Near-infrared spectroscopy noise reduction method for pesticide residue detection
A technology of pesticide residue detection and near-infrared spectroscopy, which is applied to measuring devices, material analysis through optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult source pollution noise, unsatisfactory unstable noise, etc., achieve good real-time performance and improve reliability Extraction, the effect of improving the signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0049] In this embodiment, a near-infrared spectrum noise reduction method for pesticide residue detection is provided, comprising the following steps:
[0050] Step 1. Data collection
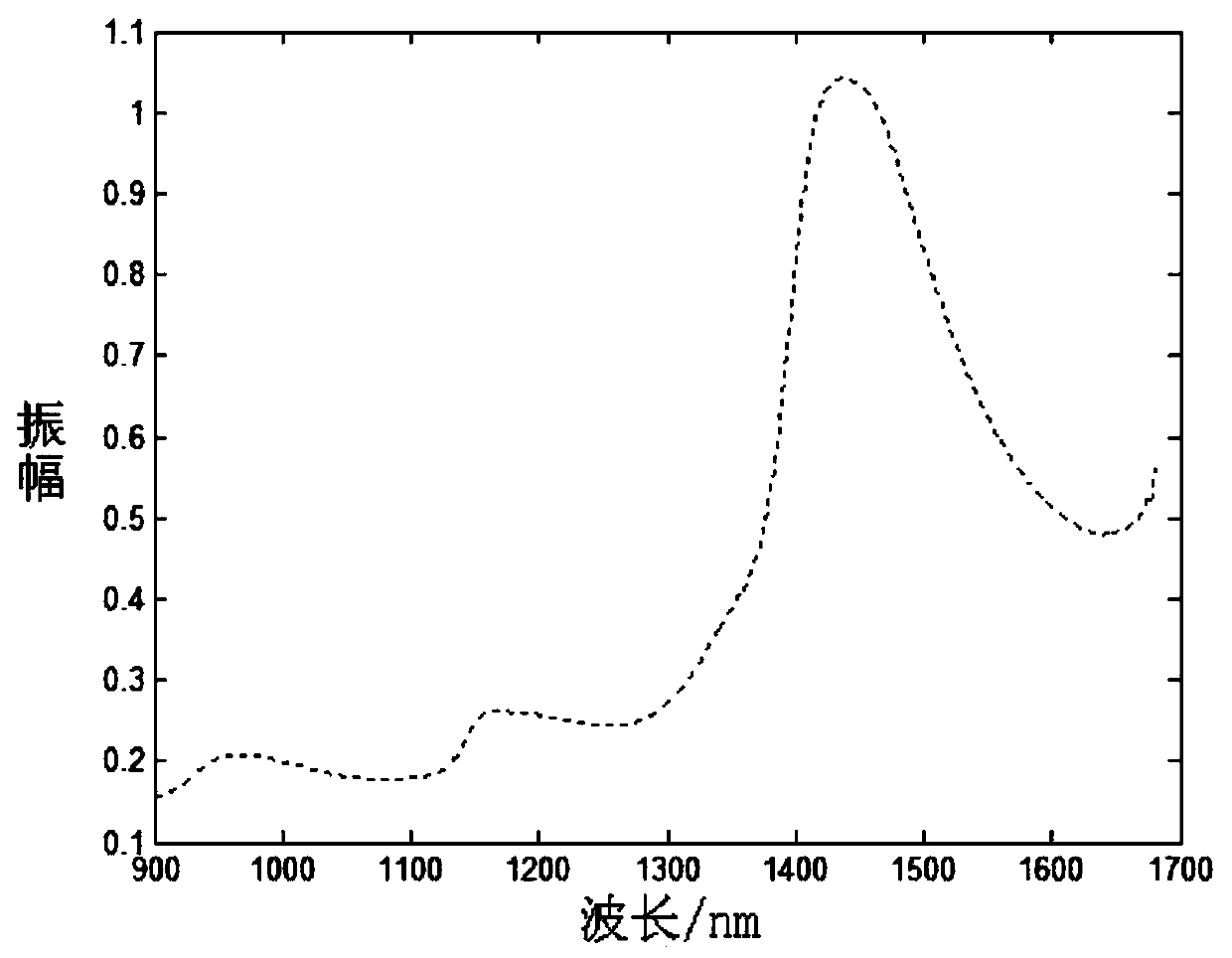
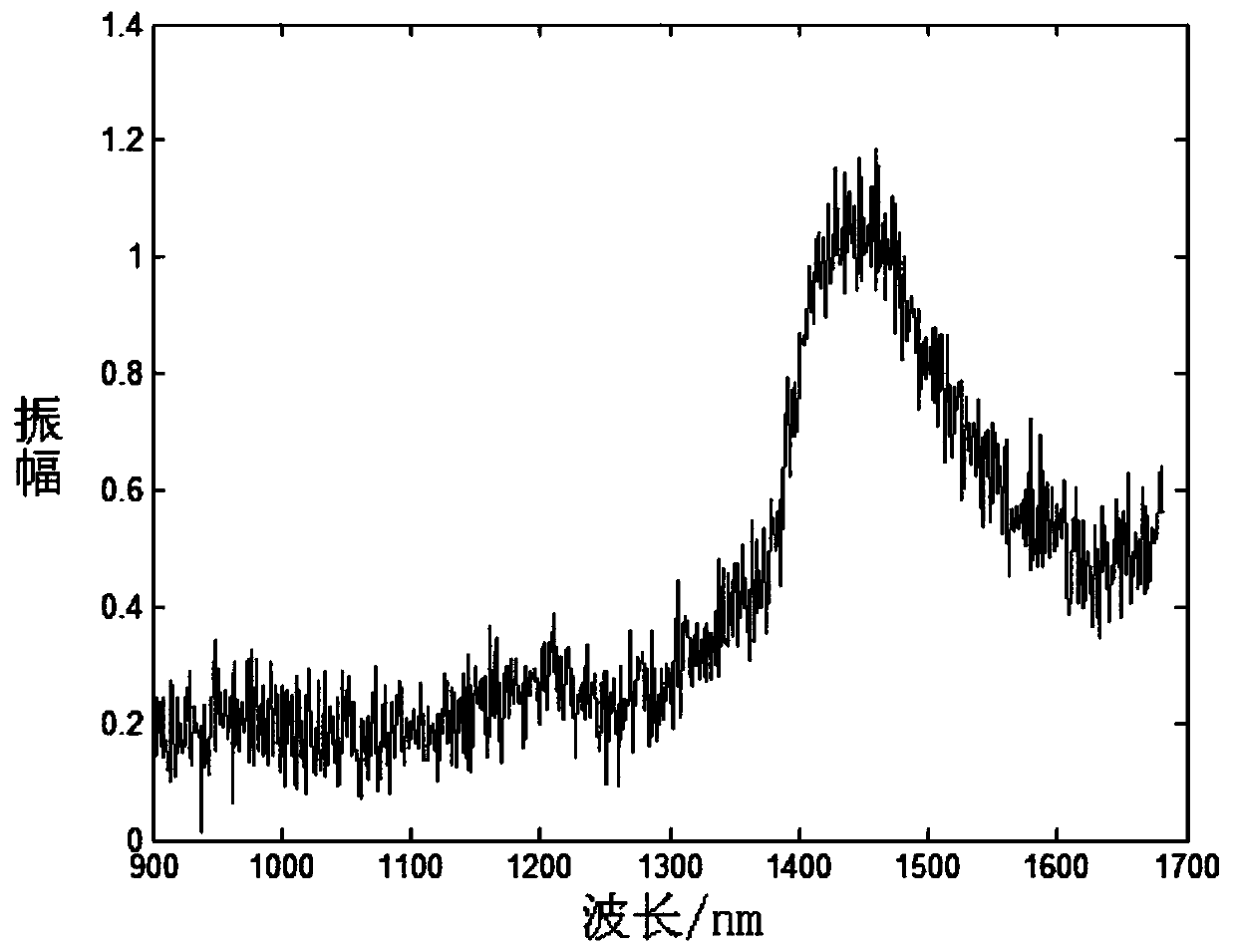
[0051] Utilize the near-infrared spectrometer to collect the near-infrared spectrum on the surface of the object to be tested (preferably fruits and vegetables in this embodiment), and the near-infrared spectrum collected now contains noise, and the collected near-infrared spectrum signal with noise is expressed as:
[0052] x(λ)=s(λ)+z(λ) formula (1)
