Microsatellite unstable site screening and analysis model construction method and device
A microsatellite instability and microsatellite locus technology, applied in the field of biological information, can solve the problems of difficulty in covering all types of samples, low detection efficiency, unsatisfactory specificity and sensitivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Example 1 Construction of a screening model for microsatellite instability sites
[0080]The present embodiment provides a method for constructing a microsatellite instability site screening model, comprising the steps of:
[0081] (1) Select the reference genome. In this example, select the human reference genome, use the gene capture chip to capture, and then use the microsatellite repeats (Satellite repeats) in the UCSC repeat mask database. The file address is http: / / hgdownload.cse.ucsc .edu / goldenPath / hg19 / database / rmsk.txt.gz, select the single-base repeat region in the gene capture chip region, and use the selected microsatellite sites as candidate MS sites;
[0082] (2) Compare several cancer tissue samples with their paired samples. The type of cancer tissue samples is not limited. In this embodiment, lung cancer tissue samples are selected, and the microsatellite instability (MSI) status of the cancer tissue samples is detected by immunohistochemical method. ...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2 Construction of Microsatellite Instability Analysis Model
[0093] This implementation provides a method for the construction of a microsatellite instability analysis model, including using the model constructed by the microsatellite instability site screening model construction method in Example 1, and performing microsatellite instability analysis on the above basis Model construction:
