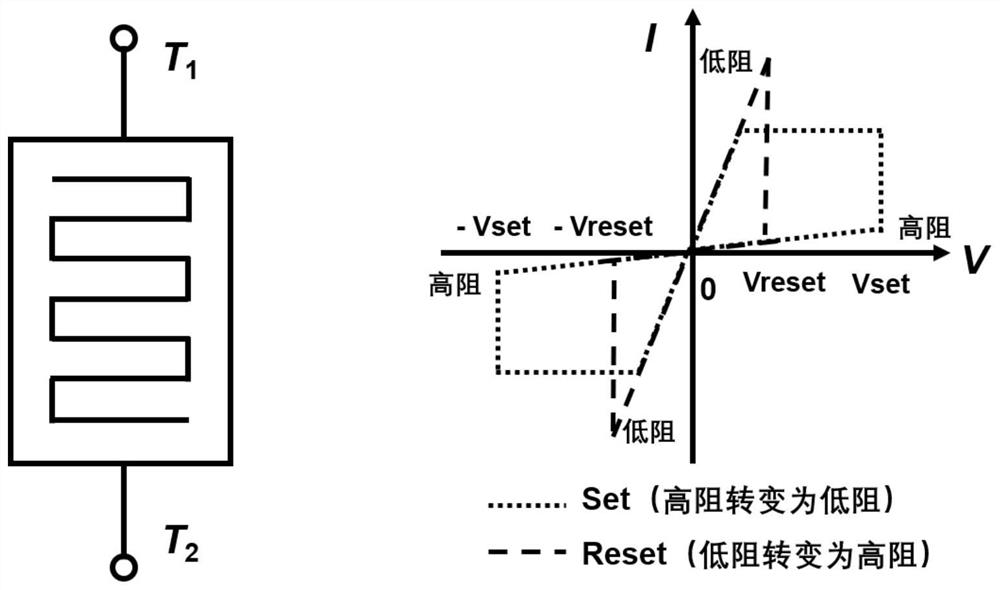
A complete non-volatile logic implementation method based on unipolar memristor and its application
An implementation method and unipolar technology, which can be used in instruments, static memory, digital memory information, etc., and can solve the problems of poor non-volatile logic completeness and single function.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
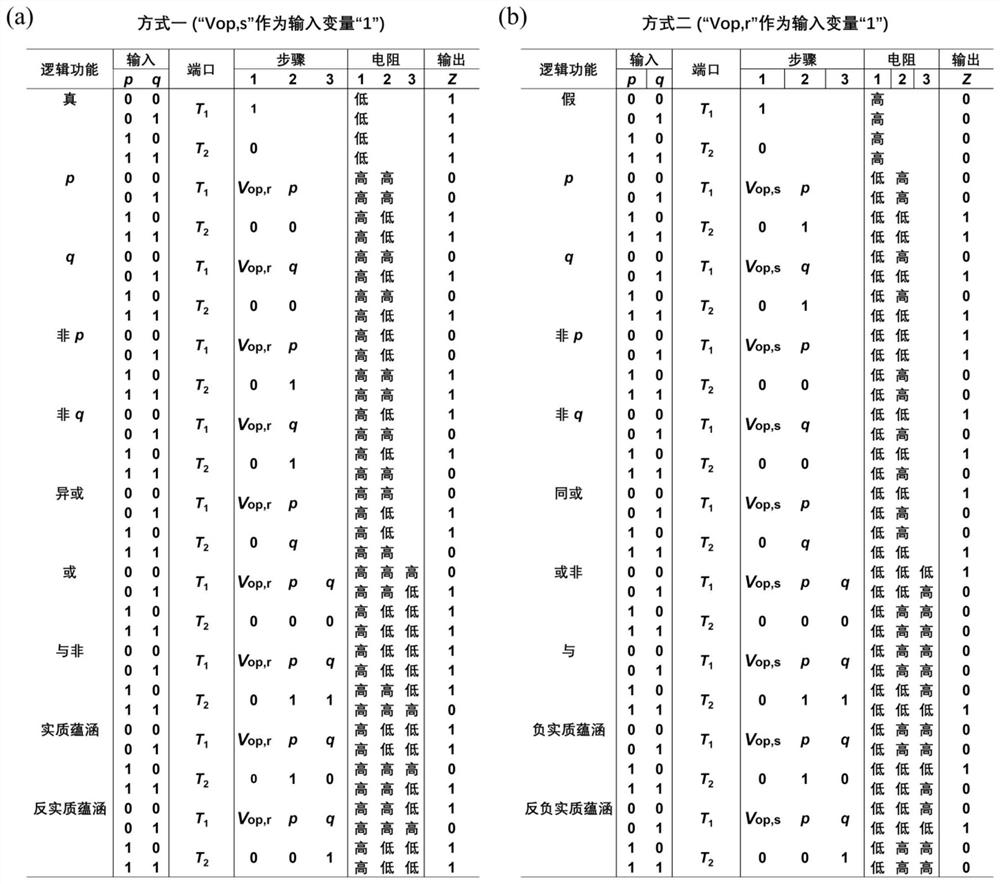
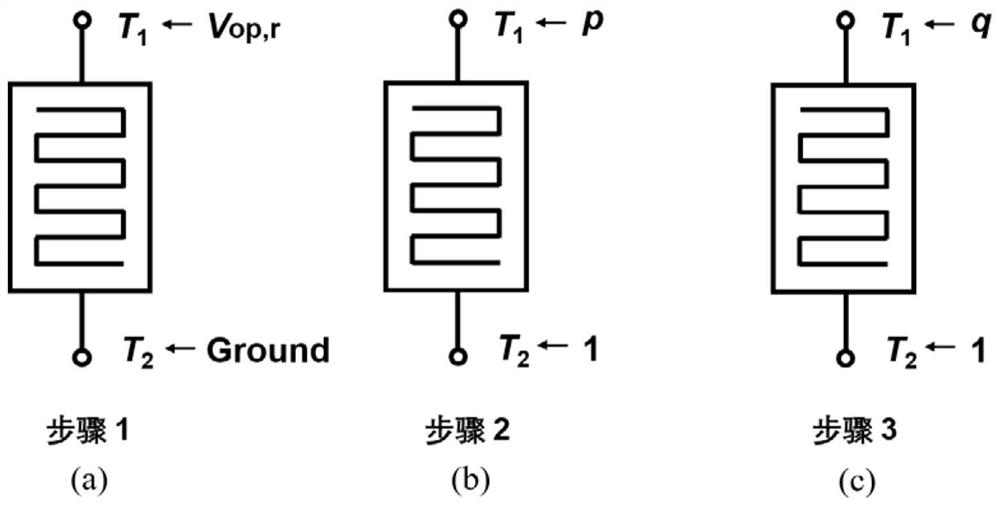
[0058] Taking the realization of NAND logic function as an example, the specific steps of realizing basic Boolean logic function based on unipolar memristor are described. A total of three steps are required to realize the NAND logic function, including one-step initialization and two-step logical operation, such as image 3 shown. Step 1: Initialize by applying the voltage "T 1 =V op,r ,T 2 = 0" to initialize the unipolar memristor to a high-impedance state, that is, "Z' = 0", and then start the logic operation step. op,s " as the input variable "1"; step 2: put "T 1 = p, T 2 =1" respectively applied to both ends of the device to realize not-p logic (NOTp); Step 3: put "T 1 =q,T 2 =1" are respectively applied to both ends of the device to realize NAND logic (p NAND q). Expressions (5)-(7) respectively provide the logical expressions corresponding to each step:
[0059] Z step1 =0 (5)
[0060] Z step2 =TRUE·Z step1 +(T 1 XOR T 2 ) NOT Z step1
[0061] =TRUE·0+(...
Embodiment 2
[0066]Here is an example to specifically illustrate how to use the unipolar memristive cross array to realize the calculation of the Hamming distance. When calculating the Hamming distance of two 16-bit binary numbers "1111001100101100" and "0010100110101001", it is necessary to perform an