Molecular marker related with cotton fertility restoration, and application thereof
A cotton and restorer line technology, applied in the field of molecular biology genetics and breeding, can solve the problems of speeding up the field selection and backcross improvement process of excellent restorer lines, easy loss of restorer genes, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., and achieves good commercial application prospects, Improve selection efficiency and accuracy, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Embodiment 1, the extraction of genomic DNA
[0082] Four restorer line materials were extracted by the improved CTAB method: Zhonghui 46 (H46), Zhonghui 80 (H80), DR and ZR, two transgenic insect-resistant three-line hybrids Zhongmiansuo 83 and Zhongmiansuo 99, And 4 conventional cotton varieties: Zhongmian 45, Zhongmian 69, Zhongmian 100 and Zhongmian 110, a total of 10 materials (or leaves) genomic DNA, the specific method is as follows:
[0083] (1) First peel off the shell of the cotton seeds, grind each seed into powder separately, transfer to a 2ml centrifuge tube, and quickly add 800μl of preheated CTAB lysate (65°C), mix it upside down and place in 65°C water bath for 30-40 minutes, and slowly invert and mix once every 10 minutes.
[0084] (2) After the water bath, take out the centrifuge tube, add 800 μl of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), invert for about 30-50 times, and mix until no layering occurs.
[0085] (3) Centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min at 4°C. ...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Example 2, Gene Mapping and Molecular Marker Development
[0094] (1) Population construction and fertility survey
[0095] In this experiment, the "three lines" of upland cotton: Hackney cotton cytoplasmic male sterile line ZBA, maintainer line ZB and restorer line Zhonghui 46 (H46) were used as parents to construct restorer gene near-isogenic lines and F 2 Separate groups. The test materials were planted in the East Field Test Base of the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (East of Baibi Town, Anyang County, Henan Province; 36°10'N, 114°35'E), and the field was managed according to conventional methods. Fertility investigation method: During the flowering period from early July to mid-to-late August, try to choose sunny weather, and start investigating the near-isogenic line of the restorer gene and the F 2 Fertility of individual plants in a population. In order to improve the accuracy of group physical survey, a total of 5 s...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Example 3, Fertility recovery correlation verification of molecular markers
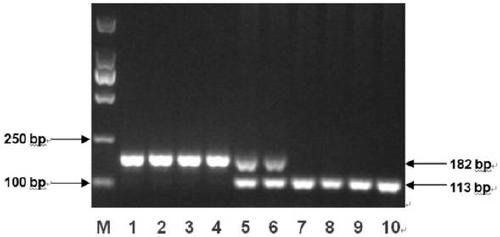
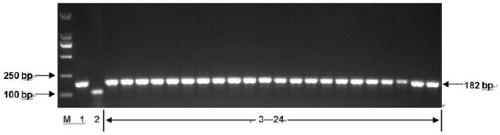
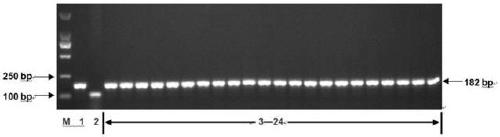
[0104] Using the above primers, the polymorphism and amplification stability of the InDel molecular marker were verified by PCR amplification and agarose gel electrophoresis detection. Specifically, using the genomic DNA of 10 cotton material seeds extracted in Example 1 as a template, the above-mentioned amplification primers were used to perform PCR amplification, wherein:
[0105] (1) PCR reaction system and conditions:
[0106] 20 μl reaction system: 1 μl of DNA template and 19 μl of PCR reaction solution (10 μl of Kangwei Century Company 2×Es TaqMasterMix (Dye), 0.8 μl of each 10 μM InDel primer pair, 7.4 μl of ddH2O), and mix well.
[0107] The amplification program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 2 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 56°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 15 sec, 30 cycles; storage at 4°C.
[0108] (2) Analysis of results:
[0109] After the PCR ampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com