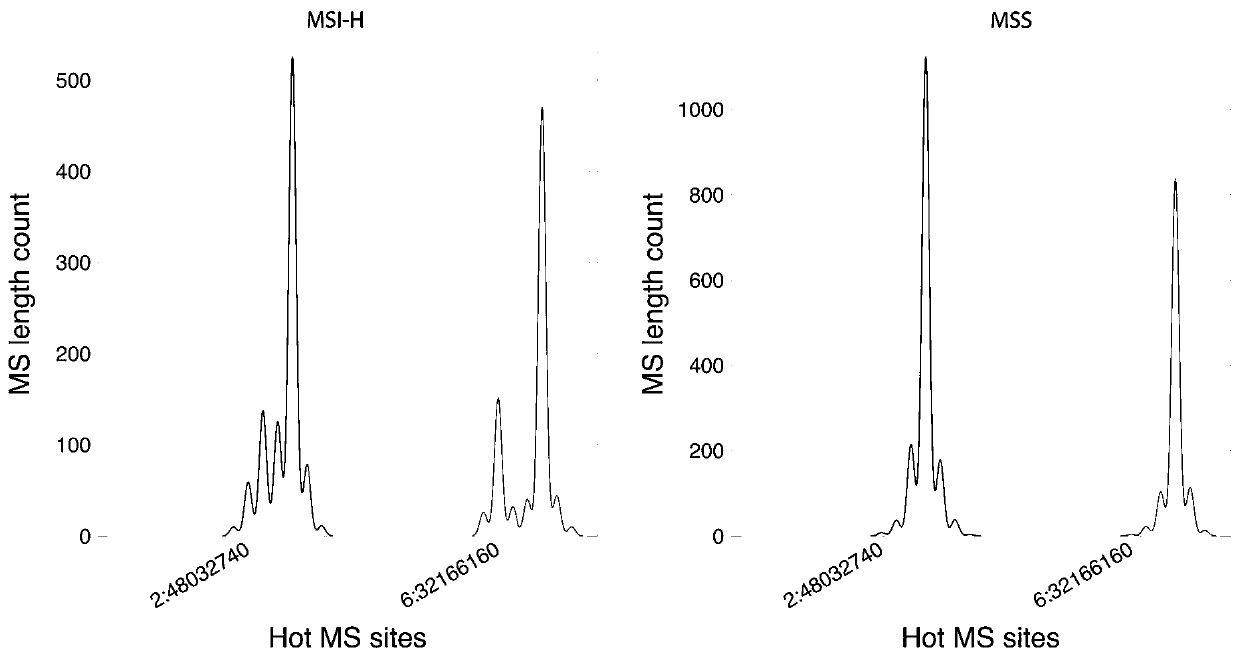
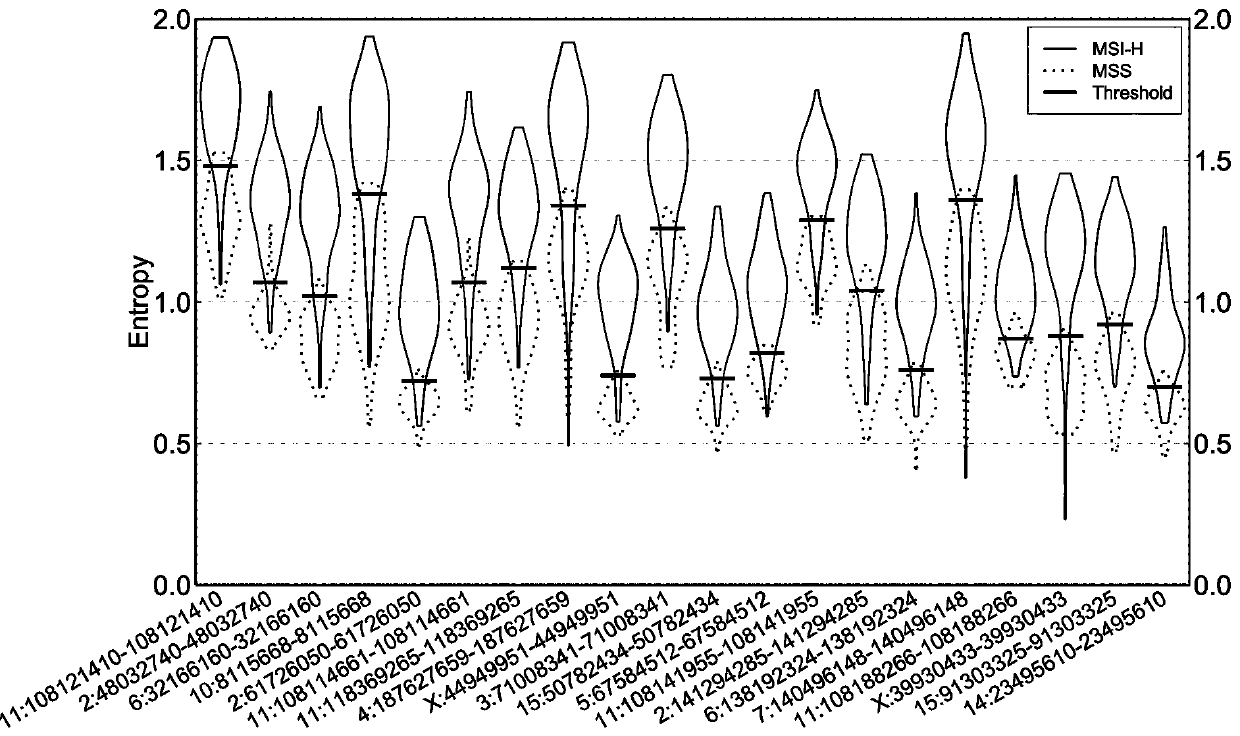
[0094] Take the lung cancer sample to be tested and calculate the information entropy of the MSI site according to the step (2) in Example 1, and compare the obtained information entropy value with the entropy threshold of the MSI site. When >30% of the sites are MSI-positive, the lung cancer sample to be tested is high-frequency microsatellite instability; when there are ≥10% of all MSI sites in the lung cancer sample to be tested, and ≤30% of the sites are When MSI is positive, the lung cancer sample to be tested is low-frequency microsatellite instability; when <10% of a...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3 Construction and verification of microsatellite instability analysis model
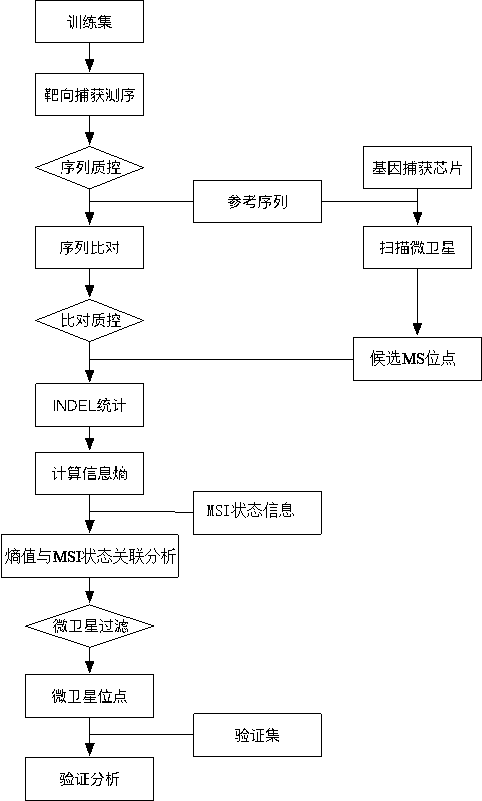
[0096] This embodiment provides a method for building a microsatellite instability analysis model, the flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
[0097] (1) Take hg19 as the reference genome, use the gene capture chip (1021panel chip of C1021OncoD product) to capture, and then use the scan step of MSIsensor software to scan the microsatellite position in the region of the gene capture chip (1021panel chip of C1021OncoD product) point, and then use bedtools to pick out the microsatellite loci that fall within the region of the gene trap chip (1021panel chip of C1021OncoD product), and select a total of 370 microsatellite loci as candidate MS loci;
[0098] (2) Select PCR technology, compare several colorectal cancer tissue samples with their corresponding paired samples, and detect the microsatellite instability (MSI) status of colorectal cancer tissue samples, and the tes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com