Molecular marker and application of intron 2-based identification of barley semi-dwarf multi-tiller gene hvhtd
A molecular marker, semi-dwarf technology, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve the problems of increasing fertilizer input, increasing production cost, environmental pollution, etc., and achieving the effect of improving selection efficiency and speeding up progress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
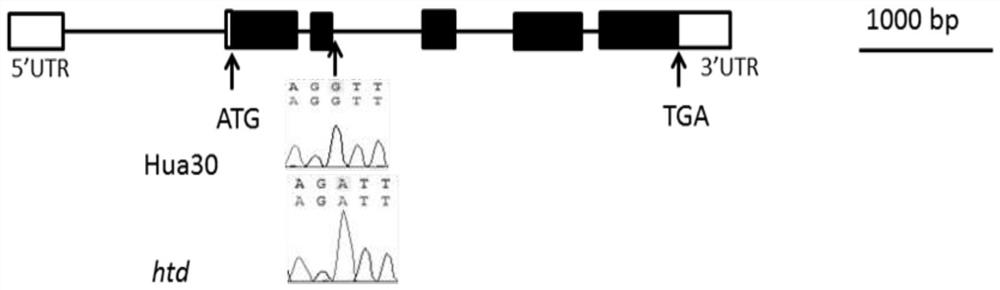
[0043] Example 1. Design of molecular marker SNP62
[0044] 1), test materials: mutant htd and its wild-type Hua30 (ie, Hua30, Hua30);
[0045] Mutant htd was obtained by EMS mutagenesis: using 0.03mol / L EMS to treat malting barley variety Hua 30, from 1710 individual plants M 2 According to the phenotype observation in the generation, a semi-dwarf and multi-tiller mutant was obtained. After multi-generation observation, it was found that the semi-dwarf and multi-tiller mutant was inherited stably, and we named it htd. Compared with its wild-type flower 30, its external manifestations are: the leaves become thinner and narrower, the leaf color becomes darker, the plant height becomes shorter, and the number of tillers increases.
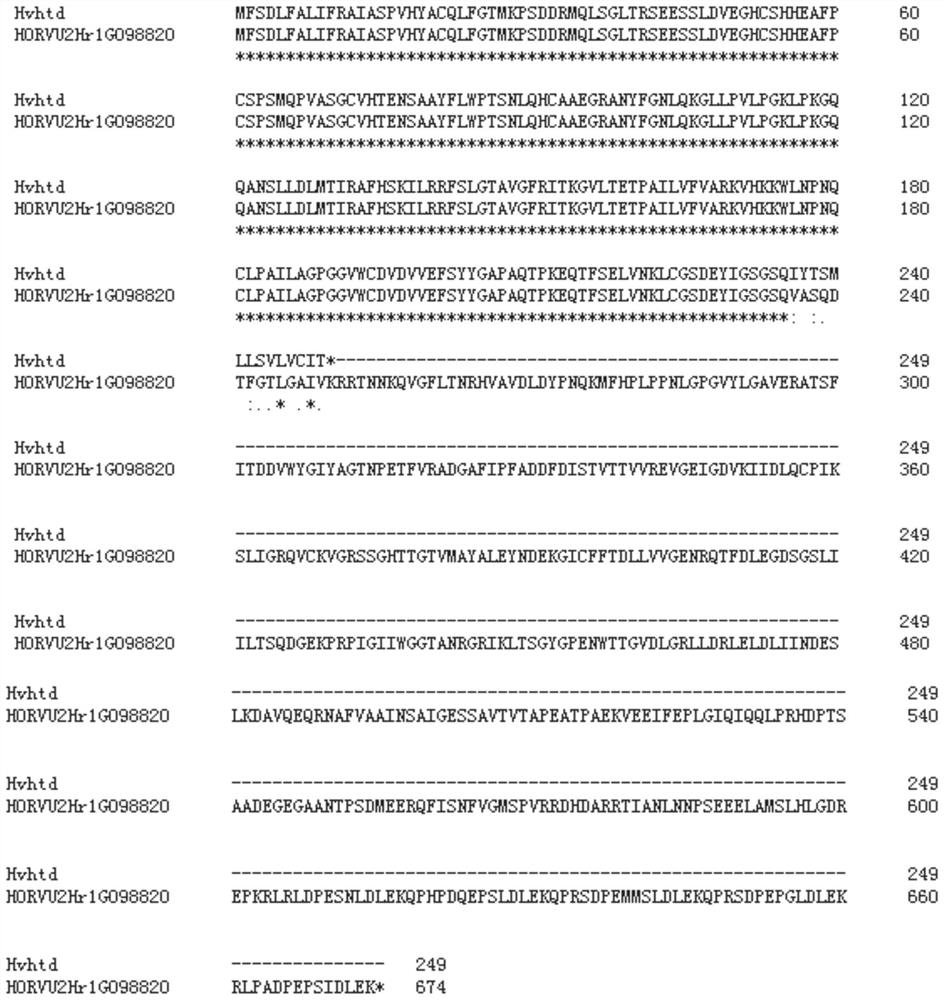
[0046] A gene Hvhtd controlling semi-dwarf and multi-tiller traits was cloned from the mutant htd, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The protein encoded by the semi-dwarf multi-tiller gene Hvhtd has the amino acid seq...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2. Using molecular markers to identify sequence differences between mutant htd and its wild-type flower 30:
[0055] 1), DNA extraction: Take 100 mg of barley leaves, and use the CTAB method to extract DNA. The specific steps are as follows:
[0056] ① Grind the sheared leaves in liquid nitrogen and put them into 1.5ml centrifuge tubes, add 600 μL of CTAB to each tube and place in a warm water bath at 65°C for 50-60 minutes (take out every 10 minutes and shake gently);
[0057] ②Add 600 microliters of chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (24:1) and mix well for 15 minutes. Slowly, weigh in pairs, and after balancing, centrifuge at 9600 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C;
[0058] ③Pipe the supernatant to another 1.5ml new centrifuge tube, add 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol and mix slightly (precipitate in -20°C refrigerator for 30-60min);
[0059] ③ Pick out the precipitate with a pipette tip, put it in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, wash it twice with 70% ethanol and air dry; ...