[0053] In formula (1), x(λ) is the near-infrared spectral signal contaminated with noise at the wavelength λ, s(λ) is the near-infrared spectral signal not contaminated with noise at the wavelength λ, and z(λ) is the near-infrared spectral signal at the wavelength λ Random noise signal at;
[0054] Step 2. Signal decomposition
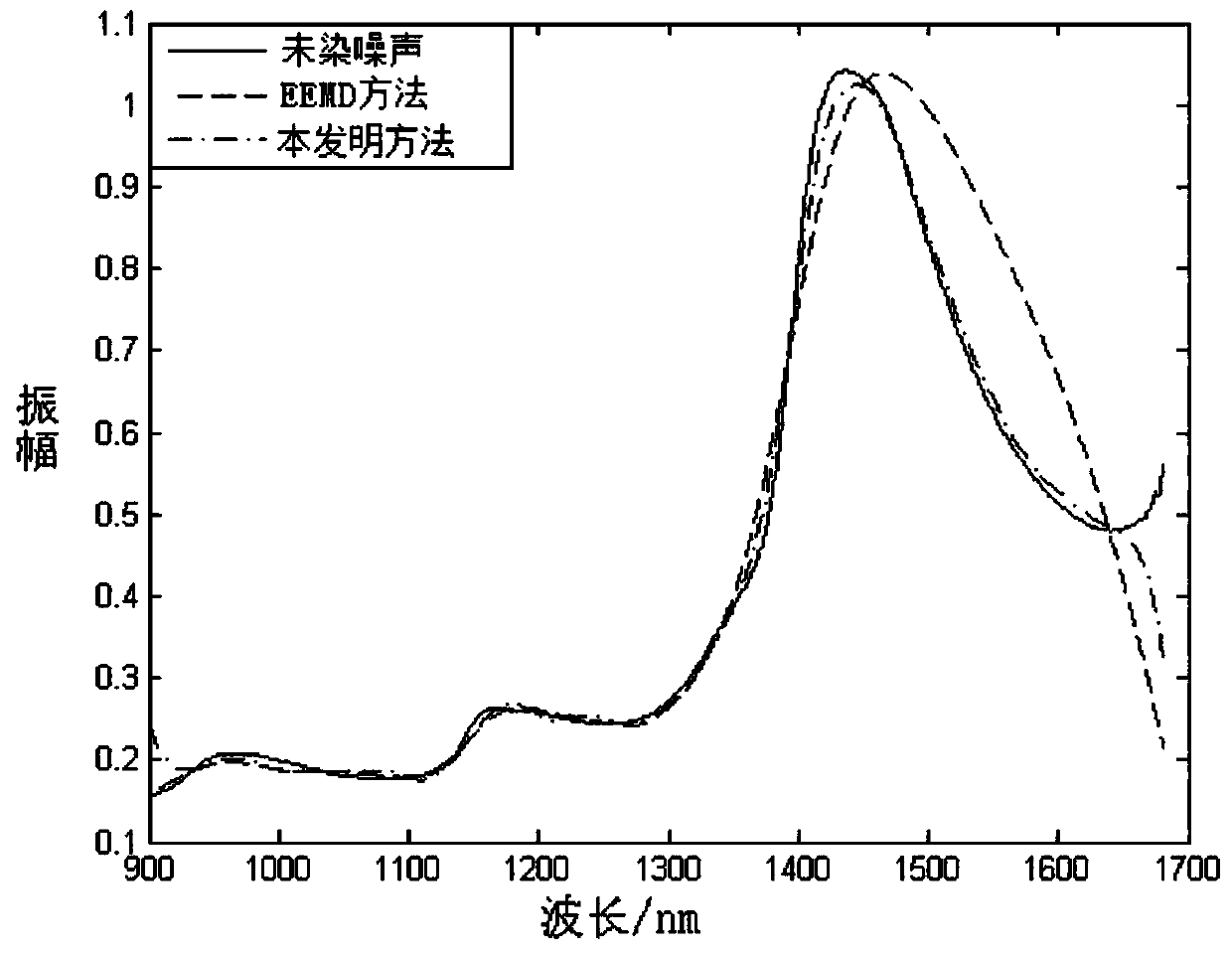
[0055] Using the EEMD method to decompose the near-infrared spectrum signal in step 1, several IMF components and a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com