Architecture and method for carrying out multiply-add operation on floating-point numbers or fixed-point numbers
A floating-point number and addition operation technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, digital data processing components, calculations, etc., can solve the problems of single-precision or half-precision floating-point operations, low precision, and incompatibility between precision and efficiency. To achieve the effect of avoiding the decline of calculation accuracy, high adaptability and improving calculation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
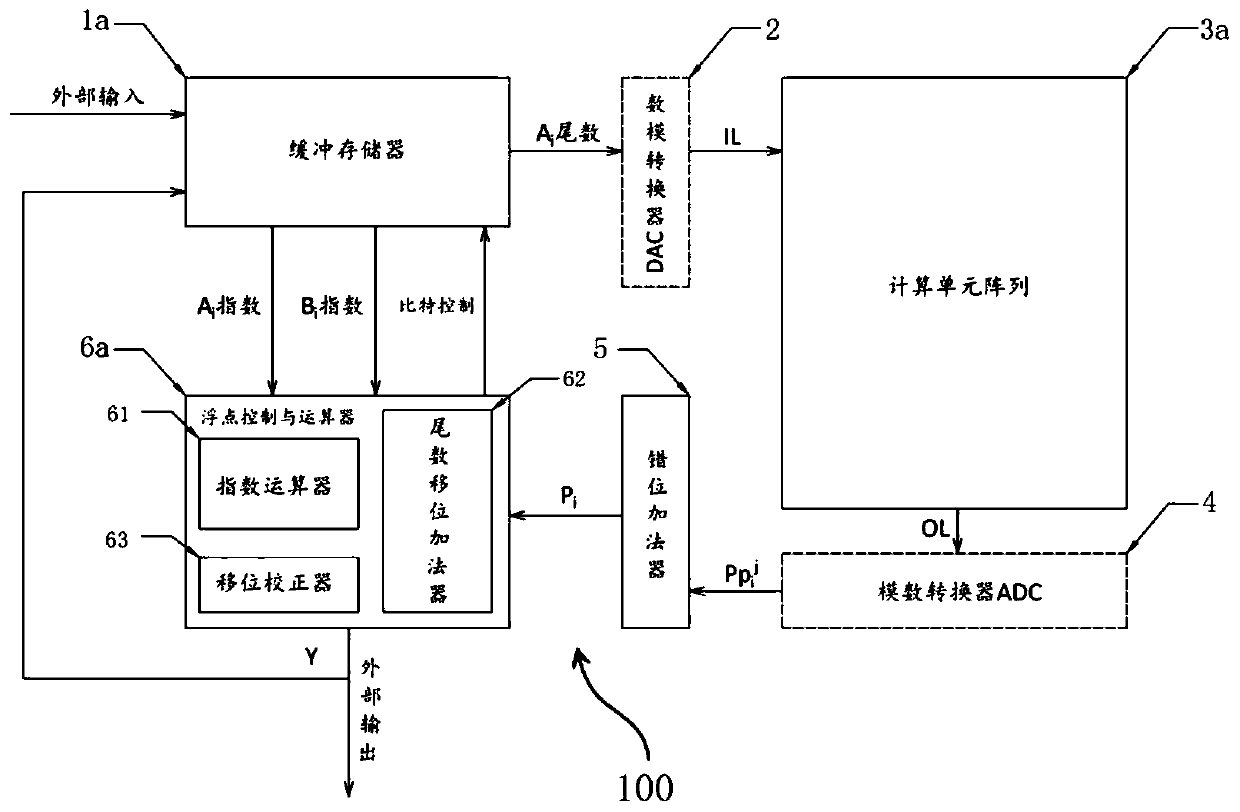
[0044] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the architecture for multiplying and adding floating-point numbers in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, the architecture 100 for multiplication and addition of floating-point numbers includes a buffer memory 1a, a plurality of digital-to-analog converters 2, a computing unit array 3a, a plurality of analog-to-digital converters 4, a dislocation adder 5, and a floating-point control and arithmetic unit module 6a and the external input and output interface 7.
[0046] The buffer memory 1a is used for buffering externally input data and intermediate calculation results, that is, for buffering a plurality of input floating-point numbers and intermediate results. The cached floating-point numbers contain floating-point exponents and floating-point mantissas.
