A kind of low temperature starting method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell
A proton exchange membrane and fuel cell technology, applied in the direction of fuel cells, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems affecting the overall performance of fuel cells, and achieve the same temperature rise rate, simple method operation, and smooth start-up process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
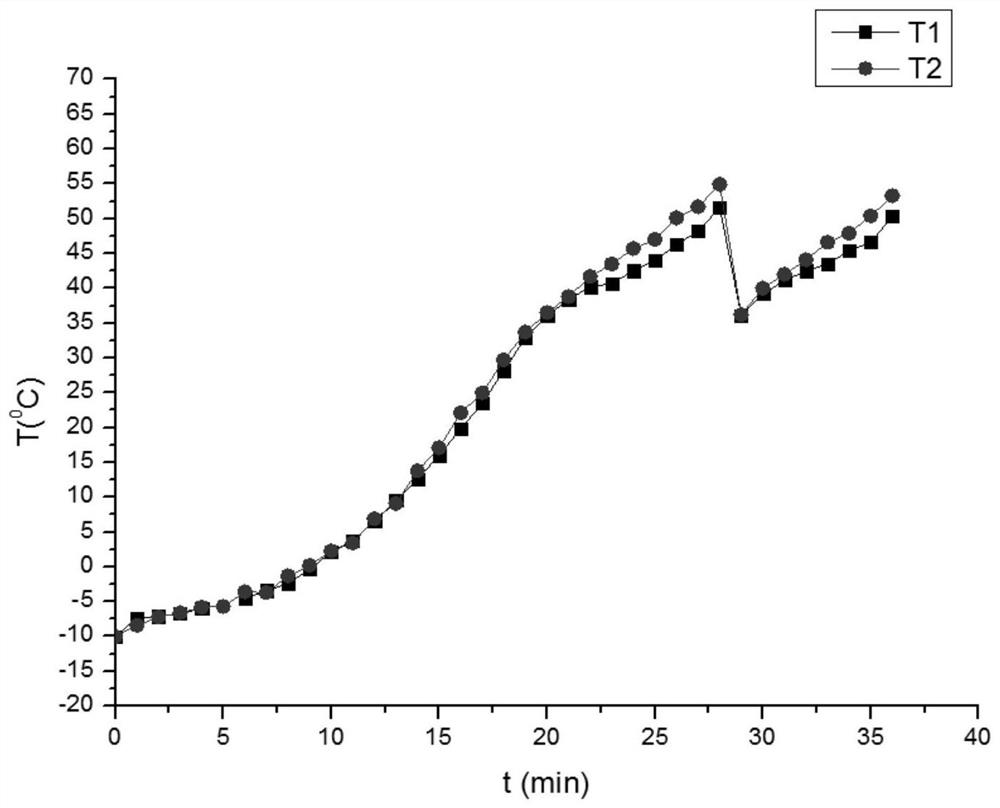
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, low temperature startup at -10°C:
[0031] In a low temperature environment, first turn off the battery according to the conventional method; after the battery is turned off, before the temperature of the battery drops to freezing point, switch the air intake to the dry nitrogen channel, adjust the pressure balance on both sides of the cathode and anode, and maintain it at 0.1MPa. Remove any remaining moisture from these parts. When the battery temperature reaches -10°C, the load is used to balance the load on the fuel cell.
Embodiment 2
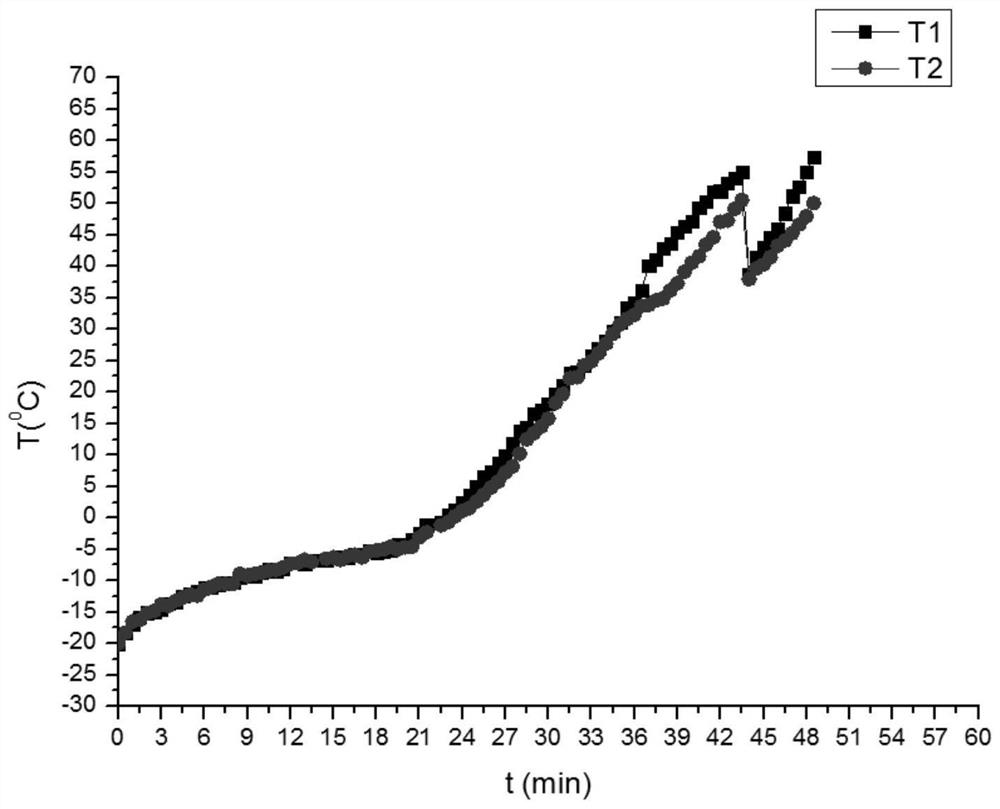
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, low temperature startup at -20°C:
[0034] The measured specific heat capacity of the 5-cell fuel cell stack is 2014J.kg -1 K -1 ;
