Method for training switching parameters of a magnetic control valve in a vehicle braking system and braking system
A technology for switching parameters and braking systems, applied in braking safety systems, general control systems, braking control systems, etc., can solve problems such as inaccurate driving and control of service brakes, inability to compensate tolerances, and asymmetric driving and control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] specific implementation plan
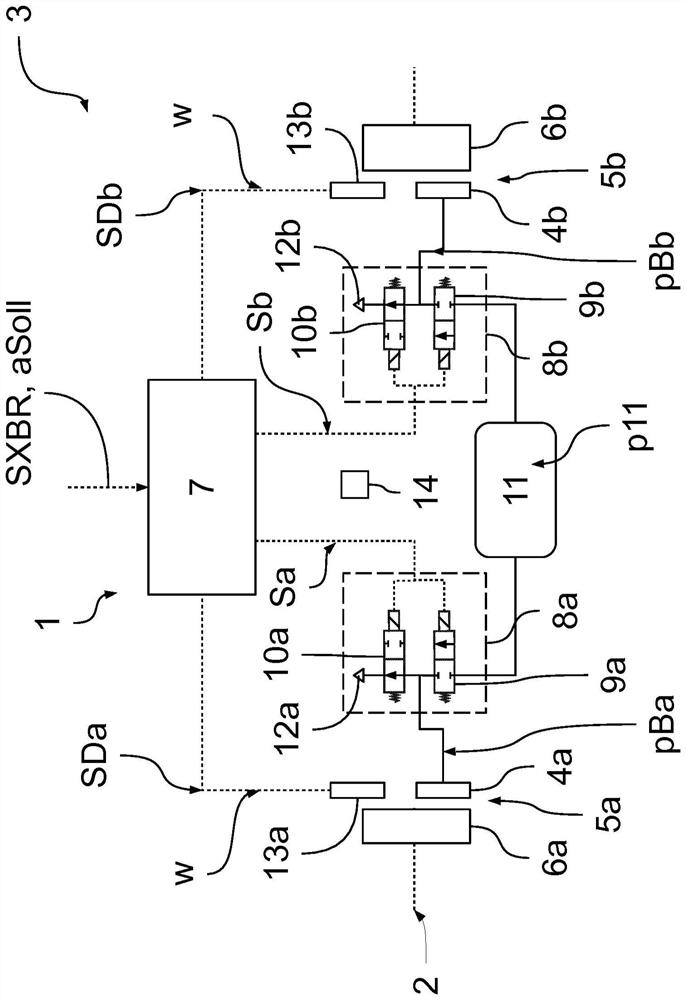
[0050] figure 1 An exemplary and schematic fragment of a braking system 1 in the region of the rear axle 2 of a vehicle 3 is shown, wherein the braking system 1 is embodied according to this embodiment as a pneumatic braking system. The respective wheels 6a, 6b on the rear axle 2 can thus be braked in a targeted manner by building up brake pressures pBa, pBb in the brake cylinders or brake chambers 4a, 4b of the service brakes 5a, 5b. Here, the designations "a" and "b" distinguish the wheel sides of the rear axle 2, wherein "a" designates the left side and "b" designates the right side.
[0051] Presetting of the braking pressures pBa, pBb in the service brakes 5a, 5b on the rear axle 2 is realized electropneumatically, specifically, the control device 7 of the braking system 1 uses the control signal Sa, Sb to control the respective service brakes Modulators 8a, 8b before 5a, 5b. according to figure 1 Each modulator 8a, 8b has an inle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com