Cobaltous oxide slice, preparation method thereof and application of cobaltous oxide slice in visible-light photocatalysis total-decomposition of water
A cobalt oxide, flake technology, applied in the field of photocatalytic water splitting, to achieve the effect of excellent performance, high activity and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] The invention provides a method for preparing cobaltous oxide flakes, comprising the following steps:
[0039] S1. Using sodium chloride as a template and cobalt acetate as a cobalt source, obtain precursor flakes through hydrothermal reaction or solvothermal reaction;
[0040] S2. Calcining the precursor flakes at 200-300° C. in an inert atmosphere to obtain sphalerite-type cobaltous oxide flakes.
[0041] Aiming at the status quo of visible light catalytic total water splitting in the prior art, this application provides a preparation method of sphalerite-type CoO ultra-thin flakes. The ultra-thin flakes prepared above can realize the catalytic decomposition of water under visible light, and the product Has high stability.
[0042] Specifically, the embodiment of the present invention discloses a preparation method of sphalerite-type CoO ultrathin flakes, including the following steps:
[0043] Sodium chloride and cobalt acetate are dispersed and reacted in water or...
Embodiment 1
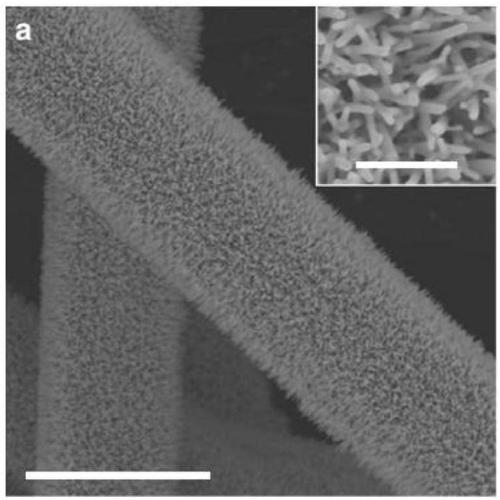
[0063] Add 320mg of sodium chloride and 500mg of cobalt acetate tetrahydrate into 20mL of water, stir vigorously at room temperature for 30min, pre-cool the resulting reaction solution, put it into a freeze dryer, and freeze-dry for 24h to obtain a precursor powder; take 50mg of the obtained precursor powder In a tube furnace, calcined at 240°C for 3 hours in a high-purity argon atmosphere, took it out after natural cooling to obtain a powder product, washed with water to remove sodium chloride, centrifuged to obtain a sample, and dried the sample in a vacuum oven at 60°C for 10 hours to obtain 10-13mg of powder, that is, sphalerite-type CoO flakes.
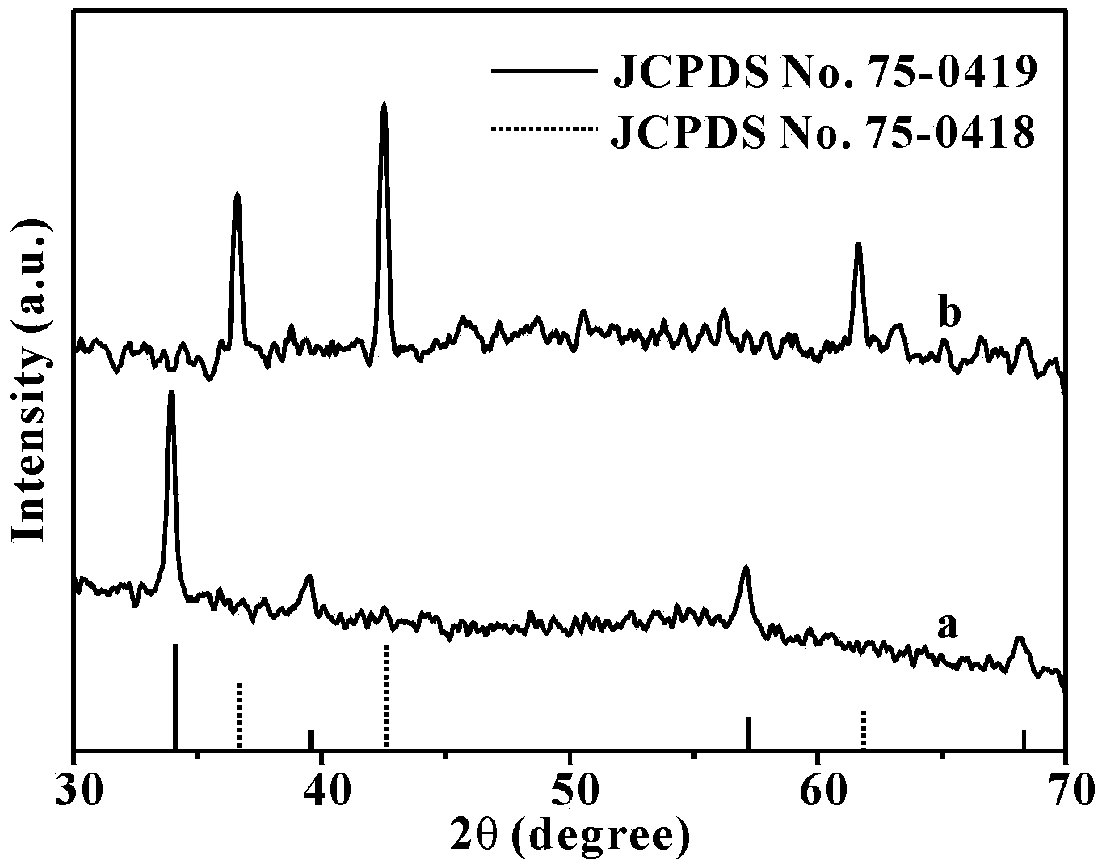
[0064] The compound prepared in Example 1 is carried out structural identification, the results are shown in Figure 3 ~ Figure 6 , image 3 The curve a in the middle is the X-ray diffraction (XRD diffraction) pattern of the sphalerite-type CoO flakes prepared in this example, where the ordinate is the intensity (Intensity), and...
Embodiment 2
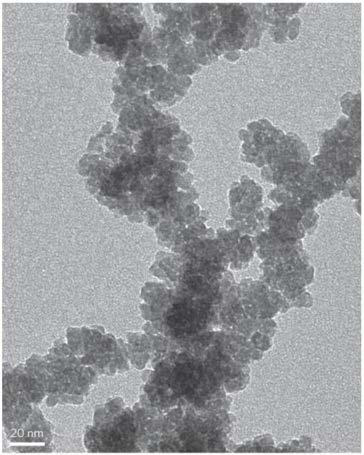
[0073] Add 320mg of sodium chloride and 500mg of cobalt acetate tetrahydrate into 20mL of water, stir vigorously at room temperature for 30min, and dry the resulting reaction solution at 65-75°C for 24h to obtain a precursor powder; take 50mg of the obtained precursor powder in a tube furnace, Calcined at 240°C for 3 hours in a high-purity argon atmosphere, cooled naturally to obtain a powder product, washed with water to remove sodium chloride, and then centrifuged to obtain a sample, dried the sample in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for 10 hours to obtain 10-13 mg of powder, That is, sphalerite-type CoO flakes, whose TEM photos are as follows Figure 12 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com