Embodiment 3
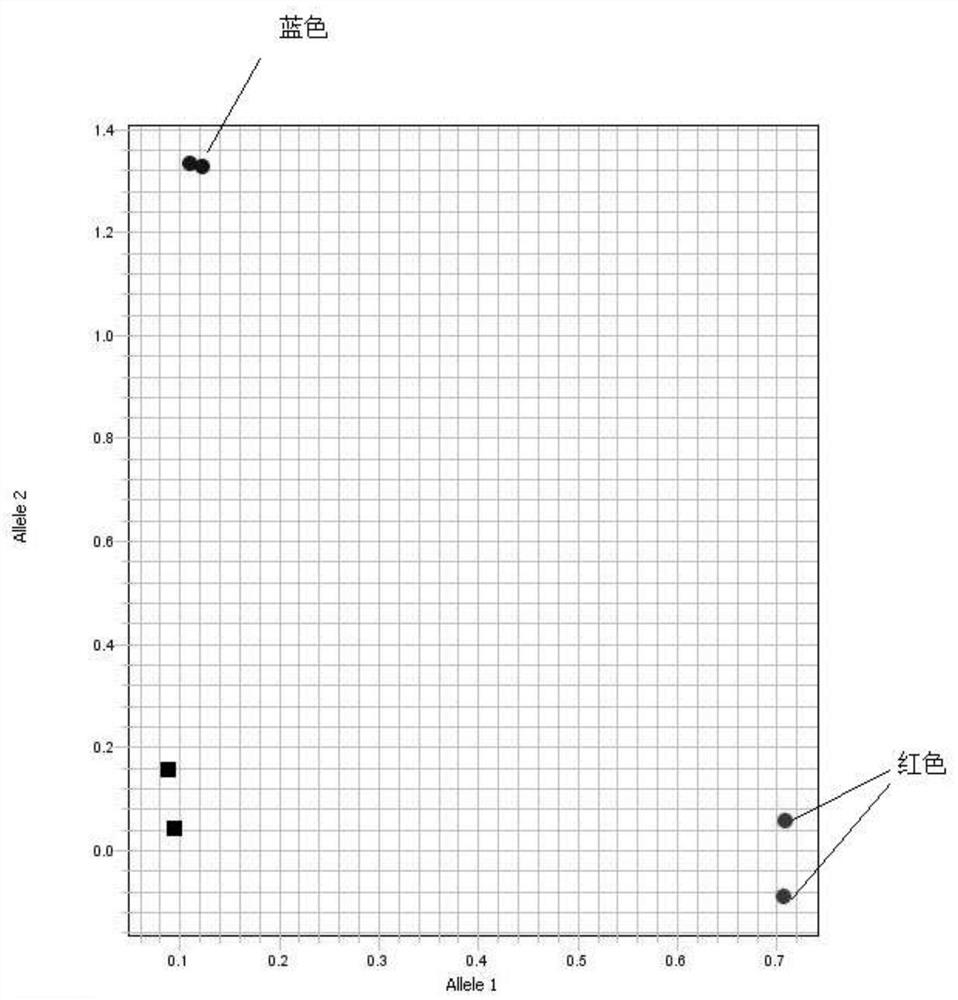
[0069] Example 3. Using the molecular marker SNP62 to detect 32 barley germplasm resources (including mutant htd and flower 30, 2 repetitions) according to the method described in Example 2, the barley germplasm resources include wild barley, local varieties and from around the world The barley varieties bred from various places and the F 1 (See Table 1);
[0070] The result is as Figure 4 shown.
[0071] The test results show that the F of htd / Zhepi No. 8 in these materials 1 The hybrid is heterozygous, and the mutant htd is a mutant genotype; other materials are wild-type genotypes, and their phenotypes are also different from the semi-dwarf multi-tiller phenotype of the mutant htd, indicating that they are not Containing the Hvthd mutant gene also proves that this molecular marker can be used in the detection of barley germplasm resources.
[0072] Table 1. Information on 32 barley germplasm resources detected by molecular marker SNP62
[0073]
[0074]
[0075]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com