Human body activity recognition system and method based on conditional variational auto-encoder
An autoencoder and human activity technology, applied in the field of human activity recognition, can solve the problems of difficulty in selecting the window size, hindering the accuracy of activity recognition, and inability to fully mine the similarity between classes, so as to improve the accuracy and generalization. effect of ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0048] The OPPORTUNITY data set of activity recognition in this embodiment is taken as an example, and the implementation manner is described in detail.
[0049] The OPPORTUNITY data set is a data set used to evaluate the effect of the activity recognition model, and it includes many activity recognition tasks of different semantic levels. This embodiment selects gesture recognition of intermediate semantics for specific description. Gesture recognition includes 17 kinds of real activities and 1 inactive state. The inactive state can indicate that the person does not take any gesture at this time. These 17 gestures are collected in the real scene of preparing breakfast, so these gestures involve the interaction process with some furniture in the kitchen. The 17 real poses are shown in Table 1:
[0050] Table 1 Summary of pose names
[0051]
[0052]
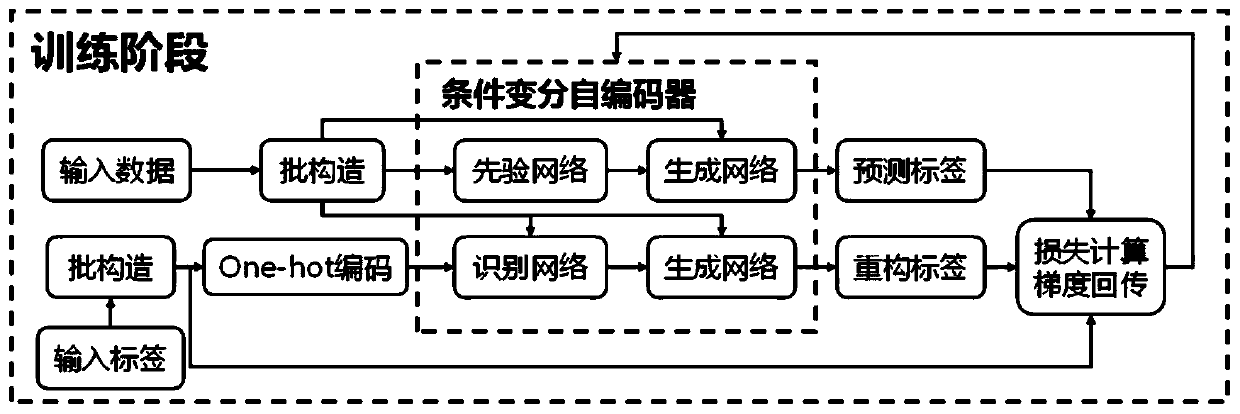
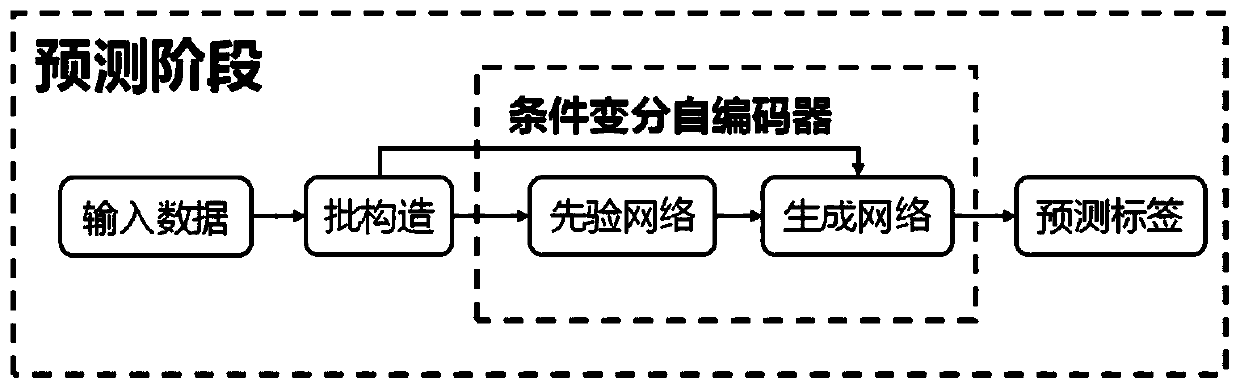
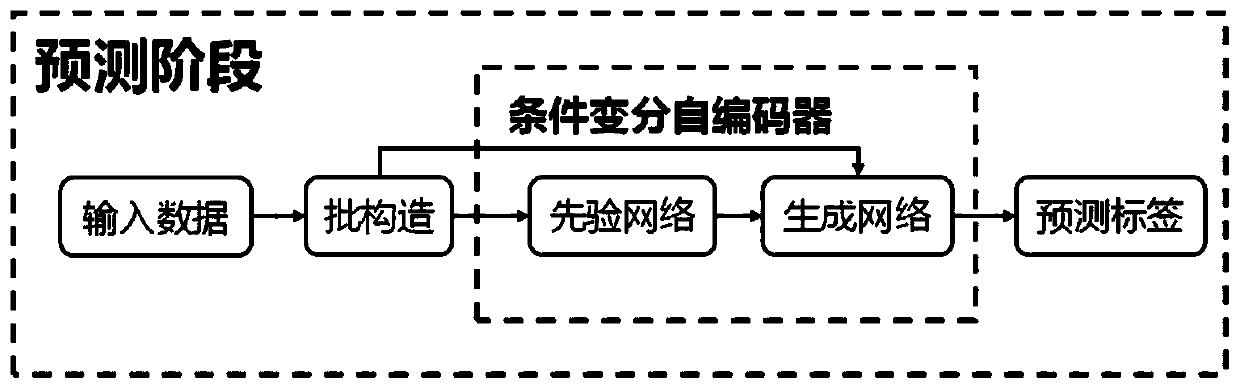
[0053] This embodiment provides a system for human body activity recognition based on conditional variational autoencod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com