Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2 and application thereof
A technology of Lactococcus and strains, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of slow acid production, insufficient desalination and deproteinization, and inability to effectively prevent spoilage of shrimp shell waste, etc., to achieve strong acid production ability, increase autolysis time, The effect of broad application development and market prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1 strain isolation, purification and identification
[0049] 1. Isolation and purification of Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2
[0050] Buy fresh vannamei (Penaeus vannamei) from the market, rinse with clean water, peel off the shrimp shell, cut it into pieces, put it into a sterilized Erlenmeyer flask, add an appropriate amount of distilled water, and seal it for fermentation for several days; use 2% CaCO 3 The conventional isolation, purification, screening and identification of the shrimp-derived lactic acid cocci were carried out in the MRS medium; the active and functional lactic acid coccus strains were preserved in routine glycerin freezing.
[0051] 2. Preliminary identification of Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2
[0052] (1) Morphological characteristics
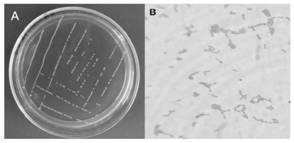
[0053] Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2 has no transparent ring formation on the MRS agar medium containing 2% calcium carbonate, and the colonies are small, milky white or light yellow, with round protrusions on th...
Embodiment 2
[0072] One of the decalcification effects of embodiment 2 Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2 on shrimp shells
[0073] Weigh several portions of shredded fresh Penaeus vannamei shrimp shells, 5g each, and put them into sterilized conical flasks respectively. Use the shrimp shells as raw materials, add 30% glucose, the initial pH is 6.8, and the temperature is 37°C. The rotation speed was 60r / min, the fermentation was 36h, and the concentration of inoculating 4mL was 5.1×10 8 Individual / mL Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2, different solid-liquid ratios (the ratio of the mass of the solid phase and the liquid phase in the culture solution, for example, the solid matter (shrimp head, sucrose, etc.) quality in the culture medium is 10g, at this time If the quality of the solvent water is 40g, then the solid-to-liquid ratio of the culture medium is 1:4) to measure the decalcification effect. When the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:5, the decalcification rate of Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2 is the larg...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3 The second decalcification effect of Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2 shrimp shells Weigh several portions of chopped fresh Penaeus vannamei shrimp shells, 5g each, and put them into sterilized Erlenmeyer flasks respectively, using the shrimp shells as raw materials , add 30% glucose, the solid-liquid ratio is 1:5, the initial pH is 7.0, the temperature is 37°C, the rotational speed is 60r / min, and the inoculated 4mL concentration is 5.1×10 8 Each / mL Lactococcus garvieae LGHK2 was used to determine the effect of different fermentation times on the pH and decalcification rate of the shrimp shell fermentation broth. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0078] It can be seen from Table 3 that the pH of the fermentation broth dropped rapidly to 3.3 within 0 to 36 hours of shrimp shell fermentation, and at 36 hours, the decalcification rate of the fermentation broth was the largest, reaching 77.75%. Since then, the decalcification rate has remained at a high level. In con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com