Bovine tuberculosis diagnosis marker and application thereof
A diagnostic marker and technology for tuberculosis, applied in disease diagnosis, biological testing, biomaterial analysis, etc., can solve difficulties in popularization and application, high requirements for testing environment, technology and personnel, and inability to distinguish between bacteria-expelling period and non-bacteria-excreting period Tuberculosis cattle and other problems, to achieve the effect of prevention and control, improve the efficiency of diagnosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Detection and collection of clinical samples involved in the present invention in embodiment 1
[0035] 1. Tuberculin skin test:
[0036] The tuberculin skin test was performed according to the "Diagnostic Criteria for Bovine Tuberculosis" (GB / T 18645-2002). Shave the upper 1 / 3 of the cow's neck, and inject 0.1 mL of purified tuberculin bovis (PPD-B, 250 IU / head) intradermally. The skin thickness at the injection site was measured by the same operator with a vernier caliper before and 72 hours after the injection, and the difference in skin thickness was calculated. When the difference in skin thickness is greater than or equal to 4mm, the cow is positive for tuberculosis; when the difference in skin thickness is less than 2mm, it is judged as negative for tuberculosis; The skin test was performed 60 days after the first test. If the difference in skin thickness in the second test was greater than or equal to 2mm, it was determined to be positive for tuberculosis.
...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 Screening of Molecular Markers
[0055] 1, sample pretreatment: the tuberculosis bovine PCR positive (bTB) determined in embodiment 1 of random screening PCR-P ), tuberculosis bovine PCR negative (bTB PCR-N ) and 20 tuberculosis-negative cattle (NC) each. in bTB PCR-P As an example, every 10 plasma samples were mixed in equal volumes to form 2 biologically replicated plasma pooled samples (bTB PCR-P P1 is a mixture of plasma samples from cows 1-10, bTB PCR-P P2 is a mixture of plasma samples from cows No. 11-20). According to this method, prepare bTB PCR-N (bTB PCR-N P1 and bTB PCR-N P2) and pooled plasma samples of the NC groups (NC P1 and NC P2).
[0056] 2. Removal of high-abundance proteins: Since IgG and BSA in plasma account for more than 85% of the total proteins in the sample, which will affect the detection of low-abundance proteins, high-abundance protein removal kits (purchased from Bio-Rad) were used to remove Highly abundant protein in...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Verification of molecular markers in the present invention
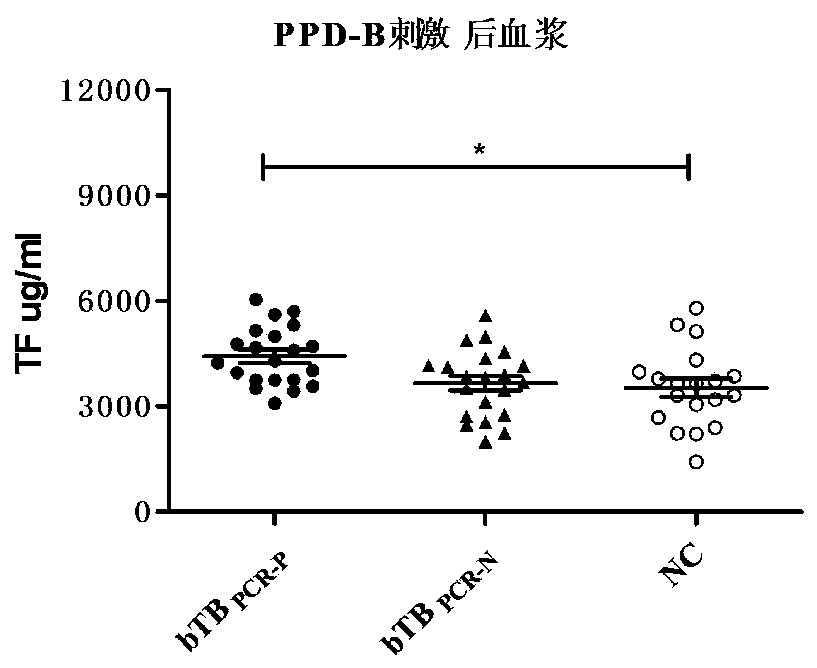
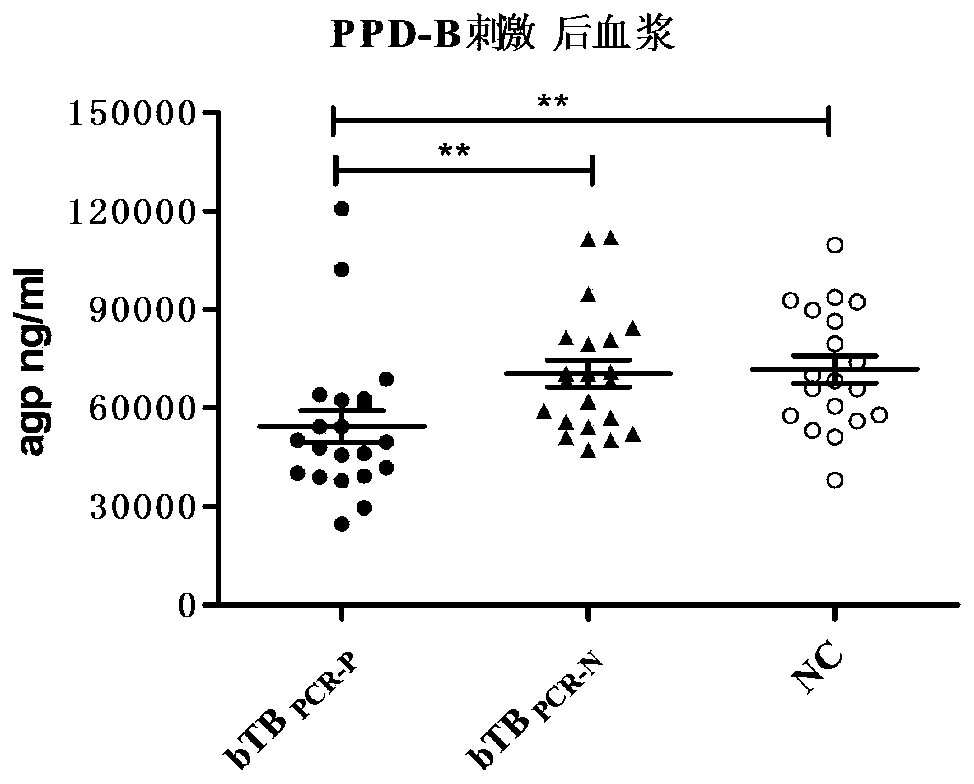
[0063] 1. PRM identification of differential proteins: refer to the method of Example 2 to process the sample, adopt the targeted analysis strategy of mass spectrometry PRM, and after passing the DDA detection, add the peptide of the identified target protein to the inclusion list of the mass spectrometry acquisition method, so that the mass spectrometry Data collection was carried out for these specific peptides, and relative quantitative analysis was carried out by extracting fragment ion information (see Table 4 for results). According to the identification results of iTRAQ and PRM (see Table 3), IL-8, agp and TF in tuberculosis bovine plasma The content of CRP is more than 1.3 times that of healthy bovine plasma, and the content of CRP in tuberculosis bovine plasma in the excretion period is more than two times that in non-excretion period tuberculosis bovine plasma, and the results of iTRAQ and P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com