High-power pulse width tunable semiconductor laser module
A semiconductor, high-power technology, applied in the field of high-power pulse width tunable semiconductor laser modules, can solve the problems of narrow pulse width tunable range, low photoelectric conversion efficiency, high cost, etc., and achieve fast rising edge of optical pulse and easy processing system The effect of integrated, high power output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
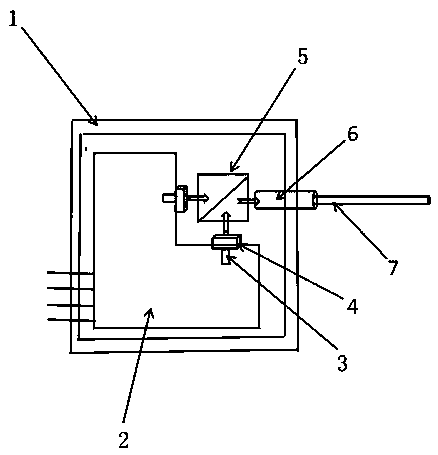
[0023] like figure 1 As shown, the laser module consists of an oxygen-free copper heat dissipation shell (1), a ceramic drive circuit substrate (2), a polarization beam combining prism (5), a self-focusing lens (6) and a coupling output optical fiber (7).
[0024] A 915nm (or 940nm / 976nm / 980nm) high-power semiconductor laser chip (3) is packaged on an aluminum nitride ceramic substrate (2) with a driving circuit.
[0025] Further, the ceramic driving circuit substrate (2) is welded to the base of the oxygen-free copper casing (1) through indium solder, silver glue or other solders.
[0026] Further, the fast-axis collimating mirror (4) is fixed on the front end of the ceramic substrate according to the working distance of the lens through ultraviolet glue, so as to collimate and compress the fast axis of the laser.
[0027] Further, the two beams of light enter the self-focusing lens (6) through the polarization beam combining prism (5), and are coupled into the optical fiber...
Embodiment 2
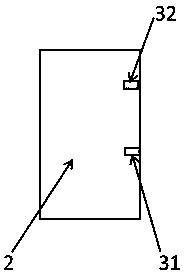
[0029] like figure 2 As shown, the laser module consists of an oxygen-free copper heat dissipation shell (1), a ceramic drive circuit substrate (2), a polarization beam combining prism (5), a self-focusing lens (6), a coupling output fiber (7), and a mirror (8) composition.
[0030] A 915nm (or 940nm / 976nm / 980nm) high-power semiconductor laser chip (3) is packaged on an aluminum nitride ceramic substrate (2) with a driving circuit.
[0031] Further, the ceramic driving circuit substrate (2) is welded to the base of the oxygen-free copper casing (1) through indium solder, silver glue or other solders.
[0032] Further, the fast-axis collimating mirror (4) is fixed on the front end of the ceramic substrate according to the working distance of the lens through ultraviolet glue, so as to collimate and compress the fast axis of the laser.
[0033] Further, after the light emitted by the laser chip 31 is reflected by the mirror (8), it enters the self-focus lens (6) with the ligh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com