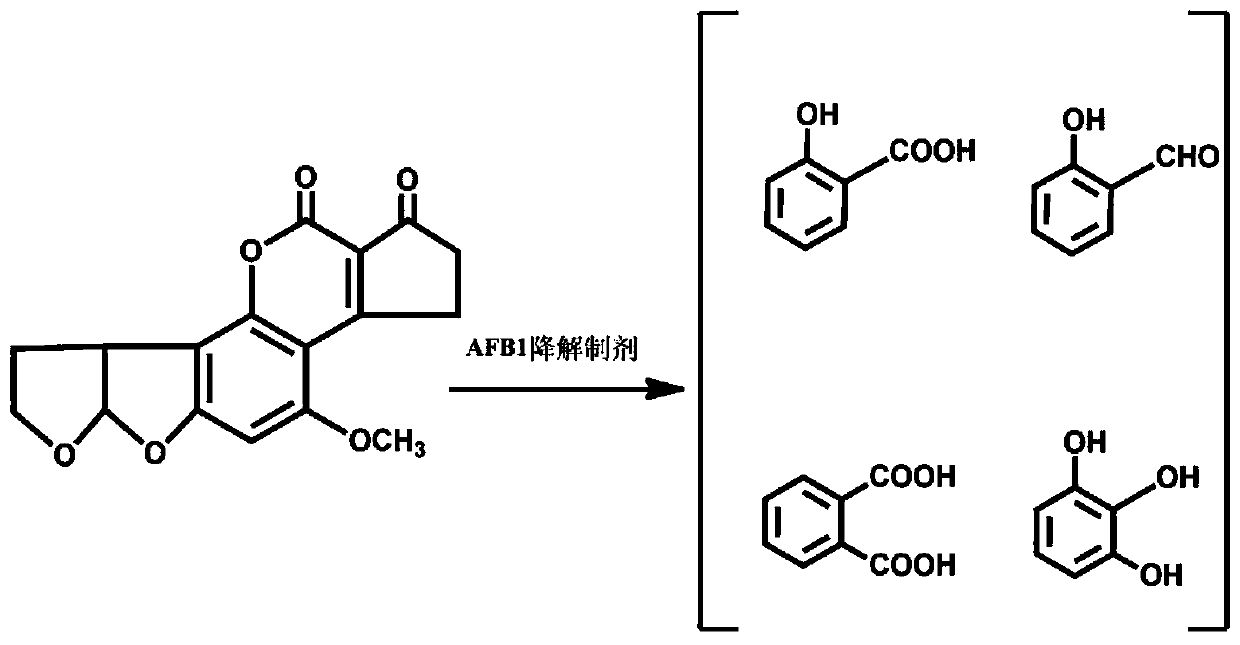
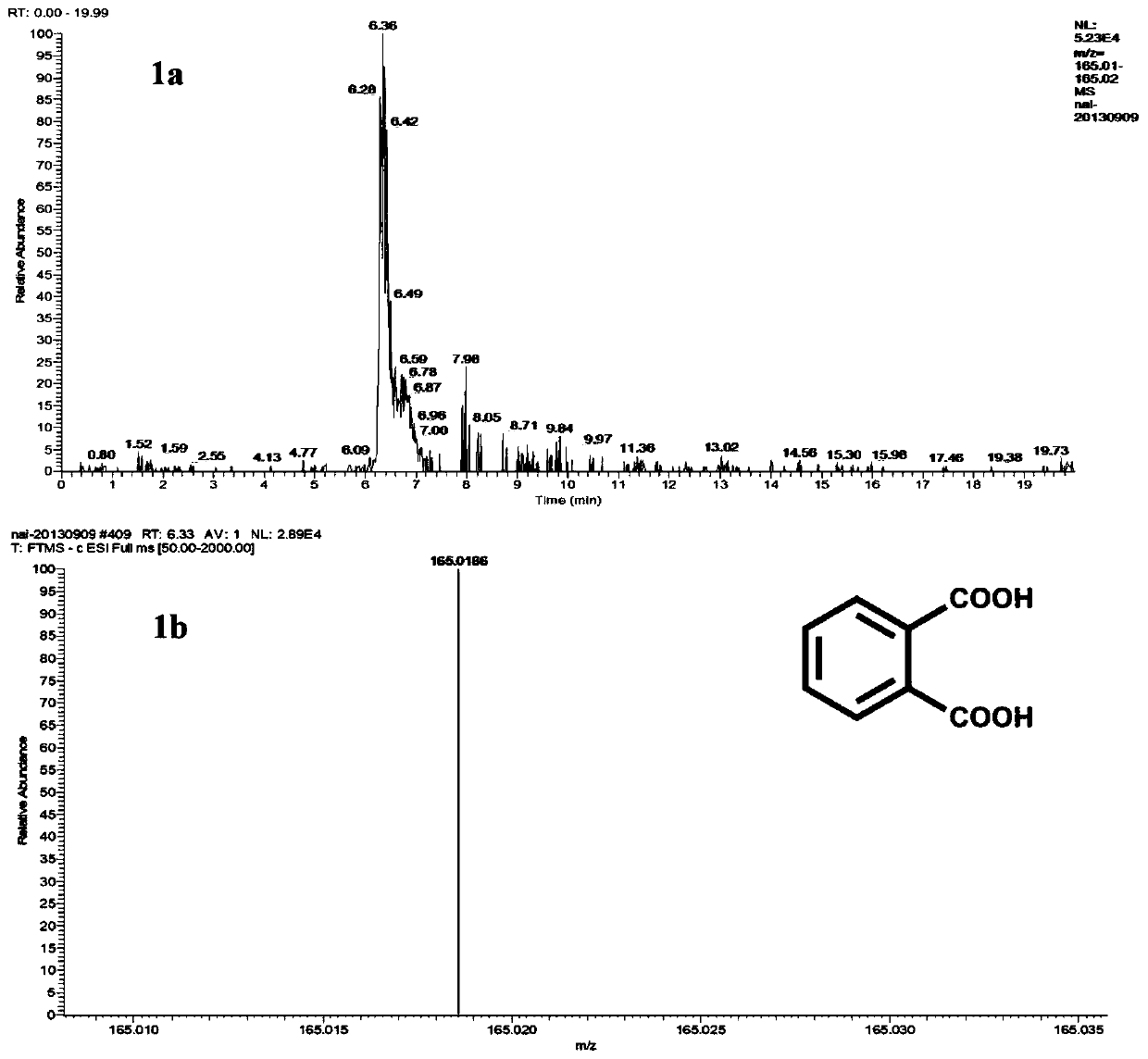
Method for preparing aflatoxin B1 degradation preparation by mixed fermentation
A kind of aflatoxin and mixed bacteria fermentation technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of limited production capacity, high cost, easy damage to grain and oil, etc., and achieve the effects of mild action conditions, efficient detoxification, and high safety factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The seeds of Aspergillus oryzae (strain from Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center, strain number CGMCC3.800) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain from Guangdong Provincial Microbial Culture Collection Center, strain number ATCC204508) seeds preserved at low temperature were inoculated in The PDA medium was cultured in a biochemical incubator at 30°C for 72 hours to complete seed rejuvenation. The rejuvenated seeds were transferred to the seed medium, kept on a constant temperature shaker at a temperature of 25° C., and rotated at 200 rpm, and cultivated for 48 hours to complete seed activation. The seed liquid is inoculated on the fermentation medium, and the volume ratio of the seed liquid is Aspergillus oryzae: Saccharomyces cerevisiae=5:1. The total inoculum amount is 5%, aerobic fermentation, ventilation and stirring are maintained, the fermentation temperature is 30°C, and the fermentation period is 96h.
[0027] Extracellular enzymes and activities after...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Seeds of Aspergillus oryzae CGMCC3.800 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC204508 preserved at low temperature were inoculated in PDA medium respectively, and cultured in a biochemical incubator at 30°C for 60 hours to complete seed rejuvenation. The rejuvenated