Method for trapping and parasitic enemy integrated control over pine shoot insects
A technology for pests and traps, which can be applied to devices for capturing or killing insects, botanical equipment and methods, and applications. , the effect of increasing the number and duration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
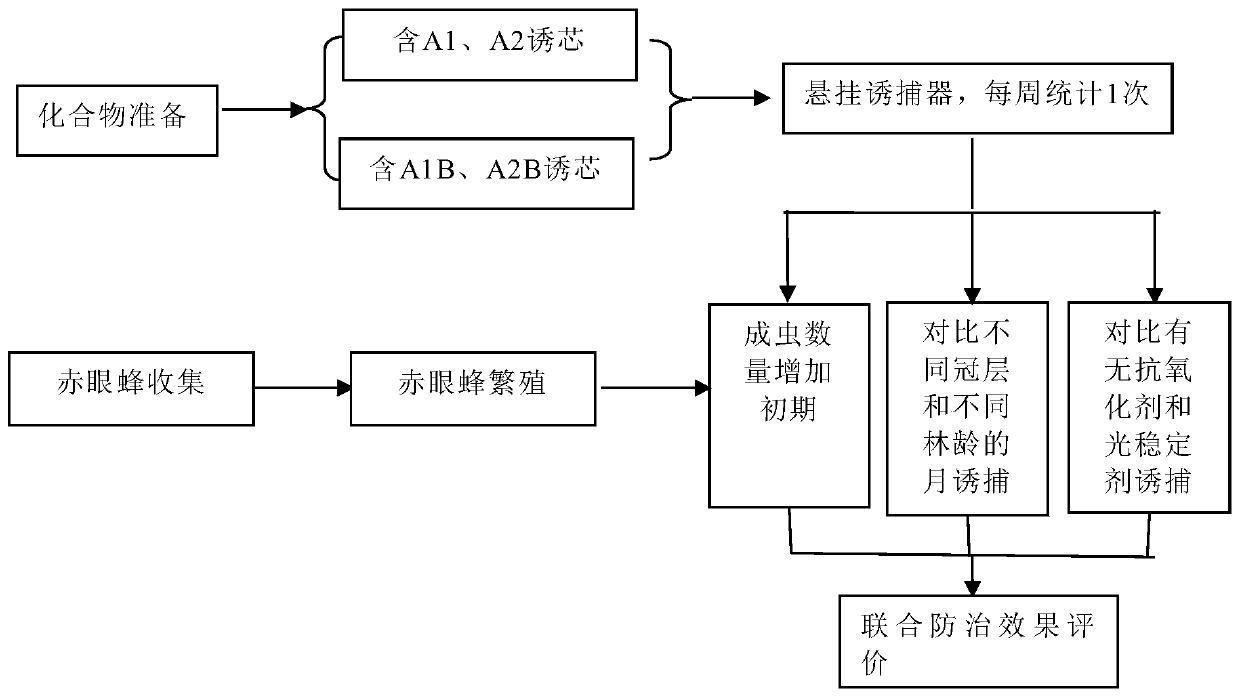
[0068] Take young pine forests as the implementation object, choose a well-ventilated woodland to hang traps, and hang the traps on the middle, upper and lower parts of the tree crown; take young forests and mature forests as the implementation objects, choose well-ventilated woodlands to hang traps separately, and place the traps separately Hang in young forests and mature forests, count the number of trapped adults every 7 days, and clean them up, and count the data for more than 9 months.
[0069] figure 2 Figures of trapping adults in different canopy layers and different stand ages provided by Example 1 of the present invention. from figure 2 It can be seen that the number of adults trapped by the trap hanging in the middle and upper part of the canopy is more than that in the lower part, and the trapping effect is significantly different. from figure 2 It can also be seen that the number of adults trapped by the trap hanging in the young forest is more than that in...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Hang the traps at 2 mu / piece in the pine demonstration forest, count the number of trapped adults every 7 days, and clean them up, and then calculate the monthly trapping amount according to the data, and make a dynamic growth and decline chart of the adult population for more than 9 months as a trap + Control data for Trichogramma.
[0072] image 3 It is a dynamic diagram of the growth and decline of the adult population of the parasitic natural enemy pine tip pest not released during the trapping period. from image 3 It can be seen that after using 2 acres of traps, the average decline rate of the peak period of the red spot moth adult is 15%, and the average decline rate of the peak period of the peach borer is 67%, so trapping has a certain effect on the peak period of adults. some control.
Embodiment 3
[0074] Hang the traps at 2 mu / piece in the pine demonstration forest, count the number of trapped adults every 7 days, and clean them up. When the number of adults rises, release the parasitic natural enemies in time, and then continue to count the monthly trappings based on the data of adults trapped in the forest. Production The dynamic growth and decline chart of the adult population over 9 months old is used as the processing data of trapping + Trichogramma.
[0075] Figure 4 A dynamic diagram of the growth and decline of the adult population of the parasitic natural enemy pine shoot pest released during the trapping period. from Figure 4 It can be seen that the method of using 2 mu / trap + release of Trichogramma at the adult stage at the end of April: the average decline rate of the adult peak period of the red spot moth is 72%, and the calibration decline rate is 57%; The period average decline rate was 96%, and the calibration decline rate was 29%. The mode of trap...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com