Method and lidar device for scanning scanning region with at least two pulse-encoded beams
A laser radar and scanning area technology, applied in the field of operating laser radar equipment, can solve problems such as faulty signal detection, laser radar equipment interruption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
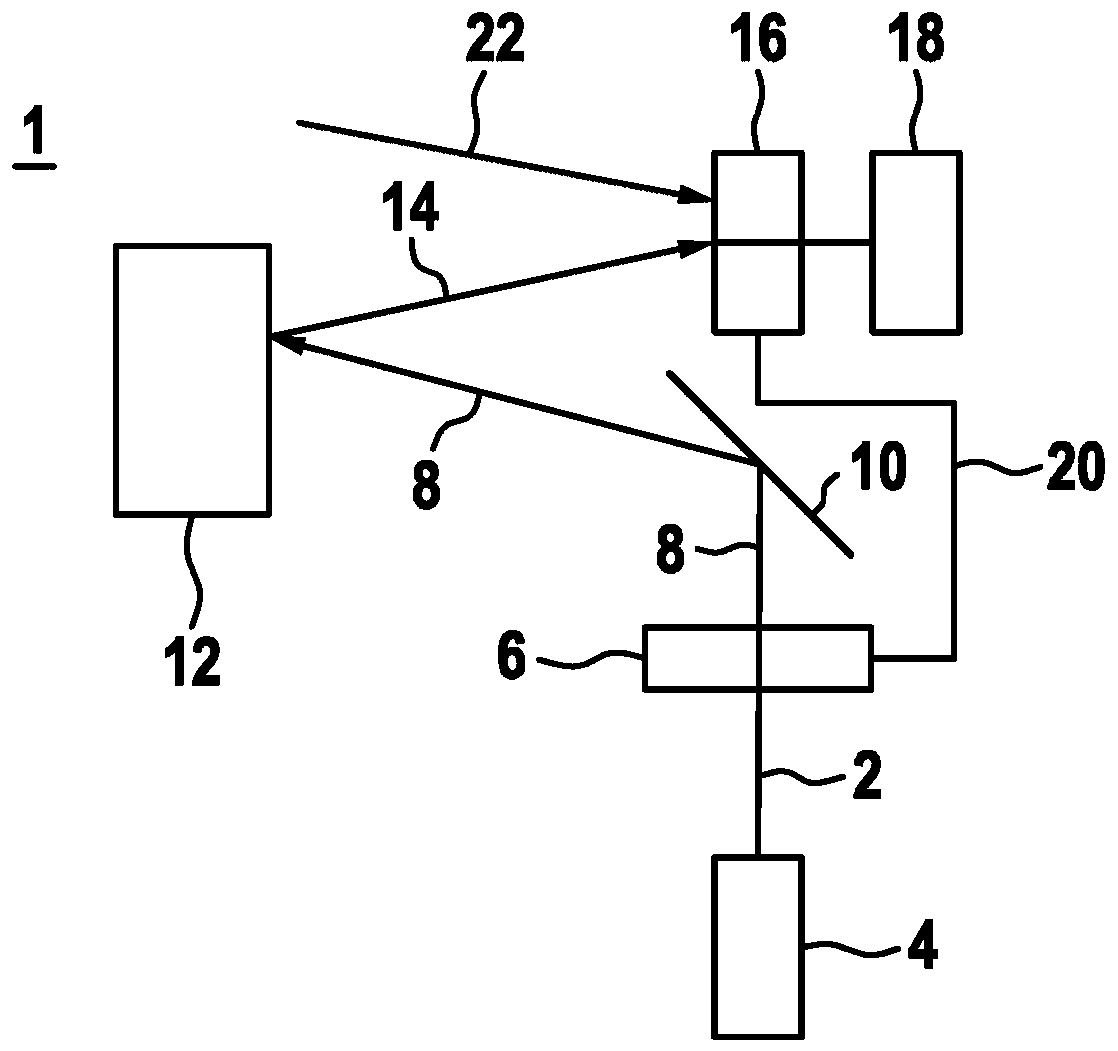
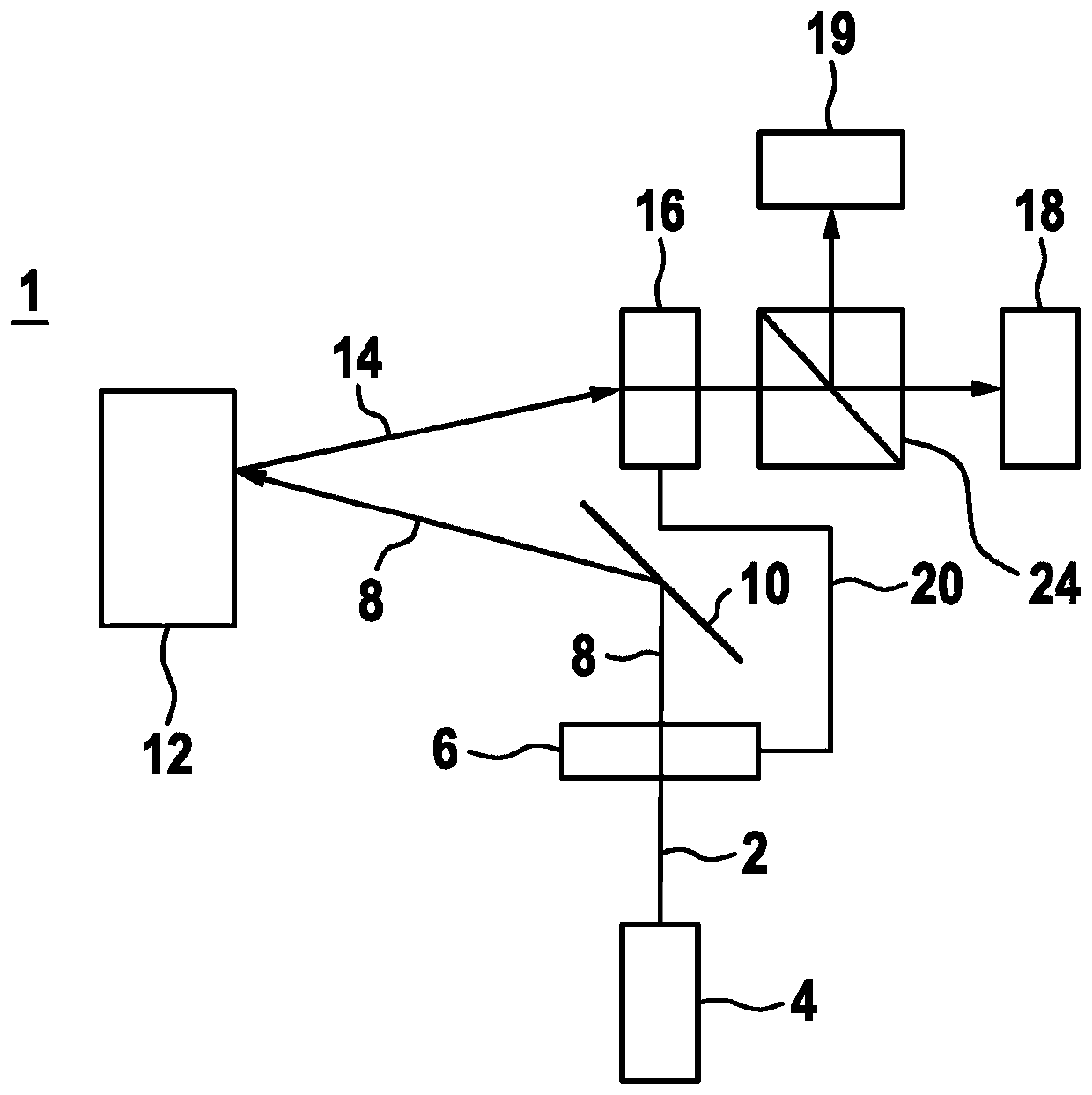
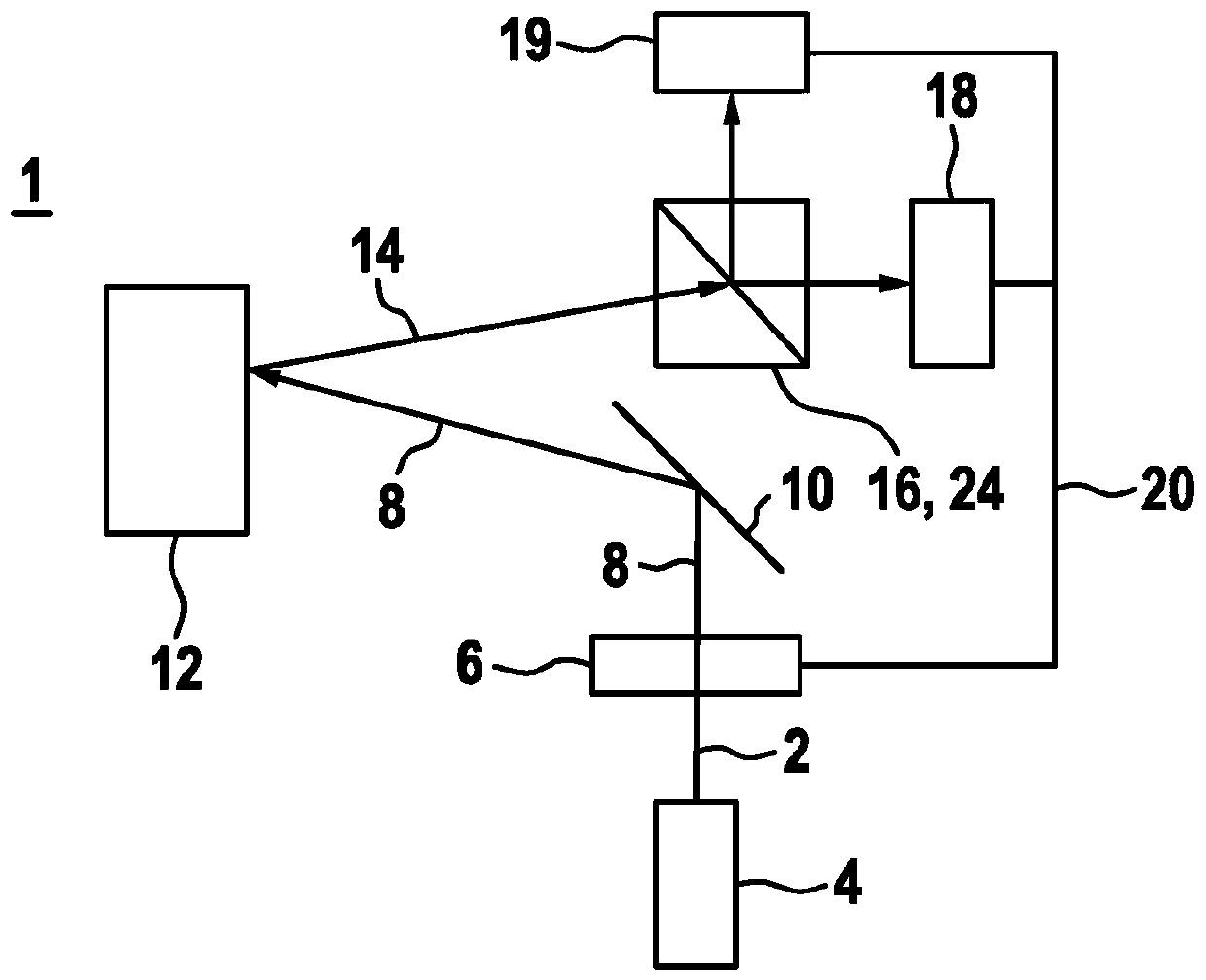
[0024] figure 1 A schematic diagram of a lidar device 1 according to a first exemplary embodiment is shown for scanning a scanning region by means of at least two beams 2 generated in temporal succession. LiDAR device 1 has a beam source 4 , for example an infrared laser 4 . A beam source 4 generates a beam 2 or laser beam 2 in the form of pulses 2 . In particular, the beam source generates at least two beams 2 following one another, which together form a pulse pattern. The pulse mode is in particular a pulse-pause mode, since each generated beam 2 or pulse 2 is followed by a pause. The generated beam 2 passes through a polarization encoder 6 after generation. The polarization encoder 6 includes in particular a linear polarization rotator and a corresponding actuation device or evaluation logic. Thus, the polarization rotator can be rotated differently, and thus an additional encoding in the form of a separate polarization for each pulse 2 can be generated for the pulse pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com