Method for recovering rare earth and iron from superfine powder waste produced in NdFeB production process
A production process and ultra-fine powder technology, applied in the electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of high labor intensity, complex process, large waste water, etc., to avoid pollution, simple process, and improve the recovery rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for reclaiming rare earth and iron from the superfine powder waste produced in the NdFeB production process, comprising the following steps:
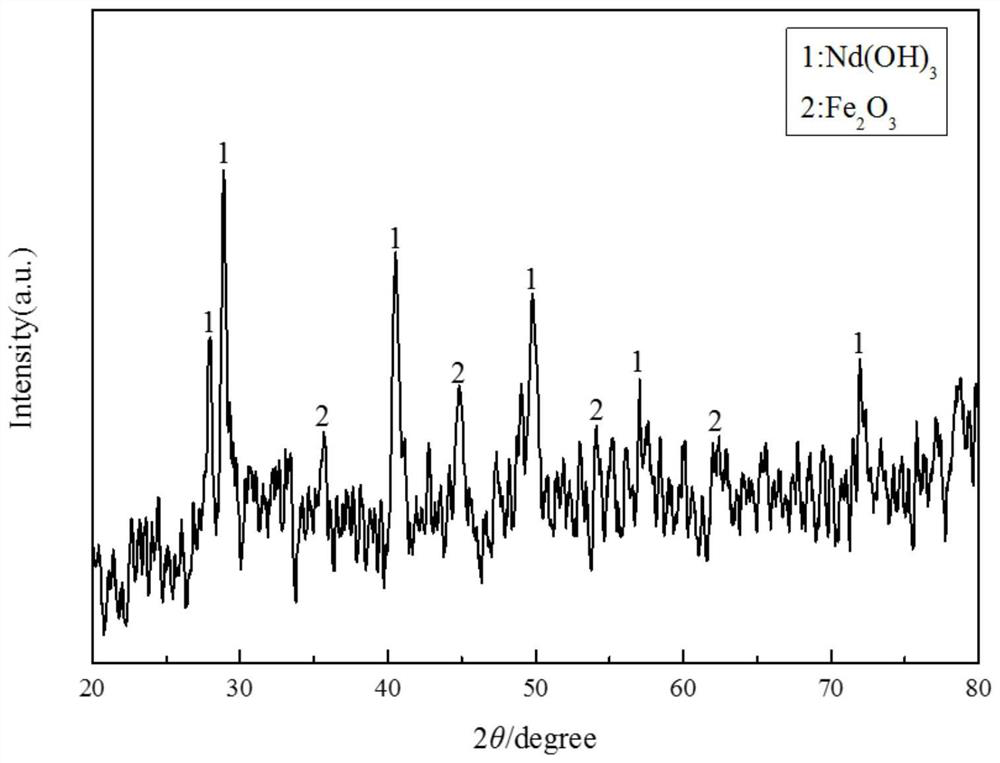
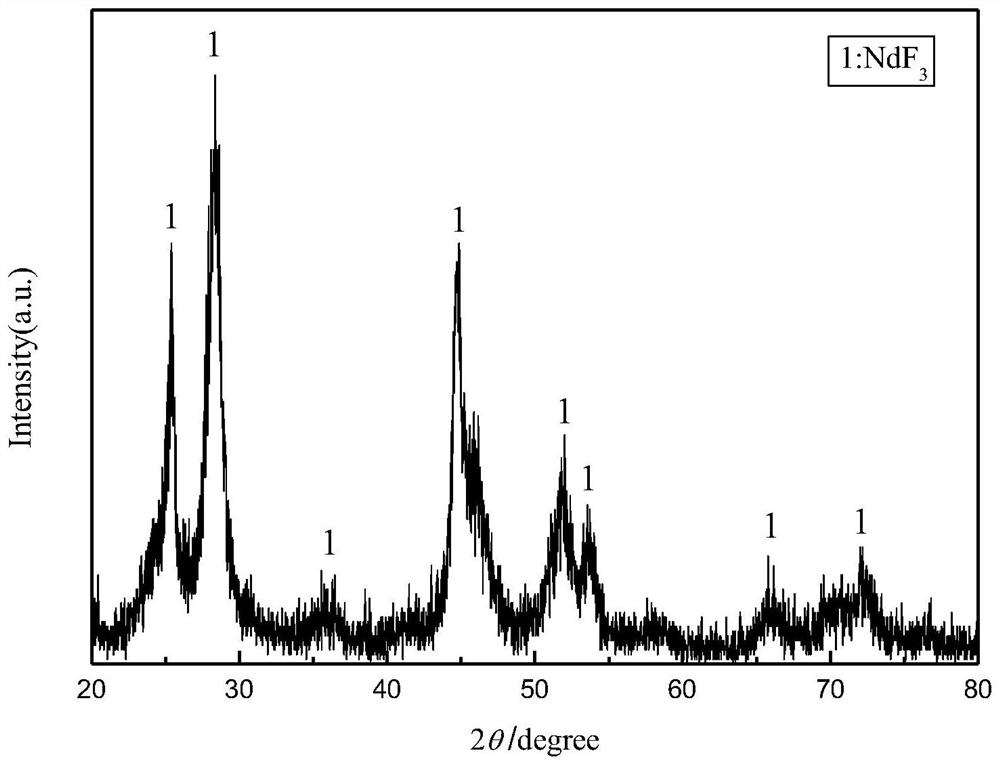
[0026] (1) The superfine powder waste produced in the NdFeB production process is acid-dissolved with hydrofluoric acid with a mass concentration of 5%, and hydrofluoric acid is added at a ratio of 40mL / g according to the liquid-solid ratio, and fully stirred at room temperature , so that iron oxide is completely dissolved, and rare earth elements form rare earth fluoride precipitation;
[0027] (2) The precipitate is filtered, washed and dried to obtain solid A1 and filtrate B1, A1 is a rare earth fluoride, and B1 is a hydrofluoric acid solution in which iron oxide is dissolved. ICP-AES analysis of B1 shows that the recovery efficiency of each rare earth element is La77.3%, Ce81.7%, Pr99.8%, Nd99.8%, Gd99.8%, Tb99.8%, Dy99.6% , Ho100%. The total recovery efficiency of rare earth is 99.7%;
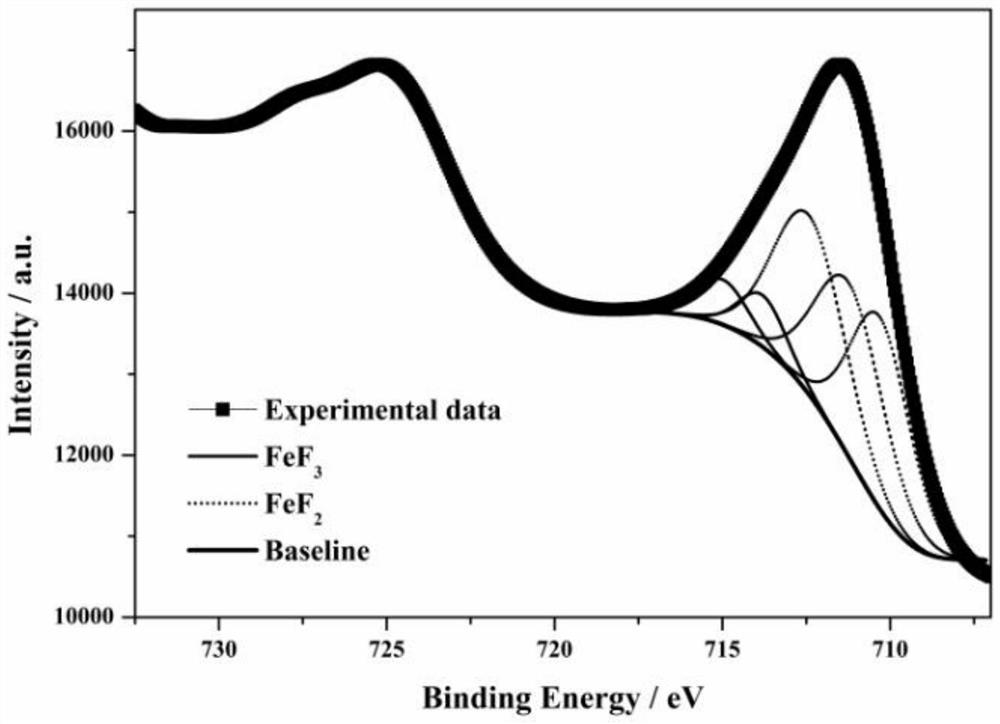
[0028] (3) The filtrate B1...
Embodiment 2
