Water depth optimization and rapid recovery method of Scirpus nipponicu wetland under saline-alkali stress
An optimization method, the technology of scutellaria, applied in the direction of botanical equipment and methods, root crop cultivation, soilless cultivation, etc., can solve the problems of restricting the restoration effect of degraded wetlands, and achieve the advantages of rapid colonization and construction, accumulation of promotion, good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The method for optimizing the water depth of the Sanjiang grass wetland under saline-alkali stress of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0027] (1) Excavate the bulbs of the Sanjiang grass in the distribution area of Eantoupao Sanjiang in the west of Jilin Province, store them in the dark and moist, and obtain the bulbs of the Sanjiang grass to be planted;
[0028] (2) Select healthy and complete bulbs with consistent growth, wash them, place them in a seedling pot, water every day to keep the water depth of 0-2cm in the pot, grow seedlings in the greenhouse, and obtain 2-5cm high Siamia sativa seedlings;
[0029] (3) sow the Sanjiang grass seedlings in the cultivation pot, the cultivation pot is 13cm high, 14cm in inner diameter, and filled with 10cm high water-washed sand;
[0030] The burial depth of the Sanjiangsi grass seedlings is 2–3 cm, and 5 bulbs are planted in each cultivation pot;
[0031] Put the culture bowl into the large water tank...
Embodiment 2
[0036]This example specifically illustrates the experimental results of the water depth optimization method in Example 1 and the rapid restoration method of the Sanjiang sage grass wetland.
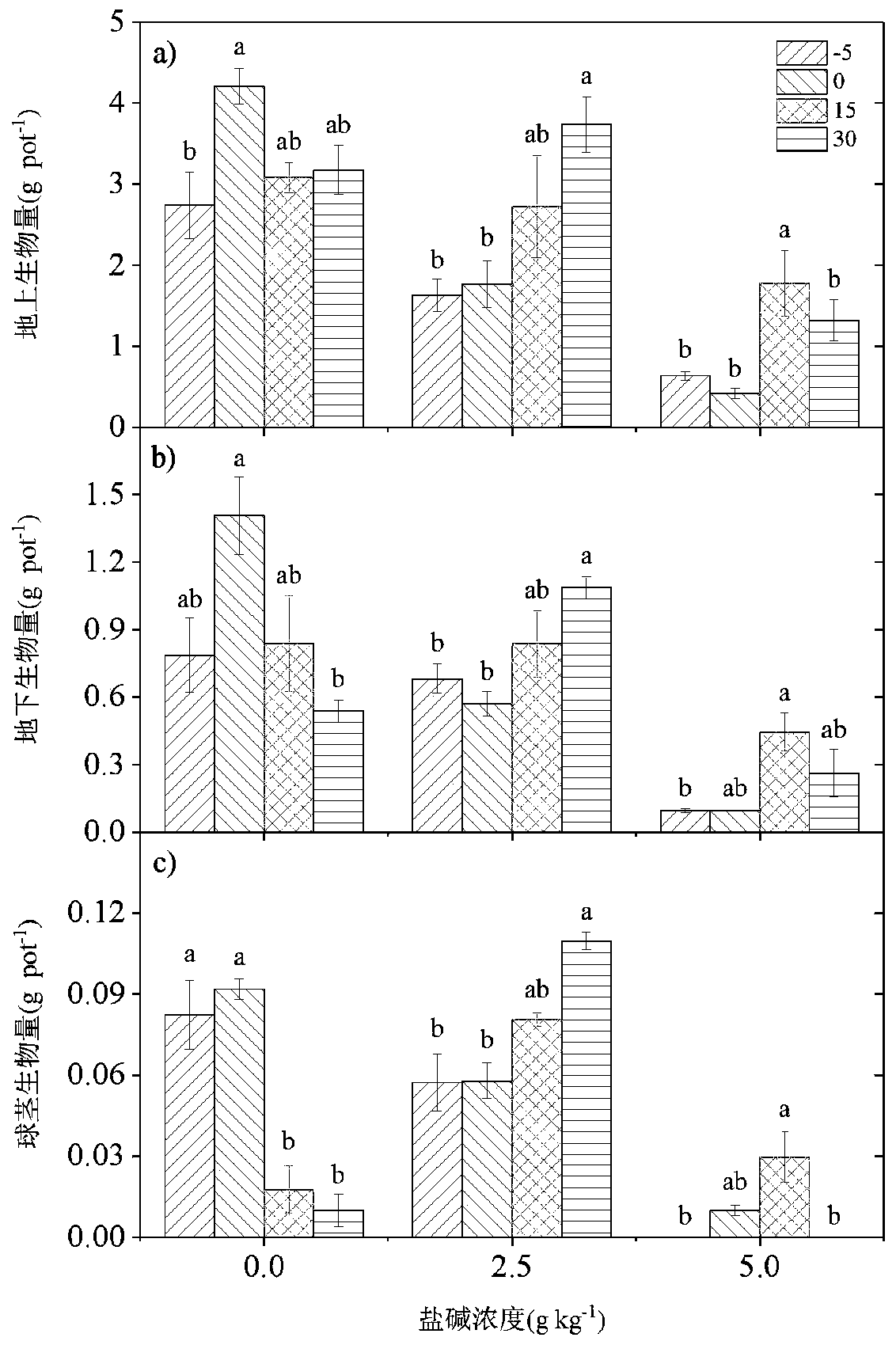
[0037] The size of aboveground biomass represents the ability of plants to obtain resources such as light and oxygen. Underground biomass can reflect the ability of plants to absorb water and nutrients. The water depth where aboveground biomass, underground biomass and bulb biomass were relatively large was regarded as the optimum water level for the growth of S. triangularis at various salinity concentrations.
[0038] figure 1 The above-ground biomass, underground biomass and biomass of newly formed bulbs of S. tricera after being treated by the method described in Experimental Example 1 are listed. The different lowercase letters in the figure indicate the difference in aboveground biomass, belowground biomass and bulb biomass of S. triangularis among different water depths (cm) under...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com