Method of using phyla to perform replacement control on mikania micrantha
An alternative control and crossing technology of vines, applied in botanical equipment and methods, applications, horticulture, etc., can solve the problems of associated plant damage, inappropriateness, waste of time, etc., to inhibit growth and reproduction, reduce occurrence density, and soil requirements. strict effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The present embodiment provides a kind of method that utilizes vine to carry out alternative control to Mikania micrantha, comprising:
[0026] Experimental site: Select the area where Mikania micrantha occurs seriously, and the specific location is: Baodao New Village, Danzhou City, Hainan Province. Manually remove the existing Mikania micrantha, and clean up other weeds, stones, etc., and level the ground after plowing.
[0027] Experimental processing settings:
[0028] (1) Divide the test site into several plots of 3m×3m, with an interval of 0.5m between plots;
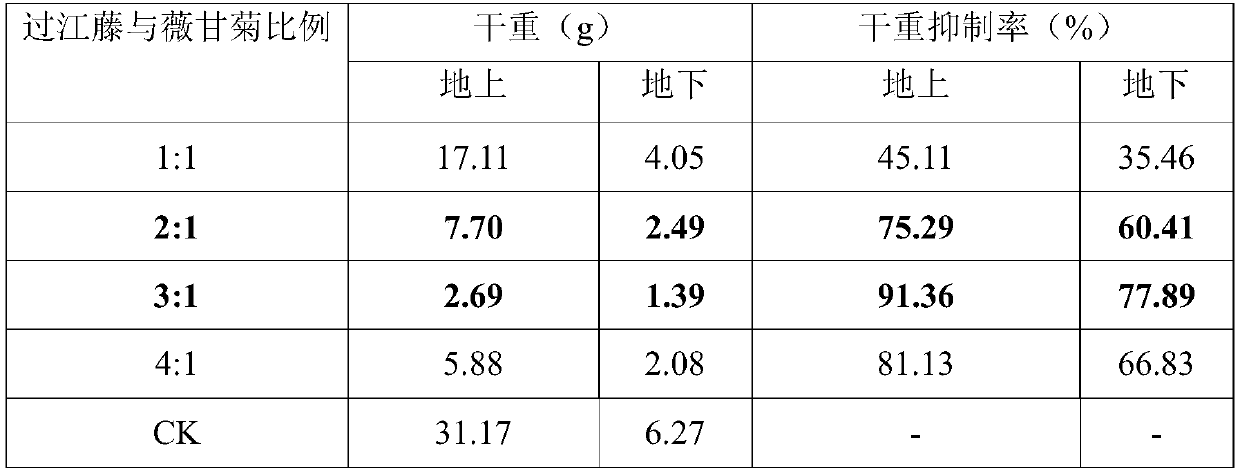
[0029] (2) Select the stem nodes of Mikania micrantha with a length of 8-10cm and substantially the same degree of lignification, and evenly cut them into the test plot; the density of Mikania micrantha is 9 plants / m 2 ;
[0030] (3) Cut the stem of the rattan crossing the river into sections, the length is 5-10cm, and ensure that there are 1-2 nodes on each stem section;
[0031] (4) Cutting or spreadi...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Similar to Example 1, the only difference is that the density of Guojiangteng and Mikania micrantha is 2:1.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Similar to Example 1, the only difference is that the density of Guojiangteng and Mikania micrantha is 1:1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com