A dynamic joint device and lower limb assisting equipment
A technology for power devices and joints, applied in the field of wearable devices, can solve the problems of high cost, large size of the torque sensor, and no disclosure of installation accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] In order to fully understand the technical content of the present invention, the technical solutions of the present invention will be further introduced and illustrated below in conjunction with specific examples, but not limited thereto.
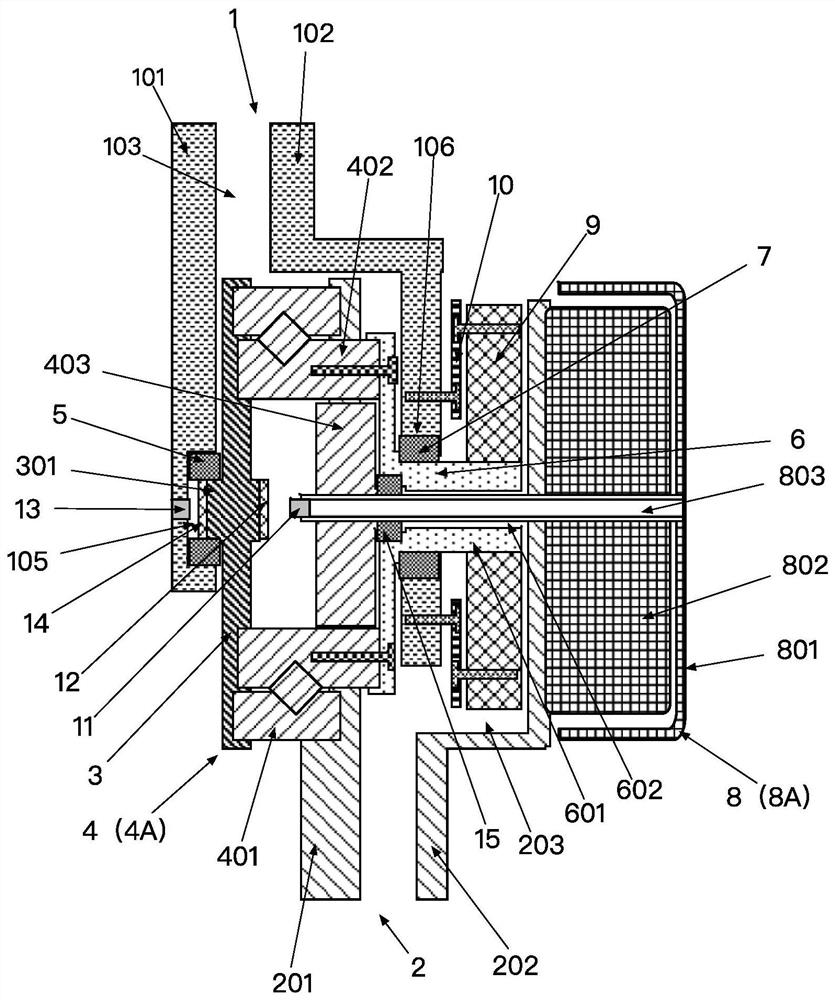
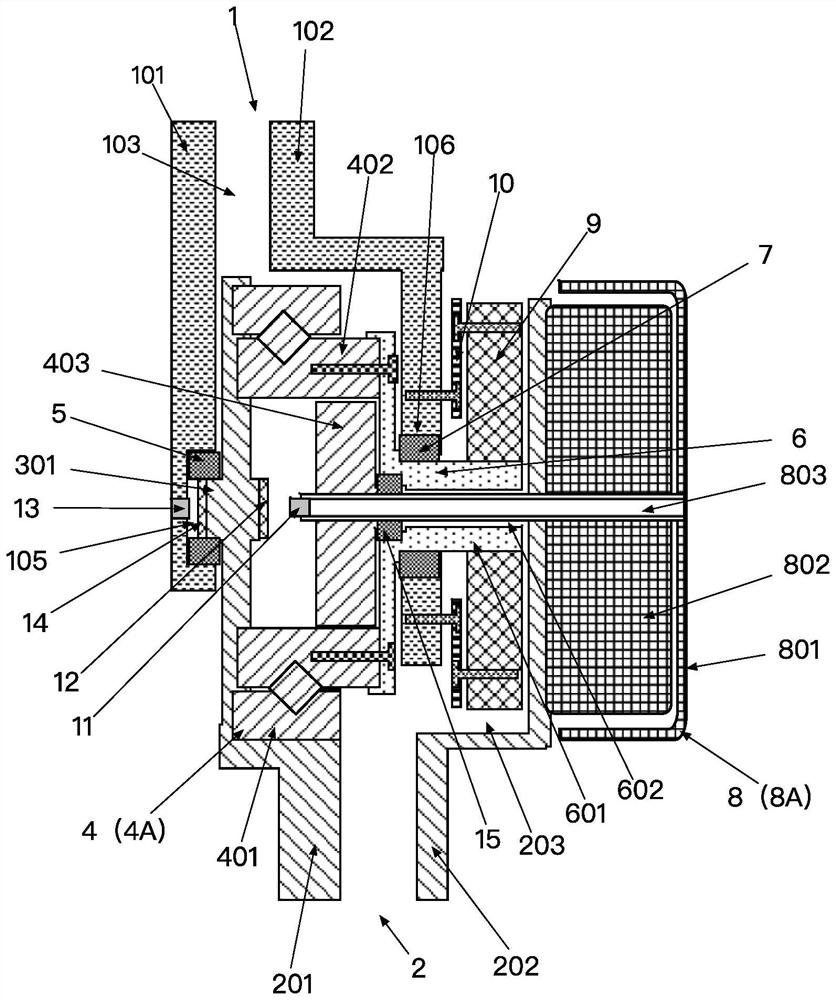
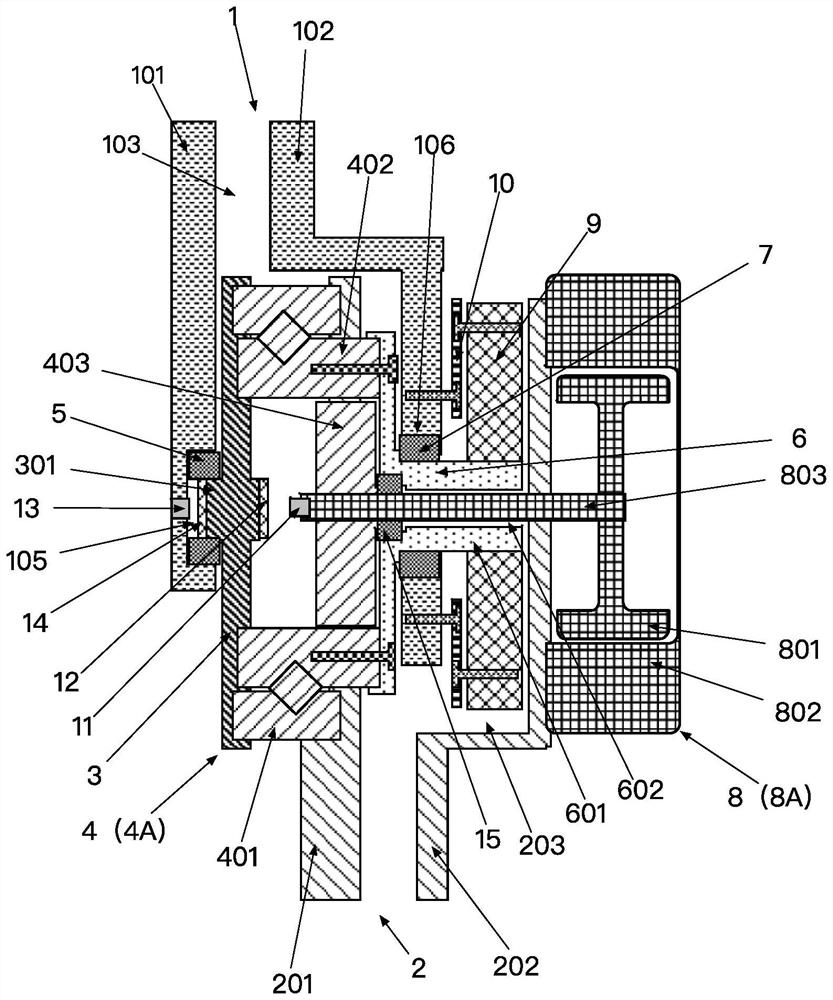
[0041] like figure 1 — Figure 8 Shown is a specific structural view of an embodiment of a portable dynamic joint device of the present invention.
[0042] A powered joint device such as figure 1 — image 3 As shown, it includes a joint body 1001 and a power device disposed on the joint body 1001 . The joint body 1001 includes an upper arm 1 and a lower arm 2 that moves relative to the upper arm 1 . The power device includes a power part 8A, and a reduction mechanism 4A fixed at the power output end of the power part 8A. The power part 8A is fixed on the lower arm 2, and the power output end of the reduction mechanism 4A is connected with the upper arm 1, so that the power part 8A drives the upper arm 1 to move relative to the lo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com