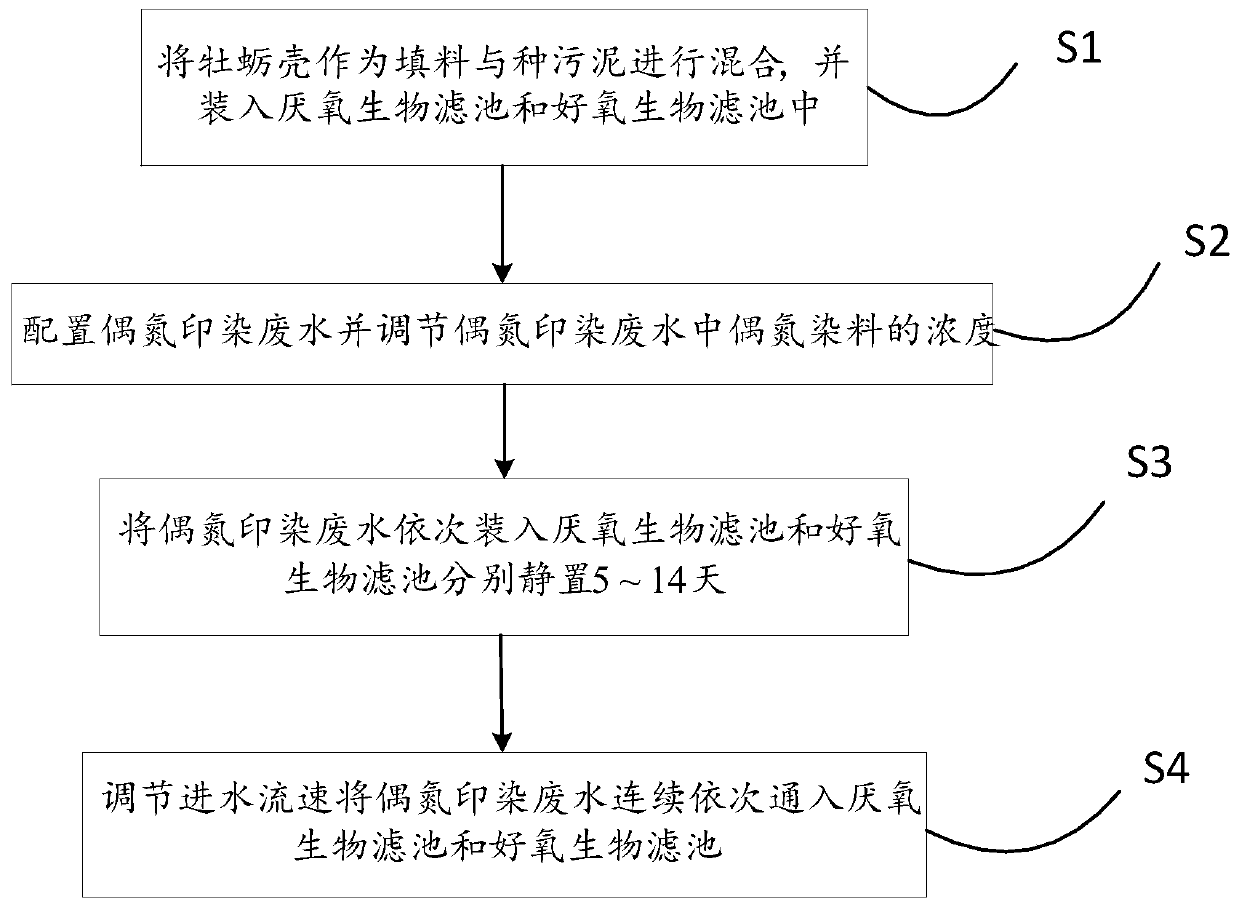
Method for treating azo printing and dyeing wastewater by using biological filters
A printing and dyeing wastewater, biological filter technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, textile industry wastewater treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, difficulty, complex treatment process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
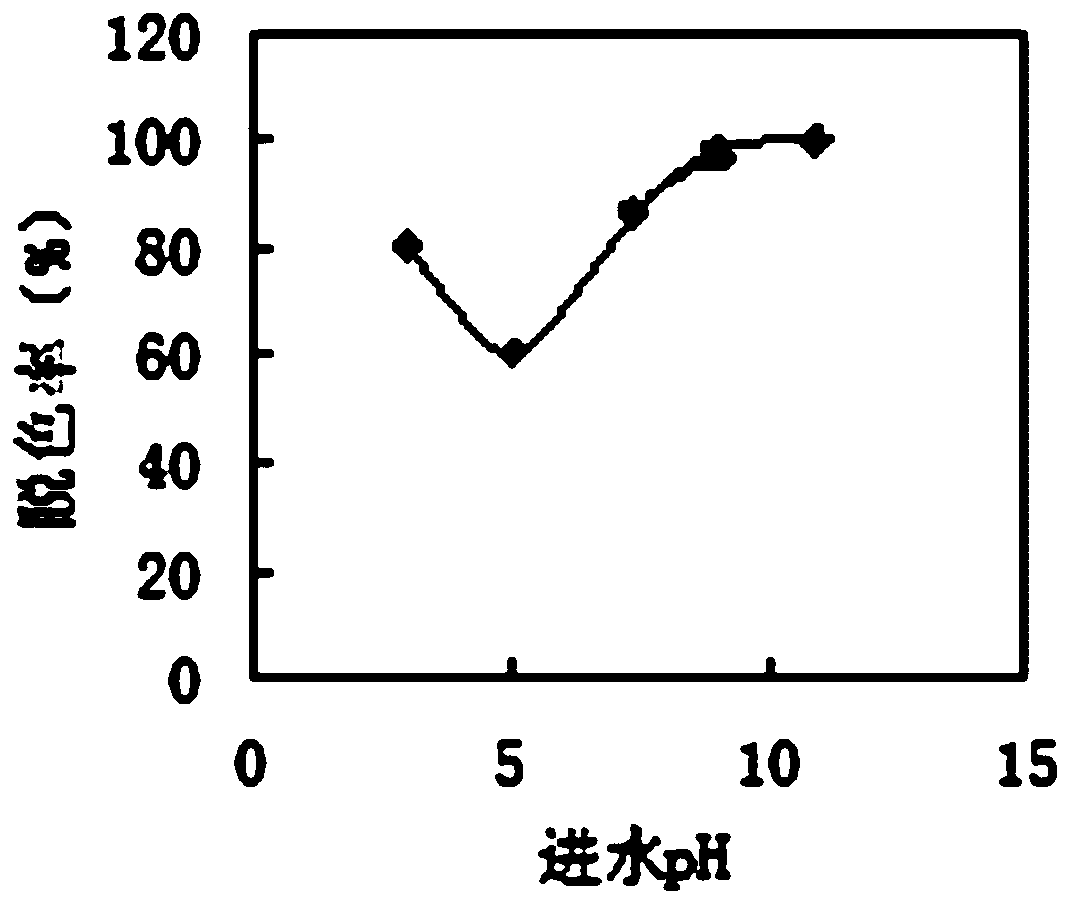
[0033] On the basis of the above experimental steps, the pH value of the azo printing and dyeing wastewater was adjusted in the range of 3 to 11.5. Such as figure 2 As shown, when the influent pH value of azo printing and dyeing wastewater changes in a large range within the range of 3.5-11.5, the decolorization rate of azo dyes in both anaerobic biofilter and aerobic biofilter can be maintained above 60%. The degradation of azo dyes by microorganisms was not greatly affected by the change of pH value. When the influent pH value of the azo printing and dyeing wastewater is in the range of 3.0 to 11.5, the decolorization rate of the effluent after passing through the anaerobic biological filter and the aerobic biological filter is 60.6% to 100.1%. When the pH value is between 3.5 and 5, the decolorization rate decreases gradually with the increase of the pH value; when the pH value is greater than 5, the decolorization rate gradually increases with the increase of the pH valu...
