A method for in-situ remediation of water bodies using bioelectrochemical enhancement of floating ecological beds
A bioelectrochemical, in-situ remediation technology, applied in the field of water body remediation, can solve the problems of short maintenance time of biological inoculants, limited contact area of biological fillers, and inability to achieve treatment effects, so as to improve the anti-pollution load capacity and convenience. The effect of post-maintenance management and high species richness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: A method for in-situ restoration of water bodies using bioelectrochemical strengthening of floating ecological beds described in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0031] 1. Select areas of polluted natural water bodies;
[0032] 2. Construct bioelectrochemical enhanced floating ecological beds in polluted natural water areas and fix them;
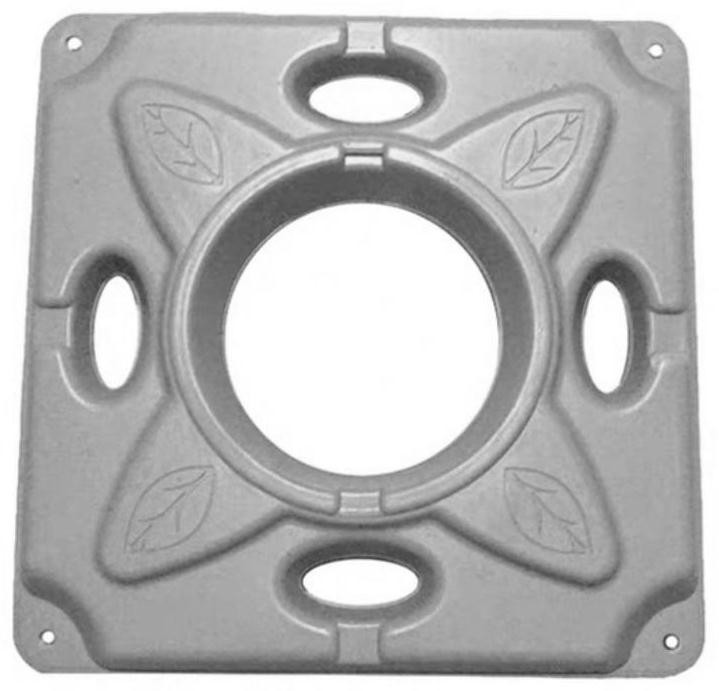
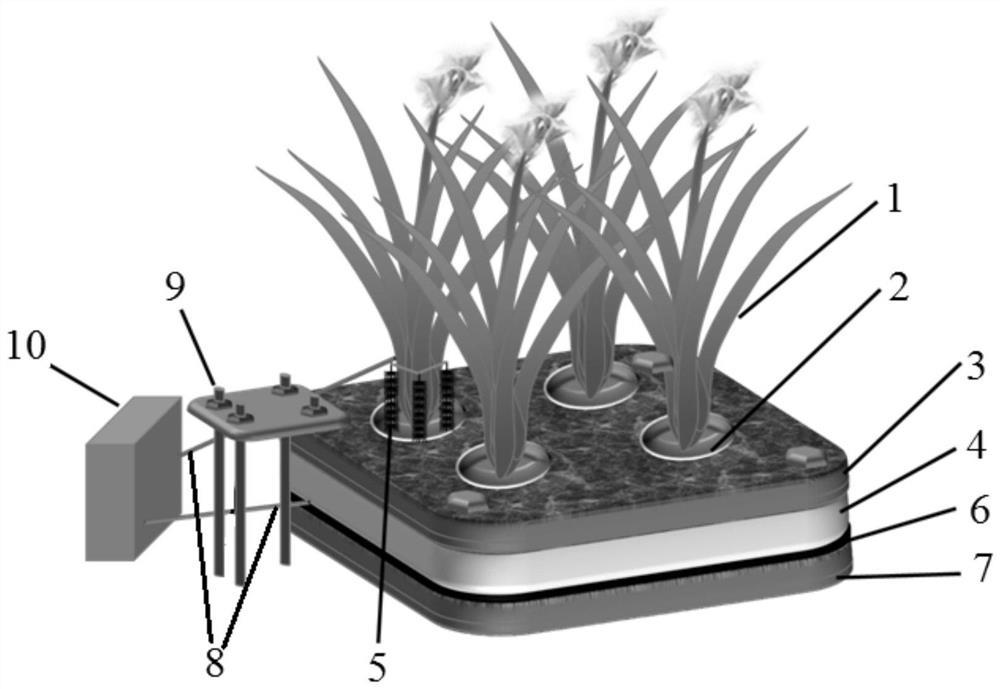
[0033] The bioelectrochemical enhanced floating ecological bed is formed by connecting a plurality of monomer bioelectrochemical enhanced floating ecological beds, and the single bioelectrochemical enhanced floating ecological bed is composed of a floating body material layer, a matrix material layer, plants and electrons. It is composed of conductive material; a layer of matrix material is arranged on the upper and lower sides of the floating body material layer, and a plurality of planting holes are arranged along the thickness direction of the single bioelectrochemical enhanced floati...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the floating body material layer described in step 2 is composed of polyvinyl chloride pipes, polystyrene foam boards, phenolic foam boards and polyvinyl chloride foam boards. one or a combination of them. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0052] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the diameter of the polyvinyl chloride pipe is 24 cm to 48 cm; the polystyrene foam board, phenolic foam board and polystyrene foam board The thickness of the vinyl chloride foam board is 1 cm to 5 cm. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com