[0035] Comparing with the fuel cell heating power (1000W), when the battery needs to heat up, when the air metering ratio is 0.1Acm -2 2.5 times lower, Q=(mCp N2 +mCp O2 )(T-T env ) = m out Cp(T-T env ), the total power required to raise the temperature from -20°C to 0°C is 688W, which is less than the heating power of the battery, which is 1000W. Note that in theory self-starting can be performed. In a low temperature environment, first turn off the battery according to the conventional method; after the battery is turned off, before the battery temperature drops to freezing point, switch to the dry nitrogen channel in the near future, adjust the pressure balance on both sides of the cathode and anode, and maintain it at 0.1MPa to eliminate residual moisture in these parts. When the battery temperatu...
Embodiment 3
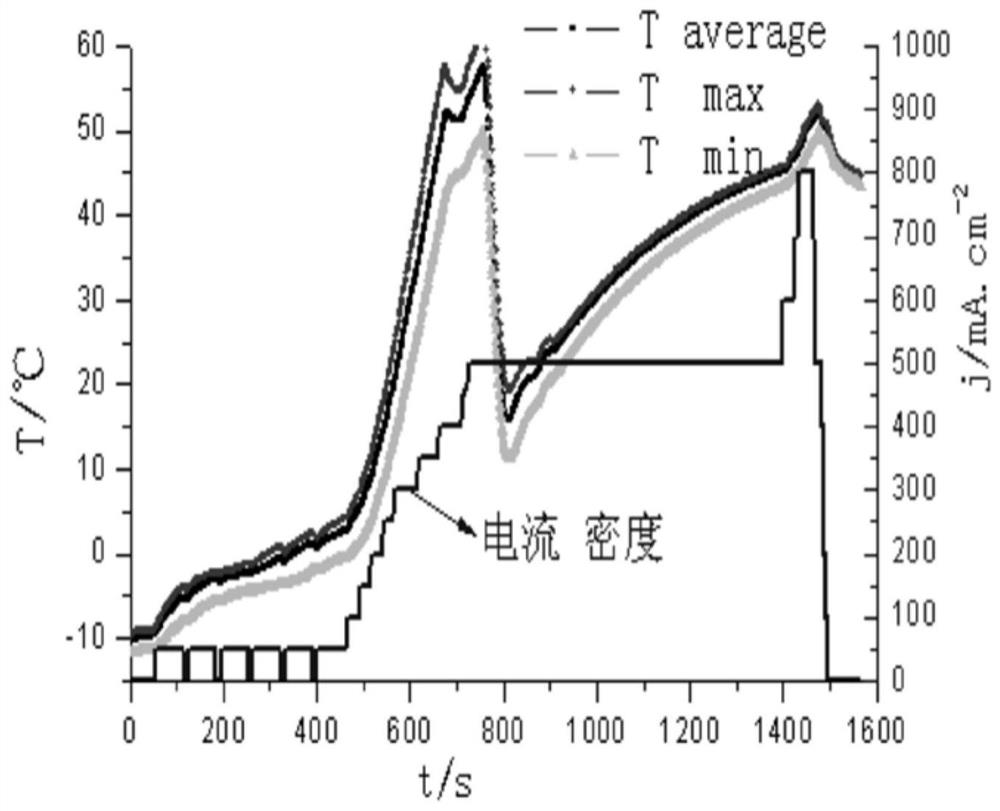
[0037] Such as image 3 .Start-up plan: experimental condition parameter setting, air metering ratio: 3, hydrogen metering ratio: 2, loading method: one cycle (loading for 50s, stopping for 10s), load evenly until the internal temperature of the stack rises above 0°C; The density is slowly loaded to the rated current density. When the internal temperature of the stack rises above 55°C, turn on the circulating refrigerant switch. The temperature inside the stack will drop with the addition of refrigerant, and then rise again. When the internal temperature of the stack rises to 55 ℃, it is considered that the stack is fully started successfully.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com