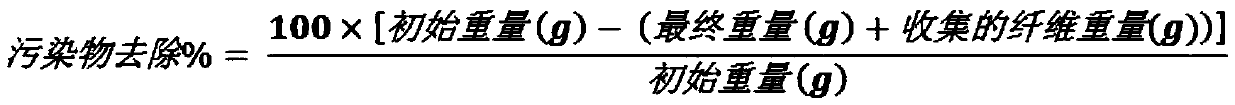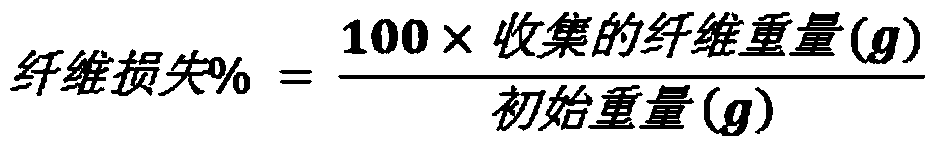Composition, its use and method for removing and preventing wet strength resins from contaminating papermaking equipment
A technology of papermaking equipment and composition, applied in the fields of removing wet strength resin pollutants in papermaking equipment and preventing it from polluting papermaking equipment, its use and method, capable of solving the problems of inapplicable safe handling, non-biodegradable, non-compliance Problems such as regeneration, to achieve the effect of preventing wet strength resin from contaminating papermaking equipment, high cleaning efficiency or cleaning ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1: Cleaning Wet Press Felt
[0052] Four sets of felt samples were used in this study, each set containing 2 samples. A circular felt sample approximately 2 inches in diameter was randomly die cut from the felt bulk sample. Three groups were from tissue and towel manufacturing plants (Paper Mills 1-3). The rest were virgin felt (VF) contaminated with PAE in the laboratory. The circular cut virgin felt samples were soaked in PAE solution and then heated in an oven at 105 °C for 2.5 h to promote crosslinking.
[0053] Each felt sample was washed and tested individually. The felt samples were washed with a tergotometer. Collect loose fibers between wash and rinse cycles. The fiber collection was rolled into pellets, dried, weighed, and recorded as "Fiber Loss" in the results. The reported results for contaminant removal are corrected for fiber loss.
[0054] One felt sample from each group was washed with 5% (w / w) of Composition A (Table 1). Dilute the comp...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2: Preventing Wet Strength Resin Contamination of Wet Press Felt.
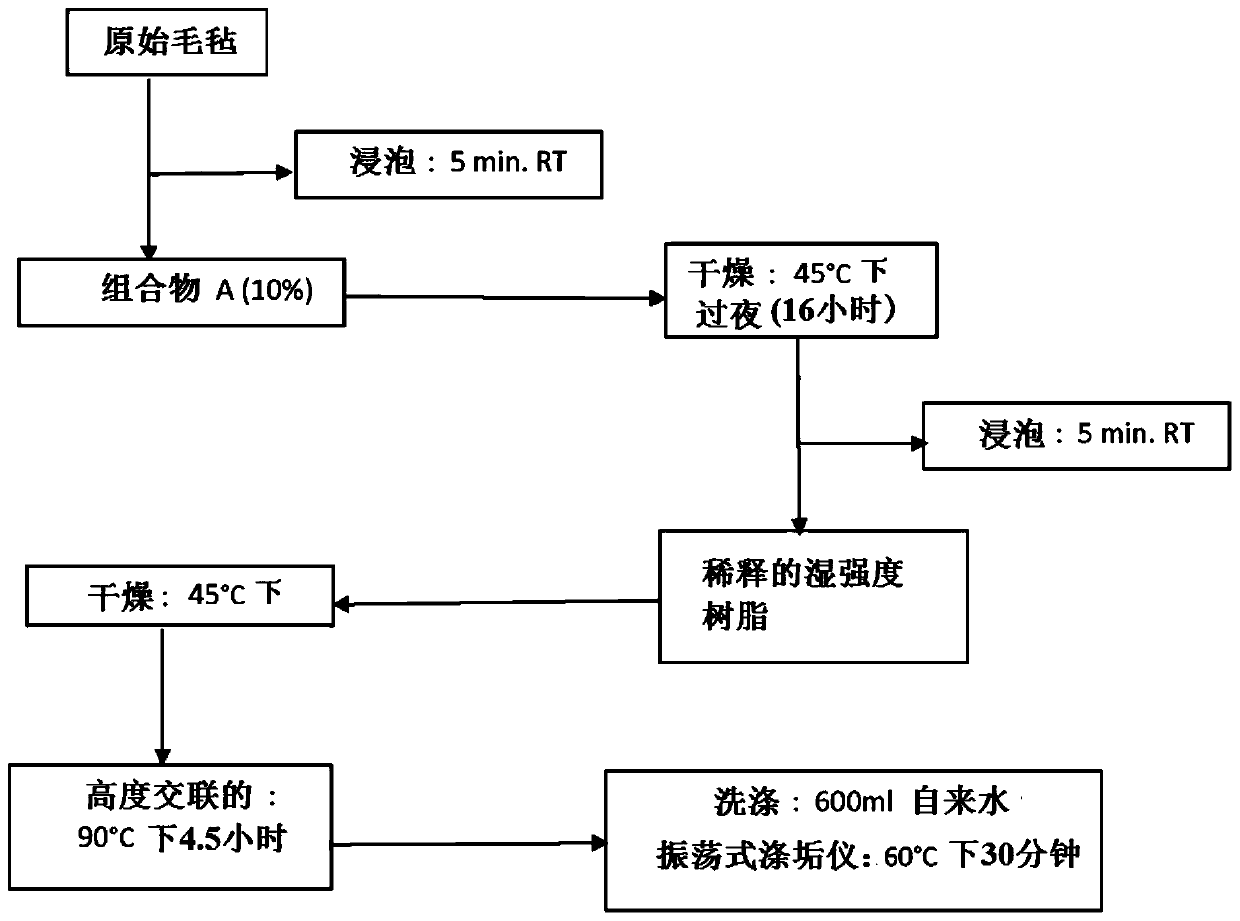
[0062] Cut a sample of raw felt approximately 2 inches in diameter with a standard die cutter. One set of samples was then placed in a 10% (w / w) aqueous solution of Composition A and the other set in water was used as a control. The samples were soaked at room temperature for five minutes and then dried overnight (16 hours) in a 45°C oven. Dilute the wet strength chemical PAE with deionized water. The dried soaked felt was placed in a diluted PAE solution (2.5%, w / w) and soaked at room temperature for five minutes, then dried in an oven at 45°C for 6.5 hours, and then cross-linked in an oven at 90°C 4.5 hours. The felt was washed in an oscillating detergent for 30 minutes in 600ml tap water at a temperature of 60°C at a speed of 150rpm ( figure 1 ). Fiber loss, porosity and water absorption rate were measured by the method described in Example 1. The percent weight gain is calculated as
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com