Semiconductor device buffer layer manufacturing method
A manufacturing method and buffer layer technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as adverse effects on device switching characteristics, increased device manufacturing costs, and expensive high-energy ion implanters. Achieve the effect of optimizing carrier concentration distribution and increasing depth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
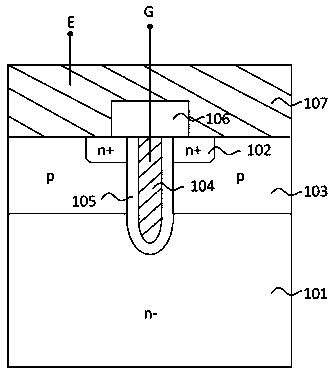
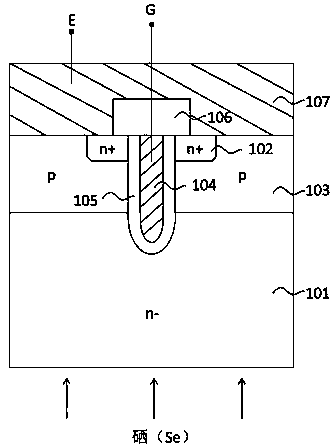
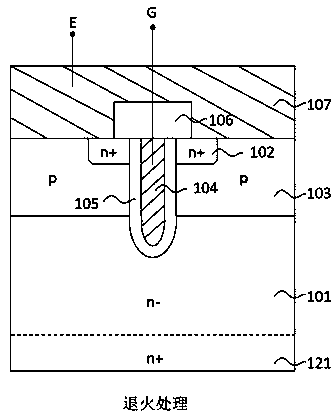
[0036] A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device buffer layer, forming an n-type buffer layer comprising a first n-type buffer layer and a second n-type buffer layer on a semiconductor substrate, or on the back of a semiconductor substrate having a p-type collector region formed on the back of the semiconductor substrate. A buffer layer, the first n-type buffer layer is formed by implanting selenium on the back of the semiconductor substrate and annealing after the implantation, and the second n-type buffer layer is formed by implanting protons on the back of the semiconductor substrate and annealing after the implantation , counting from the back surface of the semiconductor substrate, the depth of the first n-type buffer layer is deeper than the depth of the second n-type buffer layer, and the peak concentration of the first n-type buffer layer is lower than that of the second n-type buffer layer. The peak concentration of the n-type buffer layer is shallow. In the p...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A semiconductor device buffer layer manufacturing method, forming an n-type buffer layer including a first n-type buffer layer and a second n-type buffer layer on a semiconductor substrate, or on the back of a semiconductor substrate having a p-type collector region formed on the back of the semiconductor substrate , the first n-type buffer layer is formed by implanting selenium on the back of the semiconductor substrate and annealing after implantation, and the second n-type buffer layer is formed by implanting protons or phosphorus or implanting protons and phosphorus on the back of the semiconductor substrate The combination of implantation, annealing treatment is performed after implantation, counting from the back surface of the semiconductor substrate, the depth of the first n-type buffer layer is deeper than the depth of the second n-type buffer layer, and the first n-type buffer layer layer has a shallower peak concentration than the second n-type buffer layer. ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A semiconductor device buffer layer manufacturing method, forming an n-type buffer layer including a first n-type buffer layer and a second n-type buffer layer on a semiconductor substrate, or on the back of a semiconductor substrate having a p-type collector region formed on the back of the semiconductor substrate , the first n-type buffer layer is formed by implanting selenium on the back of the semiconductor substrate and annealing after implantation, and the second n-type buffer layer is formed by implanting protons or phosphorus or implanting protons and phosphorus on the back of the semiconductor substrate The combination of implantation, annealing treatment is performed after implantation, counting from the back surface of the semiconductor substrate, the depth of the first n-type buffer layer is deeper than the depth of the second n-type buffer layer, and the first n-type buffer layer layer has a shallower peak concentration than the second n-type buffer layer. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com