Embodiment 2
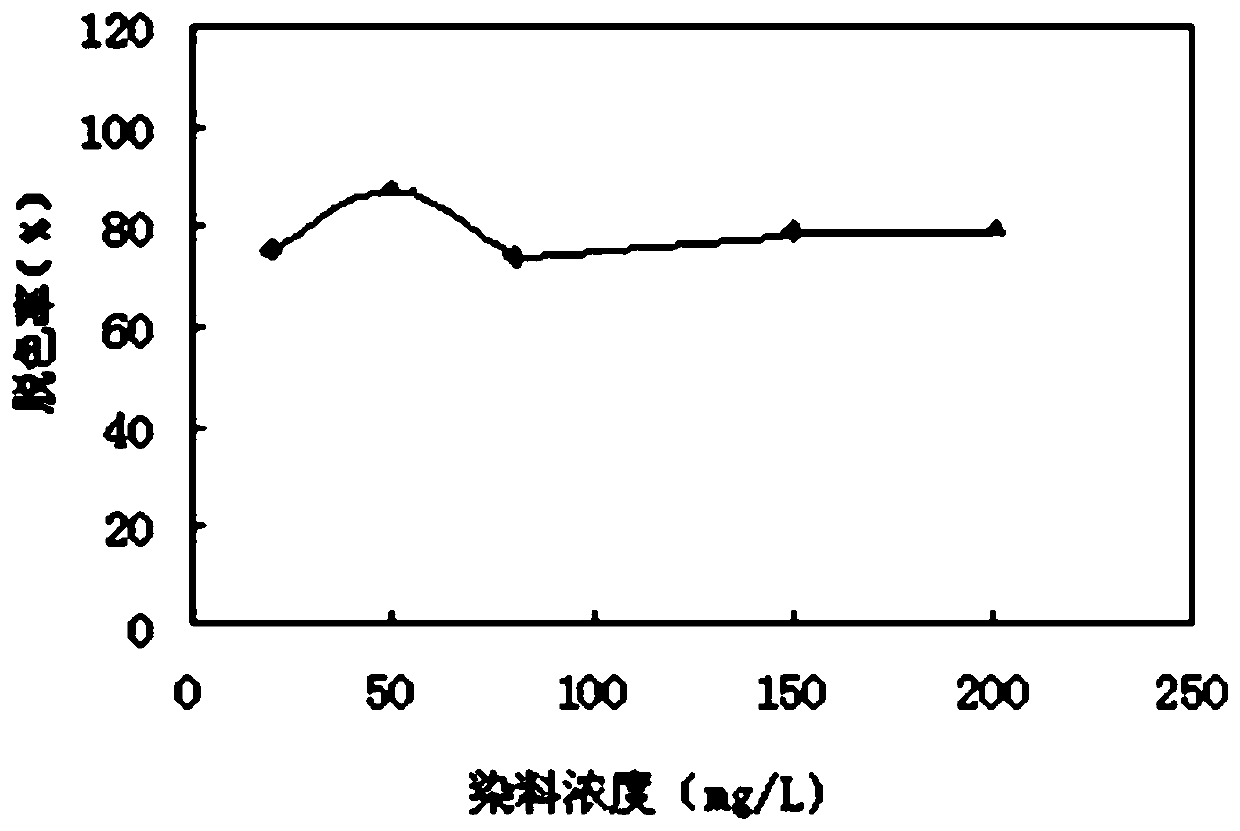
[0036]On the basis of the above experimental steps, the concentration range of the azo dye was adjusted to 20-200 mg / L. A high concentration of azo dye wastewater will block sunlight from penetrating the water body and affect the gas solubility in the water body, thereby affecting the growth of animals and plants in the water body and the self-purification process of the water body. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the influence of the concentration of azo dyes in azo printing and dyeing wastewater on the decolorization rate. By gradually increasing the concentration of azo dyes in the influent, the azo dye load and impact resistance of anaerobic / aerobic biofilters were investigated respectively. The experimental results are as follows: image 3 As shown, when the concentration of azo dyes increased from 20mg / L to 50mg / L, the decolorization rate gradually increased. The decolorization rate of the oxygen biofilter dropped from 86.9% to 74.1%, and when the concentration of...
Embodiment 3
[0038] On the basis of the above experimental steps, the types of azo dyes included RB670, fluorescent yellow and EverzolBlack B were adjusted. Figure 4 The decolorization effect of the biofilter on these several azo dyes is listed, and the decolorization rate of the anaerobic biofilter on various azo dyes is 84.3-93.7%. Therefore, the anaerobic biofilter and aerobic biofilter with oyster shells as fillers have good decolorization and degradation capabilities for various azo dyes.
[0039] Such as Figure 5 Shown, the biofilter device of the present invention comprises anaerobic biofilter 1 and aerobic biofilter 2, and aerobic biofilter 2 is provided with air distribution pipe 21 and air outlet 22, makes air distribution pipe 21 and air outlet 22 Air passes into the aerobic biological filter 2, which is beneficial to the reproduction and growth of aerobic microorganisms. Both anaerobic biofilter 1 and aerobic biofilter 2 include pool body 3, oyster shell packing 4, supporti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com