Nucleic acid sequence sequencing linker and method of using same to construct sequencing library
A technology for sequencing adapters and nucleic acid sequences, which is applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of limiting ctDNA sensitivity and specificity, large background noise interference, and low mutation frequency, and achieve the effects of improving positive prediction ability, cost saving, and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Nucleic acid sequence sequencing linker of the present invention
[0035] 1. The nucleic acid sequence sequencing adapter of the present invention
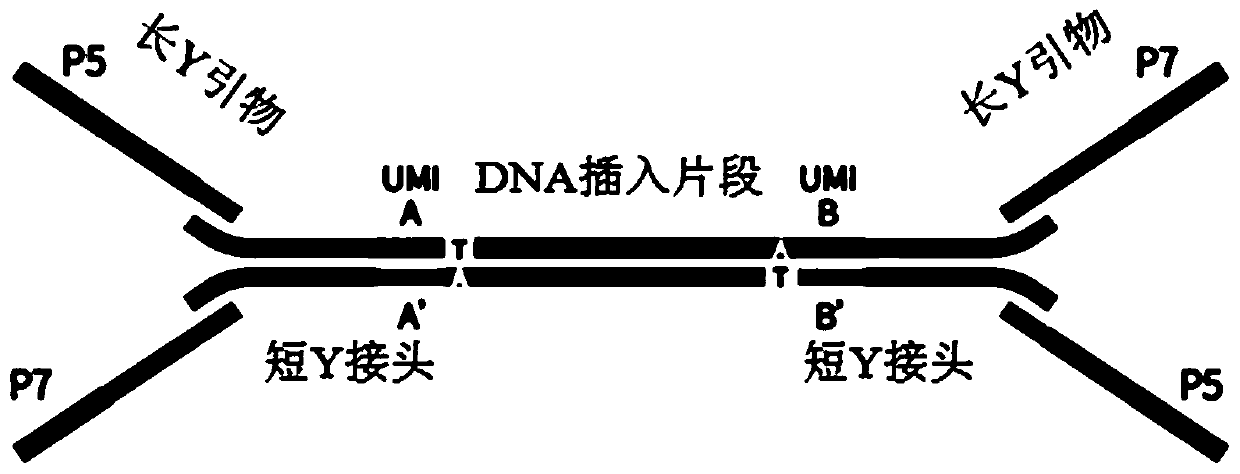
[0036] like figure 1 As shown, a short Y linker is connected to one end of the sequenced insert. The short Y linker includes an upstream primer F and a downstream primer R. The upstream primer F and the downstream primer R have partially complementary sequences, and they respectively contain complementary tag sequences UMI and UMI' , the tag sequence UMI and the tag sequence UMI' are located in the complementary region formed by the upstream primer F and the downstream primer R; a short Y linker is also connected to the other end of the sequenced insert, except that the upper and lower sequences of the upstream primer F and the downstream primer R are reversed. The tag sequence UMI is composed of any arrangement of A, G, C, and T, and the number of bases in the tag sequence UMI is preferably 4-6.
[0037] In one...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2 Construction and capture of libraries containing nucleic acid sequence sequencing adapters of the present invention
[0066] (1), library construction
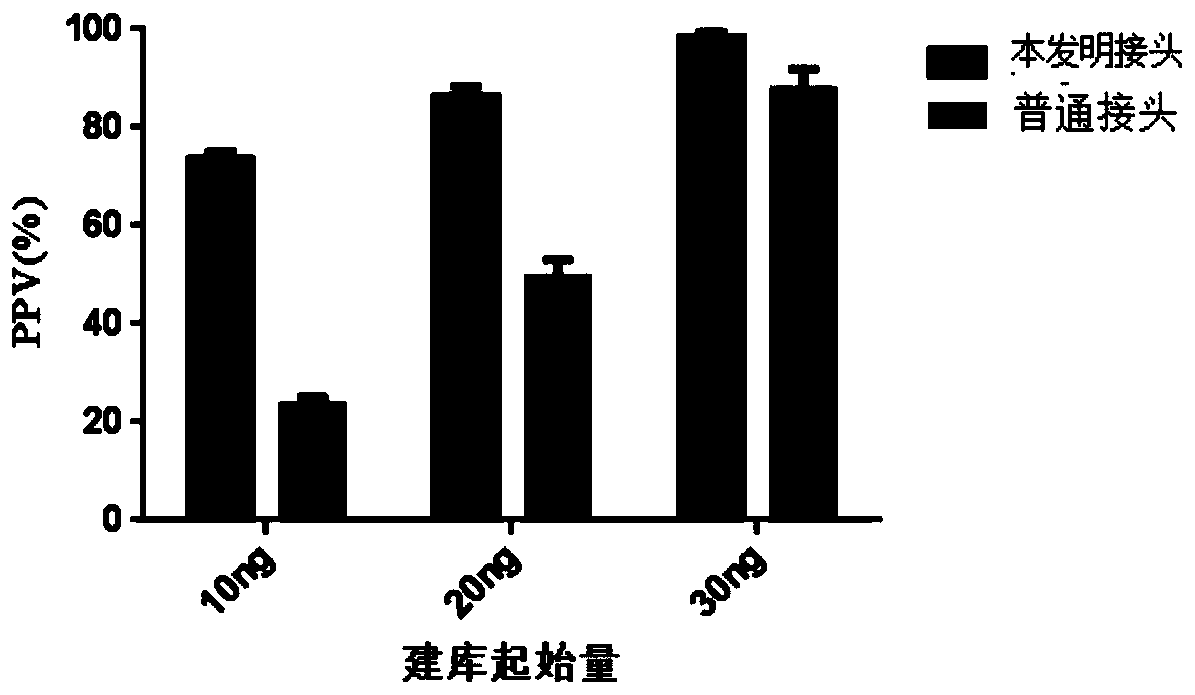
[0067] The ctDNA standard product was purchased from Horizon Discovery Company, the name is Multiplex I cfDNAReference Standard Set, and the article number is HD780. The mutation sites of the ctDNA standard product include 8 mutation sites of EGFR, KRAS, NRAS, and PI3KCA genes. The standard used in this experiment The mutation frequency of the product was 0.5%.
[0068] Divide the experiment into different groups according to different initial amounts of library construction, and take 10ng, 20ng or 30ng of standard ctDNA for sample library construction, including ctDNA end repair, end-added A and short Y adapter mixture ligation reaction, magnetic beads Purification, PCR amplification using long Y primers and other processes.
[0069] 1. Use the enzyme reaction to perform end repair and A addition on the ext...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Example 3. Sequencing result analysis and method verification
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com