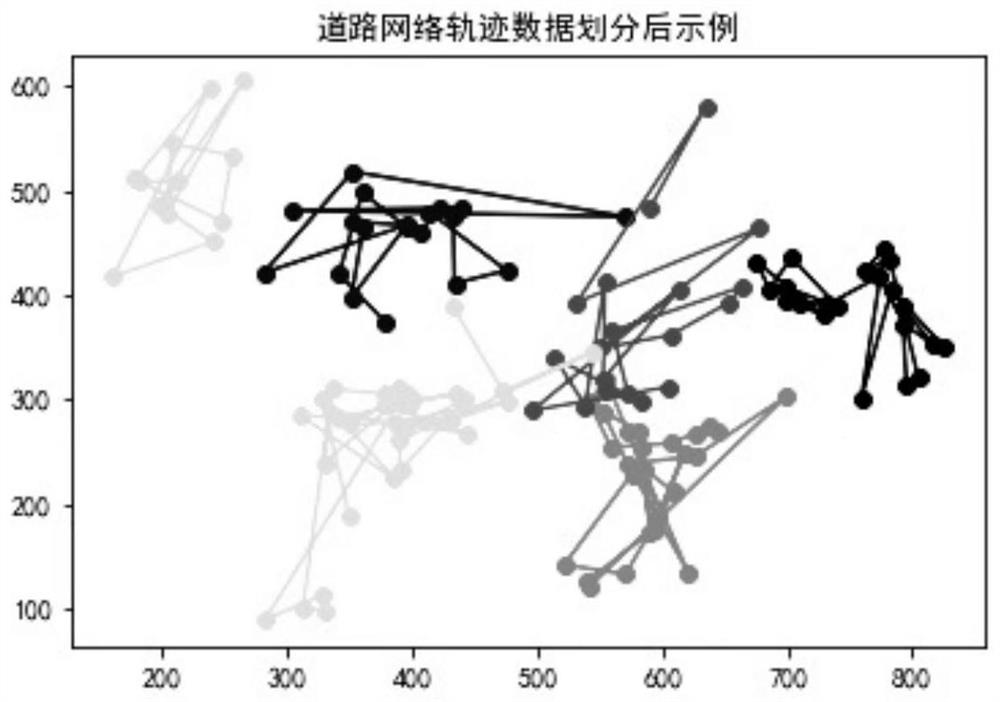
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
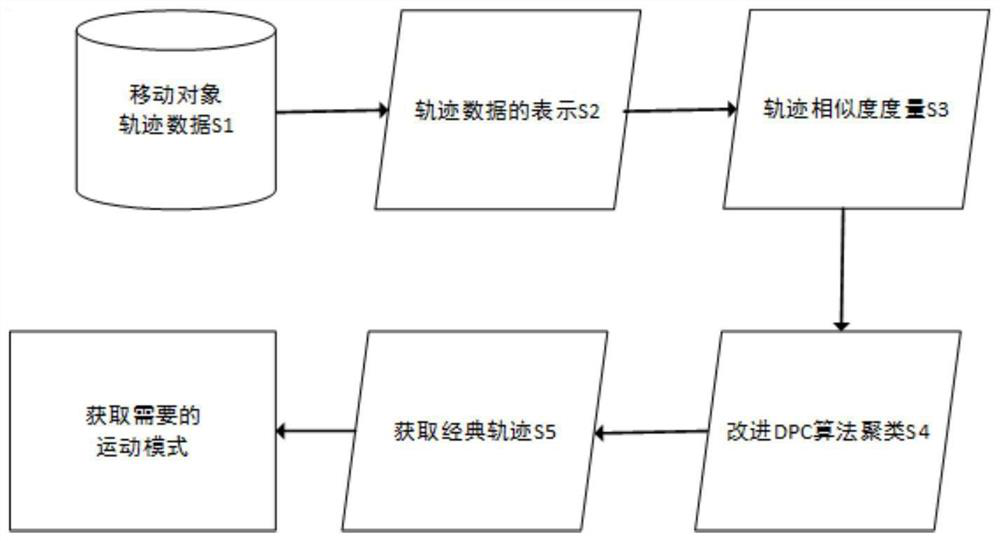
[0072] A kind of road network locus cluster analysis method based on improved DPC algorithm that the preferred embodiment of the present invention provides, comprises the following steps of carrying out successively:
[0073] A road network track clustering analysis method based on the improved DPC algorithm, comprising the following steps carried out in sequence:
[0074] S1: Data acquisition: Use vehicle-mounted and ground-based road track recording equipment to collect track data of moving objects, or collect GPS data of different moving objects, and use track data or GPS data as input data:
[0075] S2: Trajectory movement expression: obtain the sub-trajectory sequence connected by feature points from the input data of step S1;
[0076] Extract valid global trajectory data from the input data in step S1; build a model through linear interpolation and semantic extension based on the local interpolation model, output the trajectory file, and select a class of anomalous point...
Embodiment 2
[0081] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1, the expression of the trajectory movement in step S2 has the following steps:
[0082] S21: Establish a trajectory model based on the line segment trajectory representation, extract the stay point from the input data in step S1 for semantic expansion, and convert the stay point trajectory into a position trajectory;
[0083] S22: Road trajectory data expression based on local interpolation model: After discretizing the road trajectory grid, use the inverse distance weight method to calculate the attribute values of the trajectory segments falling in each grid, and calculate the trajectory segment according to the attributes of the adjacent sampling points perform interpolation;
[0084] S23: Find the feature points based on the separation method of the trajectory segment of the angle size, and obtain the sub-trajectory sequence connected by the feature points.
Embodiment 3
[0086] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1, the aggregation distance CD in the step S3 to calculate the distance between sub-trajectories has the following steps:
[0087] S31: For the sub-trajectory segments formed after any two trajectories are expressed, calculate the aggregation distance CD between the sub-trajectory segments, assuming two sub-trajectory segments ST i =b i e i and ST j =b j e j , using d ⊥ (ST i , ST j ) represents the vertical distance between two sub-trajectories, using d || (ST i , ST j ) represents the parallel distance between two sub-trajectories, using d θ (ST i , ST j ) represents the angular distance between two sub-trajectories;
[0088] S32: Sub-track ST i and ST j The aggregation distance CD(ST i , ST j ), that is, the similarity between trajectories, expressed as the weighted average of three normalized distances;
[0089] S33: Calculate the aggregation distance CD between any two sub-trajectories, and finally ob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com