[0031] A method for reclaiming rare earth and iron from the superfine powder waste produced in the NdFeB production process, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) The superfine powder waste produced in the NdFeB production process is acid-dissolved with hydrofluoric acid with a mass concentration of 10%, and hydrofluoric acid is added according to the ratio of liquid to solid ratio of 40mL / g, and fully stirred at room temperature , so that iron oxide is completely dissolved, and rare earth elements form rare earth fluoride precipitation;
[0033] (2) The precipitate is filtered, washed and dried to obtain solid A1 and filtrate B1, A1 is a rare earth fluoride, and B1 is a hydrofluoric acid solution in which iron oxide is dissolved. ICP-AES analysis of B1 shows that the recovery efficiencies of rare earth elements are La79.8%, Ce83.3%, Pr100%, Nd100%, Gd99.8%, Tb99.8%, Dy99.8%, Ho100%. The total recovery efficiency of rare earth is 99.8%;
[0034] (3) The filtrate B1 is...
Embodiment 3
[0037] A method for reclaiming rare earth and iron from the superfine powder waste produced in the NdFeB production process, comprising the following steps:
[0038] (1) The superfine powder waste produced in the NdFeB production process is acid-dissolved with hydrofluoric acid with a mass concentration of 15%, and hydrofluoric acid is added at a ratio of 40mL / g according to the liquid-solid ratio, and fully stirred at room temperature , so that iron oxide is completely dissolved, and rare earth elements form rare earth fluoride precipitation;
[0039] (2) The precipitate is filtered, washed and dried to obtain solid A1 and filtrate B1, A1 is a rare earth fluoride, and B1 is a hydrofluoric acid solution in which iron oxide is dissolved. ICP-AES analysis of B1 shows that the recovery efficiencies of rare earth elements are La80.1%, Ce85.4%, Pr100%, Nd100%, Gd99.8%, Tb99.9%, Dy99.7%, Ho100%. The total recovery efficiency of rare earth is 99.8%;
[0040] (3) The filtrate B1 is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com