seeds were transferred to the seed medium, kept on a constant temperature shaker at a temperature of 30° C., and rotated at 200 rpm, and cultivated for 48 hours to complete seed activation. Inoculate the seed liquid into the fermentation medium, and the volume ratio of the seed liquid to Aspergillus oryzae: Saccharomyces cerevisiae=15:1. The total inoculum amount is 10%, aerobic fermentation, keep ventilation and stirring, the fermentation temperature is 30°C, and the fermentation period is 84h.
[0032]Extracellular enzymes and activities after fermentation: pectinase activity 6000u / ml, xylanase activity 3000u / ml, glucose oxidase activity 80u / ml, cellulase activity 900u / ml, polyphenol oxidase activity 3000u / ml ml...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Seeds of Aspergillus oryzae strain number CGMCC3.800 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC204508 preserved at low temperature were inoculated in PDA medium respectively, and cultured in a biochemical incubator at 30°C for 72 hours to complete seed rejuvenation. The rejuvenated seeds were transferred to the seed medium, kept on a constant temperature shaker at a temperature of 30° C., and rotated at 200 rpm, and cultivated for 48 hours to complete seed activation. Inoculate the seed liquid into the fermentation medium, and the volume ratio of the seed liquid to Aspergillus oryzae: Saccharomyces cerevisiae = 20:1. The total inoculum amount is 10%, aerobic fermentation, ventilation and stirring are maintained, the fermentation temperature is 30°C, and the fermentation period is 84h.
[0037] Extracellular enzymes and activities after fermentation: pectinase activity 8000u / ml, xylanase activity 5000u / ml, glucose oxidase activity 90u / ml, cellulase activity 1000u / ml, polyphenol o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com