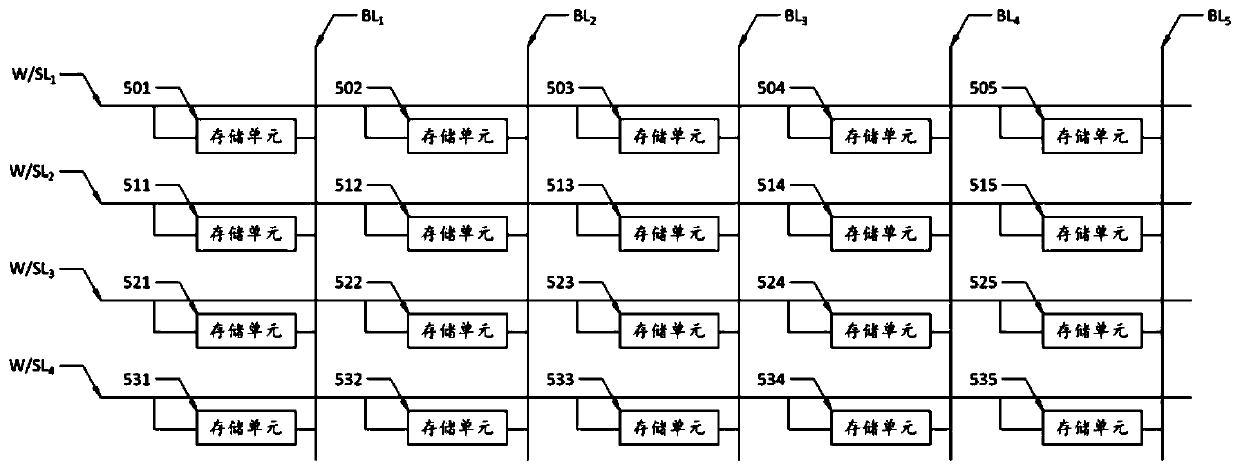
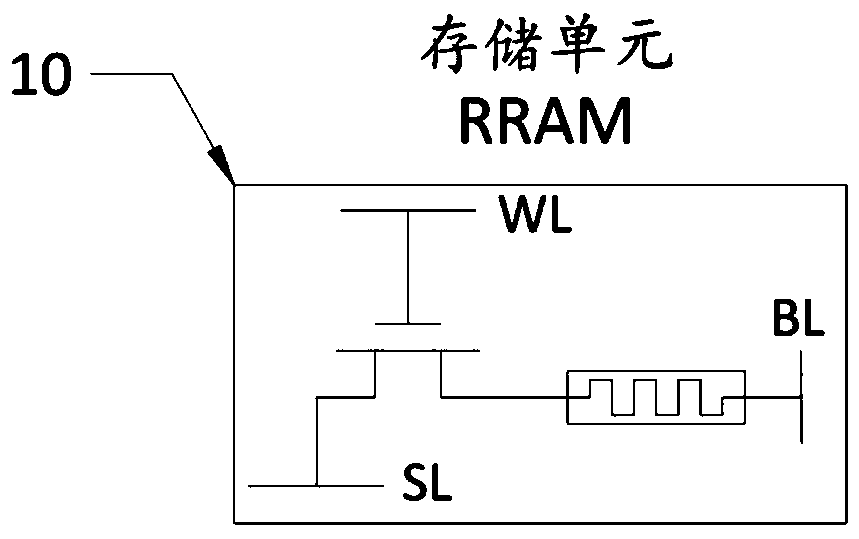
[0047] In this embodiment, the buffer memory 1a is a memory with high-speed access, which can output multi-bit data at the same time. T...
Embodiment 2
[0109] In the second embodiment, for the same structures as those in the first embodiment, the same symbols are used and the same descriptions are omitted.
[0110] Figure 14 It is a structural block diagram of the architecture for multiplying and adding floating-point numbers in Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0111] Such as Figure 14 As shown, the architecture 200 for multiplication and addition of floating-point numbers includes a buffer memory 1b, a plurality of digital-to-analog converters 2, a computing unit array 3b, a plurality of analog-to-digital converters 4, a dislocation adder 5, and a floating-point control and arithmetic unit module 6a and the external input and output interface 7.
[0112] In this embodiment, the bit width of the buffer memory 1b is equal to the sum of the required bit width of 2 floating-point exponents and the required bit width of 2 floating-point mantissas. and floating point numbers A i index (E Ai ), A i mantissa (M A...
Embodiment 3
[0117] In the third embodiment, for the same structures as those in the first embodiment, the same symbols are used and the same descriptions are omitted.
[0118] Figure 16 It is a structural block diagram of an architecture for multiplying and adding fixed-point numbers in Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0119] Such as Figure 16 As shown, the architecture 300 for multiplication and addition of fixed-point numbers includes a buffer memory 1c, a plurality of digital-to-analog converters 2, a computing cell array 3c, a plurality of analog-to-digital converters 4, a dislocation adder 5, a fixed-point controller module 6b, and an external Input and output interface 7.
[0120] In this embodiment, the buffer memory 1c is a fixed-point buffer memory, which is used to buffer and store a plurality of input fixed-point numbers and calculated fixed-point multiplication and addition results. The bit width of the fixed-point buffer memory is the required bit width of one fix...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com