Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain producing high-grade alcohols at low yield and built through regulating and controlling cell wall constitutive proteins
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and higher alcohols, which is applied in the field of bioengineering and can solve the problems of synthesizing too many higher alcohols
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with single knockout of TIR1 gene
[0064] The main construction process of the strain is as follows:
[0065] 1) Amplification of the fragment required to knock out one allele of TIR1
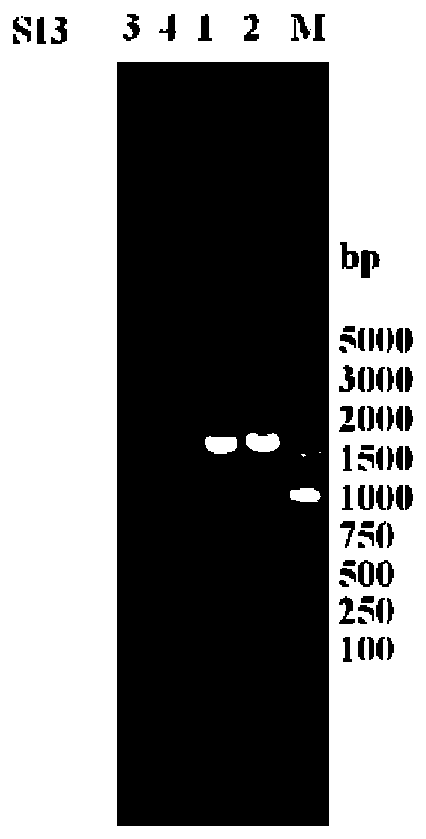
[0066] Using the S17 genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a template, T1A-F and T1A-R were used as primer pairs to PCR amplify the upstream homologous sequence fragment required for TIR1 gene knockout, with a length of 662bp; using the S17 genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a template, T1B-F and T1B-R as the primer pair PCR to amplify the downstream homologous sequence fragment with a length of 566bp; using the plasmid pUC6 genome as the template, T1K-F and T1K-R as the primer pair PCR amplification to amplify the loxP required for TIR1 gene knockout -KanMX3-loxP fragment, 1663bp in length, such as figure 1 ).
[0067] 2) Construction of a recombinant yeast strain that knocks out one allele of TIR11
[0068] After the am...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with double knockout of TIR3 gene
[0076] The main construction process of the strain is as follows:
[0077] 1) Amplification of the fragment required to knock out one allele of TIR3
[0078] Using the S17 genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a template, T3A-F and T3A-R were used as primer pairs to PCR amplify the upstream homologous sequence fragment required for TIR3 gene knockout, with a length of 496bp; using the S17 genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a template, T3B-F and T3B-R as primers to PCR amplify the downstream homologous sequence fragment with a length of 676bp; using the plasmid pUC6 genome as a template, T3K-F and T3K-R as primers to PCR amplify loxP required for TIR3 gene knockout -KanMX3-loxP fragment, length is 1663bp ( Figure 5 ).
[0079] 2) Construction of a recombinant yeast strain that knocks out one allele of TIR13
[0080] After the three amplified fragments were purified and...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Example 3: Wheat beer fermentation experiments of recombinant strains S17-Δtir1-k-p and S17-DΔtir3-k-p with low production of higher alcohols
[0099] 1) The wheat beer fermentation process route is as follows: Figure 14 Shown:
[0100] 2) Saccharification process: Weigh the crushed wheat malt and add it to warm water at 30°C with a material-to-water ratio of 1:4. After stirring well, place it in a constant temperature water bath, keep it at 30°C for 30 minutes, and raise the temperature at 2.0°C / min. to 65°C, keep for 90min, then rapidly raise the temperature to 78°C, and keep for 10min. Fully stir once every 5 minutes during the saccharification process. The saccharified wheat wort is filtered while hot, and washed with hot water at 75°C for 3 times. Place the filtrate on an induction cooker for steaming, add 3‰ of bitter hops (calculated by malt weight) 40 minutes after boiling, and boil for 70 minutes. Naturally cool to room temperature after boiling, centrifug...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com