exclusive OR (XOR) operation on the two, that is, "1111001100101100 XOR 0010100110101001", and the result is the binary number "binary 1101101010000101", The number of "1"s (8) in the result is the Hamming distance between the two. Such as Figure 4 As shown in (a), a 16×16 unipolar memristor cross array is required to realize the above process, and only 16 unipolar memristors on any diagonal line in the array are used in the realization process, here Diagonal 1 is selected to illustrate the operation method. The 16 unipolar memristors on the diagonal are named U in sequence from bottom left to top right 16 , U 15 ,...U 3 , U 2 , U 1 ; where the unipolar memristor U i The upper and l...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Here is an example to specifically illustrate how to use the unipolar memristive cross array to realize symmetric encryption and decryption. Wherein, the key is generated according to the randomness of the high-resistance states of different cycle-to-cycle cycles of the unipolar memristor. Specifically, the high-resistance state resistance (R HRS,i ) and the high-impedance state resistance of the last cycle (R HRS,i-1 ) for comparison, where i≥1. If "R HRS,i -R HRS,i-1 ≥0", the i-th bit of the key is "1", otherwise the i-th bit is "0".
[0069] The ASCII code is one of the most widely used character sets. Here, the ASCII code "01010000" of the capital letter "P" is encrypted and decrypted, and the key used is "00000111". To complete the exclusive OR (XOR) operation of 8-bit binary numbers requires an 8×8 unipolar memristive cross-array. Since they all perform parallel XOR operations, the entire logical operation process is basically the same as calculating the Hamm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com